MetaGPT-main-源码学习
学习最新版本的MetaGPT官方教程(v0.8.1 maybe)
学习教程:https://docs.deepwisdom.ai/main/zh/guide/tutorials/concepts.html
v0.8.1 改动(相比v0.4)
智能体入门
1.)在《智能体入门》章节,v0.8.1版本在创建Role时显式地创建了Context对象,与v0.4版本相比,相关的类代码并没有改动。
# v0.8.1
from metagpt.context import Context
context = Context()
role = ProductManager(context=context)
# Role类定义
class Role(SerializationMixin, ContextMixin, BaseModel):
rc: RoleContext = Field(default_factory=RoleContext)
# RoleContext
class RoleContext(BaseModel):
memory: Memory = Field(default_factory=Memory)
# Memory定义
class Memory(BaseModel):
storage: list[SerializeAsAny[Message]] = []
WARNING | metagpt.utils.common:wrapper:649 - There is a exception in role's execution, in order to resume, we delete the newest role communication message in the role's memory.
如果不显式地指定context,会报错ValueError: Invalid root
# v0.4
role = ProductManager()
# Role 对象中维护着 RoleContext 对象
class Role:
def __init__(self, name="", profile="", goal="", constraints="", desc="", is_human=False):
self._rc = RoleContext()
# RoleContext 对象中维护着 Memory 对象
class RoleContext(BaseModel):
memory: Memory = Field(default_factory=Memory)
# Memory 对象中存储Message结构体
class Memory:
def __init__(self):
self.storage: list[Message] = []
2.)定义动作 & 定义角色 & 运行角色代码没有变化,在创建角色时都需要显式地指定context,在运行自定义角色时没有显式传递context也可以正常运行。
更多细节需要阅读Role以及ProductManager源码查找原因。
多智能体入门
在创建Team运行时,由team.start_project(idea)改为了team.run_project(idea).
新增-创建和使用工具
在MetaGPT中,可以直接创建自己的函数或类作为工具,放在metagpt/tools/libs 目录下。
创建工具的步骤
- 编写专门用于与外部环境进行特定交互的函数或类,并将它们放置在
metagpt/tools/libs目录中。 - 为每个函数或类配备谷歌风格的文档字符串。这作为一个简洁而全面的参考资料,详细说明其用途、输入参数和预期输出。
- 使用
@register_tool装饰器以确保在工具注册表中准确注册。这个装饰器简化了函数或类与DataInterpreter的集成。
自定义工具案例
1.)自定义计算阶乘的工具
在 metagpt/tools/libs 中创建一个自己的函数,假设它是 calculate_factorial.py,并添加装饰器 @register_tool 以将其注册为工具
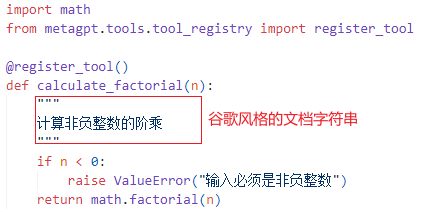
2.)register_tool装饰器函数详解
# 将一个工具类或函数注册到一个工具注册表中
def register_tool(tags: list[str] = None, schema_path: str = "", **kwargs):
"""
register a tool to registry
tags:字符串列表,用于标记工具
schema_path:表示工具的模式文件路径
"""
# 装饰器函数,cls 表示被装饰器装饰的类
def decorator(cls):
# 获取被装饰的类或函数的文件路径
file_path = inspect.getfile(cls)
if "metagpt" in file_path:
# split to handle ../metagpt/metagpt/tools/... where only metapgt/tools/... is needed
file_path = "metagpt" + file_path.split("metagpt")[-1]
# 获取被装饰类的源代码
source_code = inspect.getsource(cls)
# 将工具的信息注册到注册表中
TOOL_REGISTRY.register_tool(
tool_name=cls.__name__, # 工具名称 = 类名
tool_path=file_path,
schema_path=schema_path,
tool_code=source_code,
tags=tags,
tool_source_object=cls,
**kwargs,
)
return cls
return decorator
当导入包含 @register_tool 装饰器的模块时,装饰器会自动运行,将类注册到 TOOL_REGISTRY 中。
3.)将自定义工具集成到数据解释器DataInterpreter中,并在计算过程中使用工具
import asyncio
from metagpt.roles.di.data_interpreter import DataInterpreter
from metagpt.tools.libs import calculate_factorial
async def main(requirement: str):
role = DataInterpreter(tools=["calculate_factorial"]) # 集成工具
await role.run(requirement)
if __name__ == "__main__":
requirement = "请计算 5 的阶乘"
await main(requirement)
