Linux之防火墙
一、安全技术和防火墙
-
netfilter
- 位于内核中包过滤功能体系
- 防火墙的内核态
-
firewalld/iptables
- 默认管理防火墙规则的工具
- 防火墙的用户态
1.1安全技术
-
入侵检测系统(Intrusion Detection Systems):特点是不阻断任何网络访问,量化、定位来自内外网络的威胁情况,主要以提供报警和事后监督为主,提供有针对性的指导措施和安全决策依据,类 似于监控系统一般采用旁路部署(默默的看着你)方式。
-
入侵防御系统(Intrusion Prevention System):以透明模式工作,分析数据包的内容如:溢出攻击、拒绝服务攻击、木马、蠕虫、系统漏洞等进行准确的分析判断,在判定为攻击行为后立即予以 阻断,主动而有效的保护网络的安全,一般采用在线部署方式。(必经之路)
-
防火墙( FireWall ):隔离功能,工作在网络或主机边缘,对进出网络或主机的数据包基于一定的规则检查,并在匹配某规则时由规则定义的行为进行处理的一组功能的组件,基本上的实现都是默 认情况下关闭所有的通过型访问,只开放允许访问的策略,会将希望外网访问的主机放在DMZ (demilitarized zone)网络中
1.2防火墙的分类
按保护范围划分:
- 主机防火墙:服务范围为当前一台主机
- 网络防火墙:服务范围为防火墙一侧的局域网
按实现方式划分:
- 硬件防火墙:在专用硬件级别实现部分功能的防火墙;另一个部分功能基于软件实现,如:华为, 山石hillstone,天融信,启明星辰,绿盟,深信服, PaloAlto , fortinet, Cisco, Checkpoint, NetScreen(Juniper2004年40亿美元收购)等
- 软件防火墙:运行于通用硬件平台之上的防火墙的应用软件,Windows 防火墙 ISA --> Forefront
按网络协议划分:
- 网络层防火墙:OSI模型下四层,又称为包过滤防火墙
- 应用层防火墙/代理服务器:proxy 代理网关,OSI模型七层
mac地址,ip地址,协议端口,应用层数据
包过滤防火墙
- 优点:对用户来说透明,处理速度快且易于维护
- 缺点:无法检查应用层数据,如病毒等
应用层防火墙
- 优点:在应用层对数据进行检查,比较安全
- 缺点:增加防火墙的负载
mac地址,ip地址,协议端口,应用层数据
二、netfilter
2.1
Linux防火墙是由Netfilter组件提供的,Netfilter工作在内核空间,集成在linux内核中。Netfilter 是Linux 2.4.x之后新一代的Linux防火墙机制,是linux内核的一个子系统。
2.2防火墙工具介绍
2.2.1 iptables
由软件包iptables提供的命令行工具,工作在用户空间,用来编写规则,写好的规则被送往netfilter,告诉内核如何去处理信息包
2.2.2 firewalld
从CentOS 7 版开始引入了新的前端管理工具
软件包:firewalld
管理工具:
