线程的死锁
今天本人给大家讲解一下多线程的死锁,如有不对的或者讲的不好的可以多多提出,我会进行相应的更改,先提前感谢提出意见的各位了!!!
线程死锁
什么是线程的死锁?
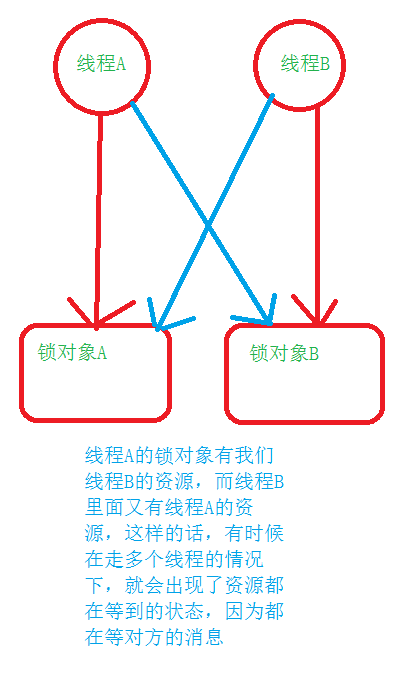
产生死锁的原因?
因为资源的竞争:线程中都是进行抢占CPU的时间片的执行权,所以开启多线程可以一次性进行多个功能的使用,可是现在因为锁对象A和锁对象B的执行时机以及顺序的的不一致,导致线程相互等待,有时候会出现死锁的现象。
预防死锁
保证我们请求的资源数据的顺序要一致即可
案例:出现死锁的案例
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { OneLock ol01 = new OneLock(); OneLock ol02 = new OneLock(); //创建线程对象 Thread thread01 = new Thread(ol01, "one"); Thread thread02 = new Thread(ol02, "two"); //开启线程 thread01.start(); thread02.start(); } } class OneLock implements Runnable { public void run() { //如果线程名称等于ONE if ("one".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())) { synchronized ("one") { System.out.println("one============"); synchronized ("two") { System.out.println("two============"); } } } if ("two".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())) { synchronized ("one") { System.out.println("two============"); synchronized ("two") { System.out.println("one============"); } } } } }
运行结果:
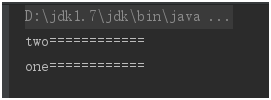
结果一:发生了死锁的现象
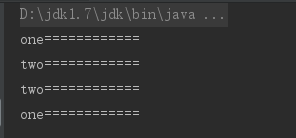
结果二:正确执行完成
案例:避免死锁的案例
修改代码:将条件判断的顺序修改为一致的,让同步的锁对象的顺序一致即可
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OneLock ol01 = new OneLock();
OneLock ol02 = new OneLock();
//创建线程对象
Thread thread01 = new Thread(ol01, "one");
Thread thread02 = new Thread(ol02, "two");
//开启线程
thread01.start();
thread02.start();
}
}
class OneLock implements Runnable {
public void run() {
//如果线程名称等于ONE
if ("one".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())) {
synchronized ("one") {
System.out.println("one============");
synchronized ("two") {
System.out.println("two============");
}
}
}
if ("two".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName())) {
synchronized ("one") {
System.out.println("two============");
synchronized ("two") {
System.out.println("one============");
}
}
}
}
}
多线程的死锁讲解完毕,又不懂或者不理解的可以在评论区给本人留言。
结果二:正确执行完成