"""
运行过程:
metagpt.tools.tool_recommend:recall_tools:194 - Recalled tools: ['calculate_factorial']; Scores: [0.0]
metagpt.tools.tool_recommend:recommend_tools:100 - Recommended tools: ['calculate_factorial']
metagpt.roles.di.data_interpreter:_write_code:153 - ready to WriteAnalysisCode
```python
# Importing the pre-defined tool for calculating factorial
from metagpt.tools.libs.calculate_factorial import calculate_factorial
# Calculate the factorial of 5
result = calculate_factorial(5)
# Print the result
print("The factorial of 5 is:", result
```
"""
注意:
- 编写谷歌风格的文档字符串(docstring),有助于
DataInterpreter选择合适的工具并理解其工作方式。- 在注册工具时,工具的名称就是函数的名称。
- 在运行 DataInterpreter 之前,记得从
metagpt.tools.libs导入自定义的calculate_factorial模块,以确保该工具已被注册。
通过上述步骤,可以无缝地创建并整合MetaGPT中Tools框架内的工具,使DataInterpreter能够有效地与外部环境交互。
人类介入
环境的创建
新增-集成开源LLM
目前,如果要得到比较稳定的代码生成结果,需要使用OpenAI的GPT-3.5或GPT-4。但目前也有很多其他优秀的开源模型可以供实验,也能够得到令人相对满意的结果。
下面将展开如何接入开源LLM并根据你的输入需求得到项目输出。
待补充
新增-为角色或动作配置不同的LLM
每个Role可以根据其特定的需求和背景,以及每个Action的特点,选择最合适的LLM,增强了团队互动的灵活性和现实性。
通过这种方式,你可以更精细地控制对话的质量和方向,从而创造出更加丰富和真实的交互体验。
设置步骤如下:
-
定义不同的LLM配置文件
from metagpt.config2 import Config # 1. 创建新的gpt-4配置文件并加载 gpt4 = Config.from_home("gpt-4.yaml") # 从`~/.metagpt`目录加载自定义配置`gpt-4.yaml` # 2. 使用默认的配置文件 gpt4t = Config.default() # 使用默认配置,即`config2.yaml`文件中的配置,此处`config2.yaml`文件中的model为"gpt-4-turbo" # 3. 修改配置文件中使用的LLM gpt35 = Config.default() gpt35.llm.model = "gpt-3.5-turbo" # 将model修改为"gpt-3.5-turbo" -
在创建Role和Action时,为其分配不同的配置文件
from metagpt.roles import Role from metagpt.actions import Action # 创建a1、a2和a3三个Action。并为a1指定`gpt4t`的配置。 a1 = Action(config=gpt4t, name="Say", instruction="Say your opinion with emotion and don't repeat it") a2 = Action(name="Say", instruction="Say your opinion with emotion and don't repeat it") a3 = Action(name="Vote", instruction="Vote for the candidate, and say why you vote for him/her") # 创建A,B,C三个角色,分别为“民主党候选人”、“共和党候选人”和“选民”。 # 虽然A设置了config为gpt4,但因为a1已经配置了Action config,所以A将使用model为gpt4的配置,而a1将使用model为gpt4t的配置。 A = Role(name="A", profile="Democratic candidate", goal="Win the election", actions=[a1], watch=[a2], config=gpt4) # 因为B设置了config为gpt35,而为a2未设置Action config,所以B和a2将使用Role config,即model为gpt35的配置。 B = Role(name="B", profile="Republican candidate", goal="Win the election", actions=[a2], watch=[a1], config=gpt35) # 因为C未设置config,而a3也未设置config,所以C和a3将使用Global config,即model为gpt4的配置。 C = Role(name="C", profile="Voter", goal="Vote for the candidate", actions=[a3], watch=[a1, a2]) -
注意配置的优先级:Action config > Role config > Global config(config in config2.yaml)
-
创建一个带有环境的团队,开始交互。
import asyncio from metagpt.environment import Environment from metagpt.team import Team # 创建一个描述为“美国大选现场直播”的环境 env = Environment(desc="US election live broadcast") team = Team(investment=10.0, env=env, roles=[A, B, C]) # 运行团队,我们应该会看到它们之间的协作 asyncio.run(team.run(idea="Topic: climate change. Under 80 words per message.", send_to="A", n_round=3)) # await team.run(idea="Topic: climate change. Under 80 words per message.", send_to="A", n_round=3) # 如果在Jupyter Notebook中运行,使用这行代码