firewall-cmd 命令行工具
firewall-config 图形工作
2.2.3 nftables
nftables是CentOS 8 新特性
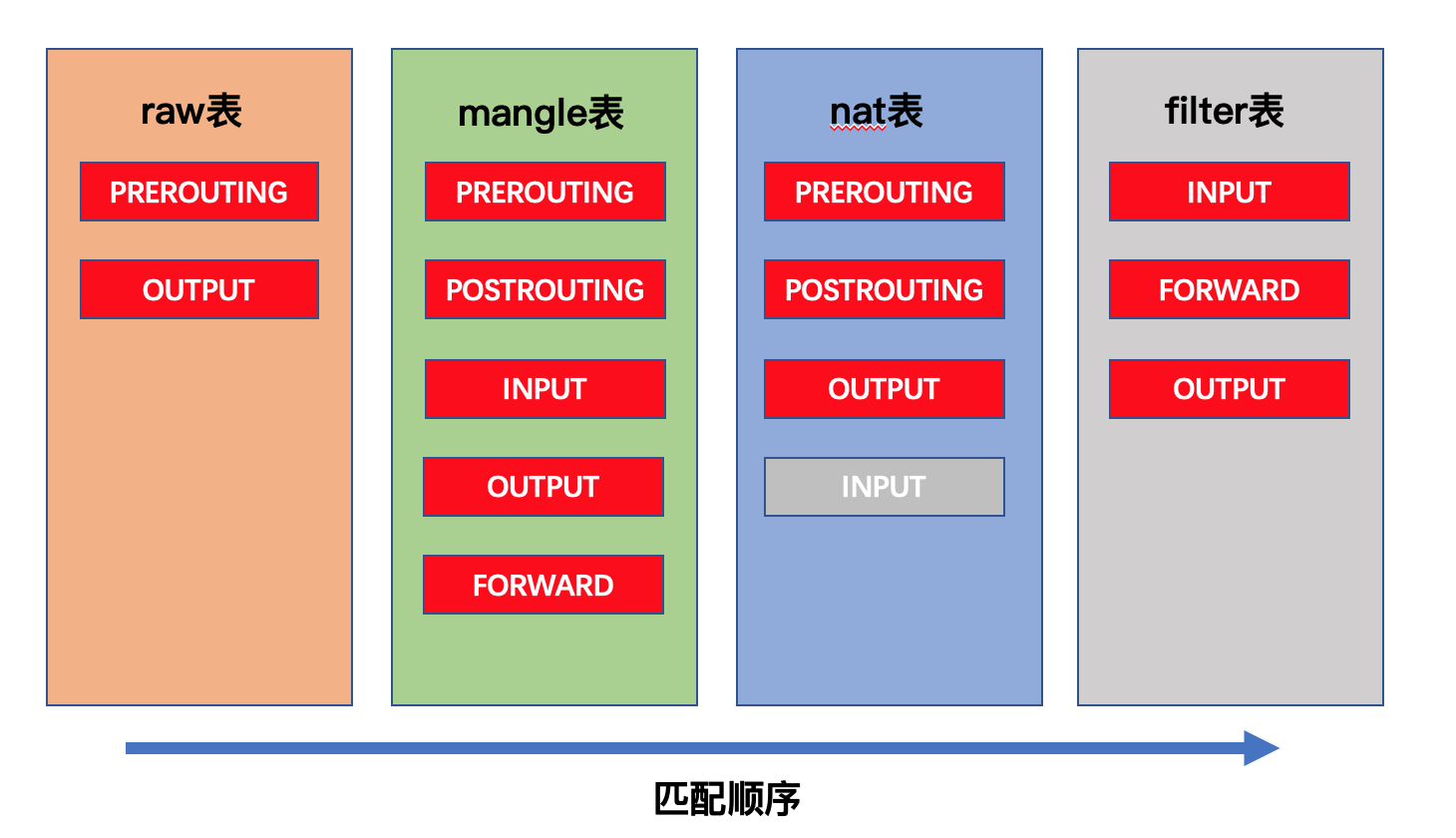
2.3netfilter五个勾子函数和报文流向
4表5连
表中有链,链中有规则
-
规则链
- 规则的作用:对数据包进行过滤或处理
- 链的作用:容纳各种防火墙规则
- 链的分类依据:处理数据包的不同时机
-
5种规则链
- INPUT: 处理入站数据包
- OUTPUT: 处理出站数据包
- FORWARD:处理转发数据包
- POSTROUTING链: 在进行路由选择后处理数据包
- PREROUTING链: 在进行路由选择前处理数据包
-
规则表
- 表的作用:容纳各种规则链
- 表的划分依据: 防火墙规则的作用相似
-
4个规则表
- raw表:确定是否对该数据包进行状态跟踪
- mangle表:为数据包设置标记
- nat表:修改数据包中的源、目标IP地址或端口
- filter表:确定是否放行该数据包 (过滤)
-
规则表之间的顺序
- raw-->manle-->nat-->filter
-
规则链之间的顺序
- 入站:PREROUTING-->INPUT
- 出战:OUTPUT-->POSTROUTING
- 转发:PREROUTING-->FORWARD-->POSTROUTING
-
规则链内的匹配顺序
- 按顺序依次检查,匹配即停止
- 若找不到相匹配的规则,则按该链的默认策略处理
三、iptable
3.1
###使用前准备 [root@localhost ~]#systemctl stop firewalld [root@localhost ~]#yum -y install iptables iptables-services [root@localhost ~]#rpm -q iptables iptables-1.4.21-35.el7.x86_64 [root@localhost ~]#systemctl start iptables.service
3.2语法
iptables [-t 表名] 管理选项 [链名] [匹配条件] [-j 控制类型] DROP(已读不回) REJECT(回复拒绝) ACCEPT(允许) #-t不加,默认filter表
查看防火墙规则
iptables -vnL --line-numbers -v 查看时显示更详细信息 -n 所有字段以数字形式显示 -L 查看规则列表 --line-numbers 显示各条规则在链内的顺序号 #无论查看,添加,删除,只有filter 表可以省略 [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 124 packets, 7828 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 76 packets, 6296 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
