Kafka实战系列--Kafka API使用体验
前言:
kafka是linkedin开源的消息队列, 淘宝的metaq就是基于kafka而研发. 而消息队列作为一个分布式组件, 在服务解耦/异步化, 扮演非常重要的角色. 本系列主要研究kafka的思想和使用, 本文主要讲解kafka的一些基本概念和api的使用.
*) 准备工作
1) 配置maven依赖
1 2 3 4 5 | <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka_2.9.2</artifactId> <version>0.8.1.1</version></dependency> |
2).配置hosts
vim /etc/hosts
把kafka集群相关的ip及其hostname, 配置到kafka客户端的本地机器
*) Kafka的基础知识
1). Broker, Zookeeper, Producer, Consumer
Broker具体承担消息存储转发工作, Zookeeper则用与元信息的存储(topic的定义/消费进度), Producer则是消息的生产者, Consumer则是消息的消费者.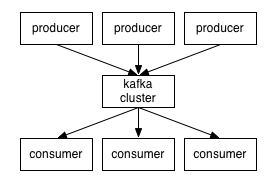
2). Topic, Partition, Replication, Consumer Group
Topic对应一个具体的队列, 在Kafka的概念中, 一个应用一个队列. 应用数据往往呈现部分有序的特点, 因此对kafka的队列, 引入partition的概念, 即可topic划分为多个partition. 单个Partition内保证有序, Partition间不保证. 这样作的好处, 是充分利用了集群的能力, 均匀负载和提高性能.
Replication主要为了高可用性, 保证部分节点失效的恶劣情况下, 队列数据能不丢.
Consumer Group的概念的引入, 很有创新性, 把以往传统队列(topic模式, queue模式)的属性从队列本身挪到了消费端. 若要使用queue模式, 则所有的消费端都采用统一个consumer group, 若采用topic模式, 则所有的客户端都设置为不同的consumer group. 其partition的消费进度在zookeeper有所保存.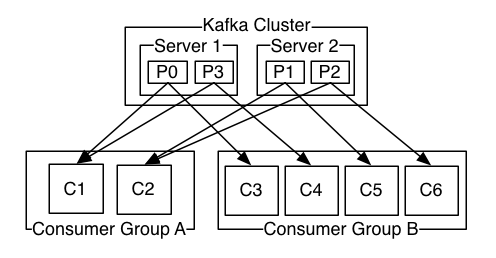
*) Kafka API的简单样列代码
1). 生产者代码
分区类代码片段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public class SimplePartitioner implements Partitioner { public SimplePartitioner (VerifiableProperties props) { } public int partition(Object key, int numPartitions) { return (key.hashCode() & 0x0FFFFFFF) % numPartitions; }} |
评注: SimplePartitioner用于对消息进行分发到具体的partition中, 有消息的key来决定, 这个有点像map/reduce中的partition机制.
生产者代码片段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | Properties props = new Properties();// 配置metadata.broker.list, 为了高可用, 最好配两个broker实例props.put("metadata.broker.list", "127.0.0.1:9092");// serializer.class为消息的序列化类props.put("serializer.class", "kafka.serializer.StringEncoder");// 设置Partition类, 对队列进行合理的划分props.put("partitioner.class", "mmxf.kafka.practise.SimplePartitioner");// ACK机制, 消息发送需要kafka服务端确认props.put("request.required.acks", "1");ProducerConfig config = new ProducerConfig(props);Producer<String, String> producer = new Producer<String, String>(config);// KeyedMessage<K, V>// K对应Partition Key的类型// V对应消息本身的类型<br>// topic: "test", key: "key", message: "message"KeyedMessage<String, String> message = new KeyedMessage<String, String>("test", "key", "message");producer.send(message);// 关闭producer实例producer.close(); |
2). 消费者代码
使用High Level Consumer的API 线程模型和Partition数最好能保持一致, 即One Thread For Partition
参考sample样例: https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/Consumer+Group+Example
代码片段如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 | public static void main(String[] args) { // *) 创建ConsumerConfig Properties props = new Properties(); // 设置zookeeper的链接地址 props.put("zookeeper.connect", "127.0.0.1:2181"); // 设置group id props.put("group.id", "group_id"); // kafka的group 消费记录是保存在zookeeper上的, 但这个信息在zookeeper上不是实时更新的, 需要有个间隔时间更新 props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000"); ConsumerConfig consumerConfig = new ConsumerConfig(props); ConsumerConnector consumer = (ConsumerConnector) Consumer.createJavaConsumerConnector(consumerConfig); String topic = "test"; int threadNum = 1; // *) 设置Topic=>Thread Num映射关系, 构建具体的流 Map<String, Integer> topicCountMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); topicCountMap.put(topic,threadNum); Map<String, List<KafkaStream<byte[], byte[]>>> consumerMap = consumer.createMessageStreams(topicCountMap); List<KafkaStream<byte[], byte[]>> streams = consumerMap.get(topic); // *) 启动线程池去消费对应的消息 ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for ( final KafkaStream<byte[], byte[]> stream : streams ) { executor.submit(new Runnable() { public void run() { ConsumerIterator<byte[], byte[]> iter = stream.iterator(); while ( iter.hasNext() ) { MessageAndMetadata<byte[] , byte[]> mam = iter.next(); System.out.println( String.format("thread_id: %d, key: %s, value: %s", Thread.currentThread().getId(), new String(mam.key()), new String(mam.message()) ) ); } } }); } try { Thread.sleep(1000 * 10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // *) 优雅地退出 consumer.shutdown(); executor.shutdown(); while ( !executor.isTerminated() ) { try { executor.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }} |
结果输出:
1 | thread_id: 18, key: key, value: message |
posted on 2014-07-22 16:00 mumuxinfei 阅读(6307) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构