源码阅读
下面调试21点游戏,跟随执行流程阅读源码,设计到相应的步骤可参考下文(无需顺序阅读,边调试边到对应部分阅读)。
运行流程总结
-
创建团队并雇佣多个角色,团队开启项目
company.run_project(idea=idea)开启项目的过程:
①将用户
Idea包装为消息发送到环境中。②环境分发消息到所有参与的角色中
role.put_message(message),发送到每个角色维护的消息队列上。 -
团队开始运行项目
company.run(n_round=5)内部进入到
Team的环境的运行self.env.run()在环境
run中,会将所有角色的run的协程对象加入到futures,通过await asyncio.gather(*futures)等待所有角色的协程对象完成 -
下面进入到具体的
Role运行,协程Role监控环境是否有新的事件发生,获取最新观察到的消息self.latest_observed_msg运行
Role的react,根据self.rc.react_mode进入对应的框架。if self.rc.react_mode == RoleReactMode.REACT or self.rc.react_mode == RoleReactMode.BY_ORDER: rsp = await self._react() elif self.rc.react_mode == RoleReactMode.PLAN_AND_ACT: rsp = await self._plan_and_act()在
_react框架中,_think和_act嵌套在最大次数为self.rc.max_react_loop的while循环中。async def _react(self) -> Message: actions_taken = 0 while actions_taken < self.rc.max_react_loop: # think todo = await self._think() if not todo: break # act rsp = await self._act() actions_taken += 1
消息传输框架
待补充
消息路由结构设计
待补充
消息中的路由信息仅负责指定消息收件人,而不关心消息收件人的位置。
ActionOutput
class ActionOutput:
content: str
instruct_content: BaseModel
def __init__(self, content: str, instruct_content: BaseModel):
self.content = content
self.instruct_content = instruct_content
RoleReactMode
class RoleReactMode(str, Enum):
REACT = "react"
BY_ORDER = "by_order" # 顺序执行
PLAN_AND_ACT = "plan_and_act" # 规划并行动
@classmethod
def values(cls):
return [item.value for item in cls]
Role
1.)初始化 & 消息的存储
Role接收的消息存放在self.rc.msg_buffer中,RoleContext对象的msg_buffer队列中。
msg_buffer: MessageQueue = Field(
default_factory=MessageQueue, exclude=True
) # Message Buffer with Asynchronous Updates
class Role(SerializationMixin, ContextMixin, BaseModel):
"""Role/Agent"""
model_config = ConfigDict(arbitrary_types_allowed=True, extra="allow")
name: str = ""
profile: str = ""
goal: str = ""
constraints: str = ""
desc: str = ""
is_human: bool = False
role_id: str = ""
states: list[str] = []
# scenarios to set action system_prompt:
# 1. `__init__` while using Role(actions=[...])
# 2. add action to role while using `role.set_action(action)`
# 3. set_todo while using `role.set_todo(action)`
# 4. when role.system_prompt is being updated (e.g. by `role.system_prompt = "..."`)
# Additional, if llm is not set, we will use role's llm
actions: list[SerializeAsAny[Action]] = Field(default=[], validate_default=True)
rc: RoleContext = Field(default_factory=RoleContext)
addresses: set[str] = set()
planner: Planner = Field(default_factory=Planner)
# builtin variables
recovered: bool = False # to tag if a recovered role
latest_observed_msg: Optional[Message] = None # record the latest observed message when interrupted
__hash__ = object.__hash__ # support Role as hashable type in `Environment.members`
2.)给角色发送消息
角色将收到的消息放置在角色自身维护的RoleContext的MessageQueue中。
发生情况:①项目启动时,Team将Idea消息发送到环境中的每个角色,每个角色接收该消息。
def put_message(self, message):
"""Place the message into the Role object's private message buffer."""
if not message:
return
self.rc.msg_buffer.push(message)
3.)Role的run协程对象
@role_raise_decorator
async def run(self, with_message=None) -> Message | None:
"""
Observe,
and think
and act
based on the results of the observation"""
if with_message:
msg = None
if isinstance(with_message, str):
msg = Message(content=with_message)
elif isinstance(with_message, Message):
msg = with_message
elif isinstance(with_message, list):
msg = Message(content="\n".join(with_message))
if not msg.cause_by:
msg.cause_by = UserRequirement
# 将消息发送到角色的消息队列中
self.put_message(msg)
# 监控角色的环境,检查是否有新的信息或事件发生
if not await self._observe():
# If there is no new information, suspend and wait
# 如果没有新的消息,Role进入等待状态
logger.debug(f"{self._setting}: no news. waiting.")
return
# 有新的消息,开始行动
rsp = await self.react()
# 重置下一步的动作
self.set_todo(None)
# 将响应消息发送到环境中,环境会将消息分发给所有的订阅者(包括角色本身)
self.publish_message(rsp)
return rsp
4.)检测环境 self._observe()
async def _observe(self, ignore_memory=False) -> int:
"""Prepare new messages for processing from the message buffer and other sources."""
# Read unprocessed messages from the msg buffer.
news = []
if self.recovered:
news = [self.latest_observed_msg] if self.latest_observed_msg else []
if not news:
# 从消息缓冲区读取未处理消息
news = self.rc.msg_buffer.pop_all()
# 存储读取的消息以防止重复处理
# old_messages 用于存储之前的消息,如果 ignore_memory 为 False,则使用 self.rc.memory.get() 获取之前的消息
old_messages = [] if ignore_memory else self.rc.memory.get()
# 添加新消息到消息列表
self.rc.memory.add_batch(news)
# 筛选消息,由 self.rc.watch 指定的发送者发送,要么发送给 self.name 指定的接收者
self.rc.news = [
n for n in news if (n.cause_by in self.rc.watch or self.name in n.send_to) and n not in old_messages
]
# 记录最新观察到的消息
self.latest_observed_msg = self.rc.news[-1] if self.rc.news else None # record the latest observed msg
# Design Rules:
# If you need to further categorize Message objects, you can do so using the Message.set_meta function.
# msg_buffer is a receiving buffer, avoid adding message data and operations to msg_buffer.
# 包含消息发送者和消息内容的列表
news_text = [f"{i.role}: {i.content[:20]}..." for i in self.rc.news]
if news_text:
logger.debug(f"{self._setting} observed: {news_text}")
# 返回筛选出的消息数量
return len(self.rc.news)
5.)开始行动 self.react()
async def react(self) -> Message:
"""Entry to one of three strategies by which Role reacts to the observed Message"""
if self.rc.react_mode == RoleReactMode.REACT or self.rc.react_mode == RoleReactMode.BY_ORDER:
rsp = await self._react()
elif self.rc.react_mode == RoleReactMode.PLAN_AND_ACT:
rsp = await self._plan_and_act()
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported react mode: {self.rc.react_mode}")
self._set_state(state=-1) # current reaction is complete, reset state to -1 and todo back to None
return rsp
6.)角色绑定的Actions
# Role
class Role(SerializationMixin, ContextMixin, BaseModel):
actions: list[SerializeAsAny[Action]] = Field(default=[], validate_default=True)
# 在对角色绑定动作时会加入到动作列表中
def set_action(self, action: Action):
self.set_actions([action])
def set_actions(self, actions: list[Union[Action, Type[Action]]]):
'''简化过程'''
for action in actions:
self.actions.append(action)
Team
1.)初始化 company = Team()
Team类维护一到多个Roles,env,idea,investment,model_config
使用Context对象创建Environment
class Team(BaseModel):
"""
"""
model_config = ConfigDict(arbitrary_types_allowed=True)
env: Optional[Environment] = None
investment: float = Field(default=10.0)
idea: str = Field(default="")
def __init__(self, context: Context = None, **data: Any):
super(Team, self).__init__(**data)
ctx = context or Context()
if not self.env:
self.env = Environment(context=ctx)
2.)Team 雇佣 Roles company.hire([ProductManager(), Architect(), ProjectManager(), Engineer(),])
雇佣的过程就是 向Team的维护的env中添加Roles
def hire(self, roles: list[Role]):
"""Hire roles to cooperate"""
self.env.add_roles(roles)
3.)启动项目 company.run_project(idea=idea)
启动项目时,负责将消息发布到环境中。
消息类型是 send_to=send_to or MESSAGE_ROUTE_TO_ALL,发送给所有Role
def run_project(self, idea, send_to: str = ""):
"""Run a project from publishing user requirement."""
self.idea = idea
# Human requirement.
self.env.publish_message(
Message(role="Human", content=idea, cause_by=UserRequirement, send_to=send_to or MESSAGE_ROUTE_TO_ALL),
peekable=False,
)
4.)await company.run(n_round=5) 运行项目,跟进之后会跳到下面的函数
def serialize_decorator(func):
async def wrapper(self, *args, **kwargs):
try:
result = await func(self, *args, **kwargs)
return result
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logger.error(f"KeyboardInterrupt occurs, start to serialize the project, exp:\n{format_trackback_info()}")
except Exception:
logger.error(f"Exception occurs, start to serialize the project, exp:\n{format_trackback_info()}")
self.serialize() # Team.serialize
return wrapper
这里的self就是company对象,Team类,但该函数却不是Team类下的方法。
相当于中转执行 await company.run(n_round=5),company.run 地址被传递到func,<function Team.run at 0x000001C55C82B550>
接着进入company.cun执行
@serialize_decorator
async def run(self, n_round=3, idea="", send_to="", auto_archive=True):
"""Run company until target round or no money"""
# idea在self里面,这里idea为空,self.idea不为空
if idea:
self.run_project(idea=idea, send_to=send_to)
while n_round > 0:
n_round -= 1
self._check_balance()
# 调用环境的run函数
await self.env.run()
logger.debug(f"max {n_round=} left.")
self.env.archive(auto_archive)
return self.env.history
Environment
class Environment(ExtEnv):
"""
环境,承载一批角色,角色可以向环境发布消息,可以被其他角色观察到
"""
desc: str = Field(default="") # 环境描述
roles: dict[str, SerializeAsAny["Role"]] = Field(default_factory=dict, validate_default=True) # 维护Roles的字典
member_addrs: Dict["Role", Set] = Field(default_factory=dict, exclude=True)
context: Context = Field(default_factory=Context, exclude=True)
1.)添加角色 add_role
将一个角色添加到环境中,意味着该角色处在此环境中,同时共享该环境的context。
def add_role(self, role: "Role"):
"""增加一个在当前环境的角色
Add a role in the current environment
"""
self.roles[role.profile] = role # role的profile作为字典键建立映射
role.set_env(self) # 设置被添加Role的env
role.context = self.context # 设置被添加Role的context
2.)发布消息 publish_message
def publish_message(self, message: Message, peekable: bool = True) -> bool:
"""
将消息分发给收件人。
根据 RFC 116 第 2.2.1 章中的消息路由结构设计,正如在整个系统的 RFC 113 中已经规划的那样,消息中的路由信息仅负责指定消息收件人,而不关心消息收件人的位置。
如何将消息路由到消息收件人是 RFC 113 中设计的传输框架所解决的问题。
"""
logger.debug(f"publish_message: {message.dump()}")
found = False
# According to the routing feature plan in Chapter 2.2.3.2 of RFC 113
# Role类型的key, addrs 是一个set集合
# 将消息发送给所有的role
for role, addrs in self.member_addrs.items():
# type(role) <class 'metagpt.roles.product_manager.ProductManager'>
# addrs {'metagpt.roles.product_manager.ProductManager', 'Alice'}
if is_send_to(message, addrs):
role.put_message(message)
found = True
if not found:
logger.warning(f"Message no recipients: {message.dump()}")
self.history += f"\n{message}" # For debug
return True
3.)环境的run函数,Team在run时会调用环境的run函数
环境的run会将所有角色的run协程对象加入futures。
等待所有角色的协程对象完成 await asyncio.gather(*futures)
*futures表示将futures列表展开为单独的参数传递给gather
async def run(self, k=1):
"""处理一次所有信息的运行
Process all Role runs at once
"""
for _ in range(k):
futures = []
for role in self.roles.values():
# future是一个由role_raise_decorator装饰器创建的协程对象
future = role.run()
futures.append(future)
'''
0 = <coroutine object role_raise_decorator.<locals>.wrapper at 0x000001C55DCE57C0>
1 = <coroutine object role_raise_decorator.<locals>.wrapper at 0x000001C55DCE5F40>
2 = <coroutine object role_raise_decorator.<locals>.wrapper at 0x000001C55ED8C8C0>
3 = <coroutine object role_raise_decorator.<locals>.wrapper at 0x000001C55ED8C9C0>
'''
await asyncio.gather(*futures)
logger.debug(f"is idle: {self.is_idle}")
在涉及到的Role中下断点,以观察具体的执行过程,这里在产品经理ProductManager中调试
ProductManager绑定的动作是self.set_actions([PrepareDocuments, WritePRD]),在这两个Action的run下断点
关键来了~~ 这里跳转到 PrepareDocuments Action的run函数中。
# PrepareDocuments Action run
async def run(self, with_messages, **kwargs):
"""Create and initialize the workspace folder, initialize the Git environment."""
self._init_repo()
# 将idea写入文件
doc = await self.repo.docs.save(filename=REQUIREMENT_FILENAME, content=with_messages[0].content)
# 发送消息通知 WritePRD action
# doc=idea
return ActionOutput(content=doc.content, instruct_content=doc)
这里产品经理的Action执行结束后,返回一个ActionOutput对象。
重点来了~~这里返回到Role的_act中的第4行代码,也就是说上面的Action发生在第三行await self.rc.todo.run(self.rc.history),返回的ActionOutput即为response。
将返回的response包装为Message,发送到Role的RoleContext对象的Memory对象的消息列表中。
# Role
async def _act(self) -> Message:
logger.info(f"{self._setting}: to do {self.rc.todo}({self.rc.todo.name})")
# 这里根据 rc.todo 决定执行哪个动作
response = await self.rc.todo.run(self.rc.history)
if isinstance(response, (ActionOutput, ActionNode)):
msg = Message(
content=response.content,
instruct_content=response.instruct_content,
role=self._setting,
cause_by=self.rc.todo,
sent_from=self,
)
elif isinstance(response, Message):
msg = response
else:
msg = Message(content=response or "", role=self.profile, cause_by=self.rc.todo, sent_from=self)
self.rc.memory.add(msg)
return msg
当Role的_act执行结束后,返回到Role的_react函数下 15行rsp = await self._act()
重点来了~~也就是说整个过程是在_react框架(函数)下运行。
某个Role在_react下:先进行Think,再进行Act,在while actions_taken < self.rc.max_react_loop下运行,最多循环两次。
# Role
async def _react(self) -> Message:
"""Think first, then act, until the Role _think it is time to stop and requires no more todo.
This is the standard think-act loop in the ReAct paper, which alternates thinking and acting in task solving, i.e. _think -> _act -> _think -> _act -> ...
Use llm to select actions in _think dynamically
"""
actions_taken = 0
rsp = Message(content="No actions taken yet", cause_by=Action) # will be overwritten after Role _act
while actions_taken < self.rc.max_react_loop:
# think
# 如果时顺序执行动作,在状态正确时返回True
todo = await self._think()
if not todo:
break
# act
logger.debug(f"{self._setting}: {self.rc.state=}, will do {self.rc.todo}")
rsp = await self._act()
actions_taken += 1
return rsp # return output from the last action
重点来了~~再次循环,进入_think中
# Role
async def _think(self) -> bool:
"""Consider what to do and decide on the next course of action. Return false if nothing can be done."""
# 如果Role只绑定了一个动作,那么只能指定这个动作
if len(self.actions) == 1:
self._set_state(0)
return True
if self.recovered and self.rc.state >= 0:
self._set_state(self.rc.state) # action to run from recovered state
self.recovered = False # avoid max_react_loop out of work
return True
# 如果时顺序执行,这里直接返回了
if self.rc.react_mode == RoleReactMode.BY_ORDER:
if self.rc.max_react_loop != len(self.actions):
self.rc.max_react_loop = len(self.actions)
self._set_state(self.rc.state + 1)
return self.rc.state >= 0 and self.rc.state < len(self.actions)
# 如果不是顺序执行
prompt = self._get_prefix()
prompt += STATE_TEMPLATE.format(
history=self.rc.history,
states="\n".join(self.states),
n_states=len(self.states) - 1,
previous_state=self.rc.state,
)
next_state = await self.llm.aask(prompt)
next_state = extract_state_value_from_output(next_state)
logger.debug(f"{prompt=}")
if (not next_state.isdigit() and next_state != "-1") or int(next_state) not in range(-1, len(self.states)):
logger.warning(f"Invalid answer of state, {next_state=}, will be set to -1")
next_state = -1
else:
next_state = int(next_state)
if next_state == -1:
logger.info(f"End actions with {next_state=}")
self._set_state(next_state)
return True
消息队列 & 消息列表
消息列表:当Role的Action执行完毕后将结果包装成ActionOutput对象返回,再被包装为Message,发送给该Role维护的消息列表中。
# 每个Role维护RoleContext对象
class Role(SerializationMixin, ContextMixin, BaseModel):
rc: RoleContext = Field(default_factory=RoleContext)
# RoleContext维护Memory对象
class RoleContext(BaseModel):
memory: Memory = Field(default_factory=Memory)
# Memory维护着Message的列表
class Memory(BaseModel):
storage: list[SerializeAsAny[Message]] = []
消息队列
class MessageQueue(BaseModel):
"""Message queue which supports asynchronous updates."""
model_config = ConfigDict(arbitrary_types_allowed=True)
_queue: Queue = PrivateAttr(default_factory=Queue)
def push(self, msg: Message):
"""Push a message into the queue."""
self._queue.put_nowait(msg)
Queue
class Queue:
"""A queue, useful for coordinating producer and consumer coroutines.
useful for 生产者和消费者协程
如果 maxsize 小于或等于零,则队列大小是无限的。
如果它是一个大于 0 的整数,那么当队列达到 maxsize 时,“await put()”将阻塞,直到通过 get() 移除一个项目。
与标准库中的 Queue 不同,您可以通过 qsize() 可靠地知道此 Queue 的大小,
因为您的单线程 asyncio 应用程序在调用 qsize() 和对 Queue 进行操作之间不会被中断。
"""
def __init__(self, maxsize=0, *, loop=None):
if loop is None:
self._loop = events.get_event_loop()
else:
self._loop = loop
warnings.warn("The loop argument is deprecated since Python 3.8, "
"and scheduled for removal in Python 3.10.",
DeprecationWarning, stacklevel=2)
self._maxsize = maxsize
# Futures.
self._getters = collections.deque()
# Futures.
self._putters = collections.deque()
self._unfinished_tasks = 0
self._finished = locks.Event(loop=loop)
self._finished.set()
self._init(maxsize)
产品经理
ProductManager目标是高效地创造出满足市场需求和用户期望的成功产品
具备准备文档和写PRD两个动作,按顺序执行 RoleReactMode.BY_ORDER
观测准备文档和用户需求动作产生的消息
class ProductManager(Role):
name: str = "Alice"
profile: str = "Product Manager"
goal: str = "efficiently create a successful product that meets market demands and user expectations"
constraints: str = "utilize the same language as the user requirements for seamless communication"
todo_action: str = ""
def __init__(self, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.set_actions([PrepareDocuments, WritePRD])
self._watch([UserRequirement, PrepareDocuments])
self.rc.react_mode = RoleReactMode.BY_ORDER
self.todo_action = any_to_name(WritePRD)
async def _observe(self, ignore_memory=False) -> int:
return await super()._observe(ignore_memory=True)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号