添加新的防火墙规则
###服务器1 [root@localhost ~]#iptables -t filter -A INPUT -s 192.168.174.102 -j DROP [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 24 packets, 1588 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 0 0 DROP all -- * * 192.168.174.102 0.0.0.0/0 Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 19 packets, 1700 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination ###服务器2 [root@localhost ~]#ping 192.168.174.100 PING 192.168.174.100 (192.168.174.100) 56(84) bytes of data. #没有回应 ###通过抓包只有主机2请求的包 [root@localhost ~]#tcpdump -i ens33 -p icmp -nn tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on ens33, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes 23:44:31.702172 IP 192.168.174.102 > 192.168.174.100: ICMP echo request, id 4469, seq 106, length 64 23:44:32.702594 IP 192.168.174.102 > 192.168.174.100: ICMP echo request, id 4469, seq 107, length 64
删除清空替换
###替换 -R [root@localhost ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.91.102 -j DROP [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 0 0 DROP all -- * * 192.168.91.102 0.0.0.0/0 Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@localhost ~]#iptables -R INPUT 1 -s 192.168.91.101 -j ACCEPT [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 192.168.91.101 0.0.0.0/0 Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination ###清空 -F [root@localhost ~]# iptables -F ###删除 -D [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy DROP 3 packets, 192 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 192.168.91.101 0.0.0.0/0 Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 396 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@localhost ~]#iptables -D INPUT 1 [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
黑白名单
白名单:在名单才可以 黑名单:在名单里的不可以 -P ####黑名单 [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 66 packets, 4784 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 57 packets, 4972 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@localhost ~]#iptables -P INPUT DROP ####白名单 [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL Chain INPUT (policy DROP 43 packets, 4056 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 12 packets, 1668 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination #### [root@localhost ~]#iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 6 packets, 364 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 384 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@localhost ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 0.0.0.0/0 -j REJECT [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 30 2188 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 47 packets, 5176 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@localhost ~]#iptables -I INPUT 1 -s 192.168.174.1 -j ACCEPT [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 192.168.174.1 0.0.0.0/0 2 40 3065 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@localhost ~]# ping 127.0.0.1 PING 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data. ^C --- 127.0.0.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2000ms ###在最后一条加了 默认拒绝所有 实现白名单功能 还可以使用iptables -F ###添加回环网卡 [root@localhost ~]#iptables -I INPUT 2 -i lo -j ACCEPT [root@localhost ~]#iptables -vnL --line-number Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 1 40 ACCEPT all -- * * 192.168.174.1 0.0.0.0/0 2 0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 3 56 4413 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@localhost ~]# ping 127.0.0.1 PING 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.019 ms 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.027 ms
四、firewalld
五、实操

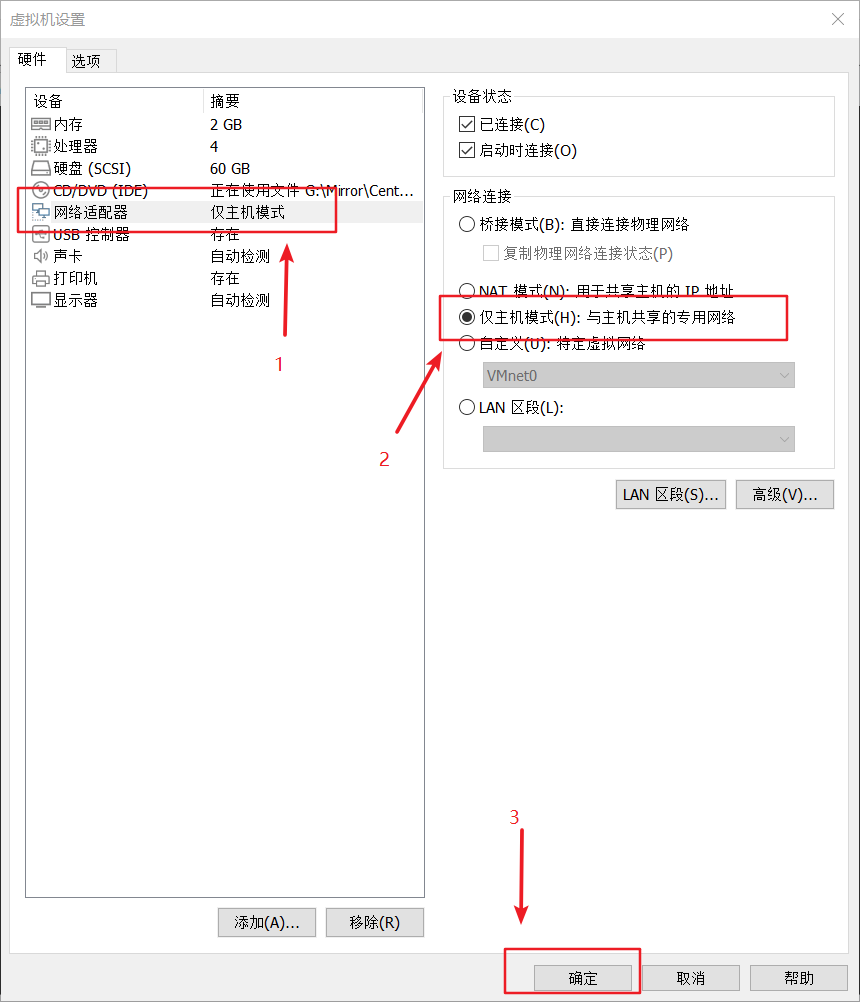
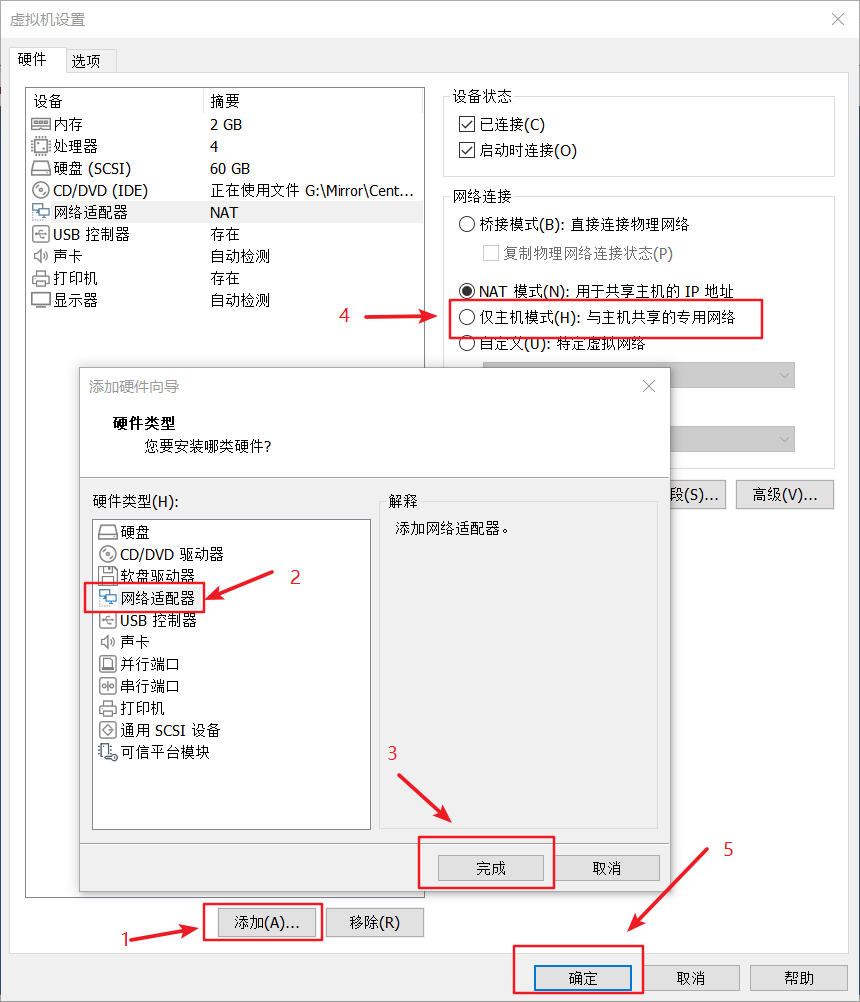
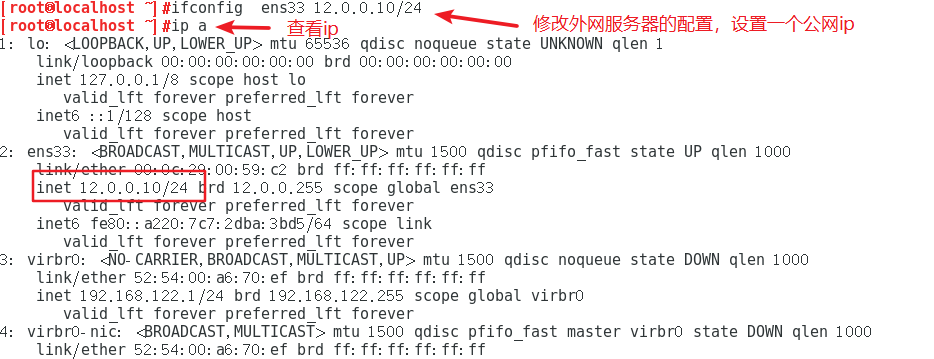
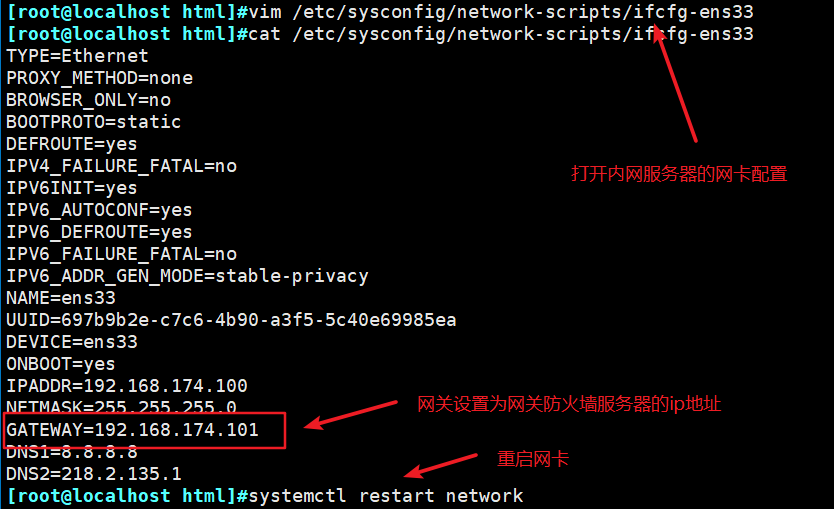
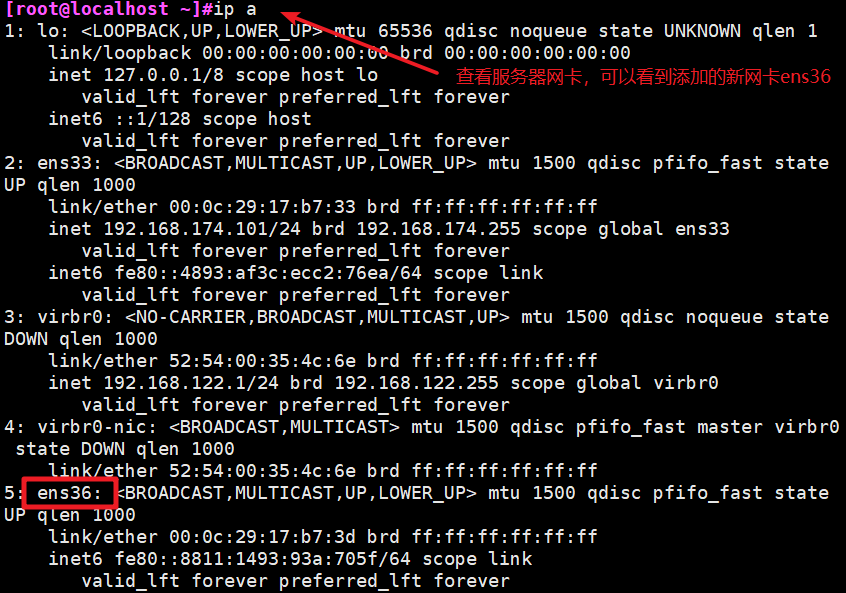

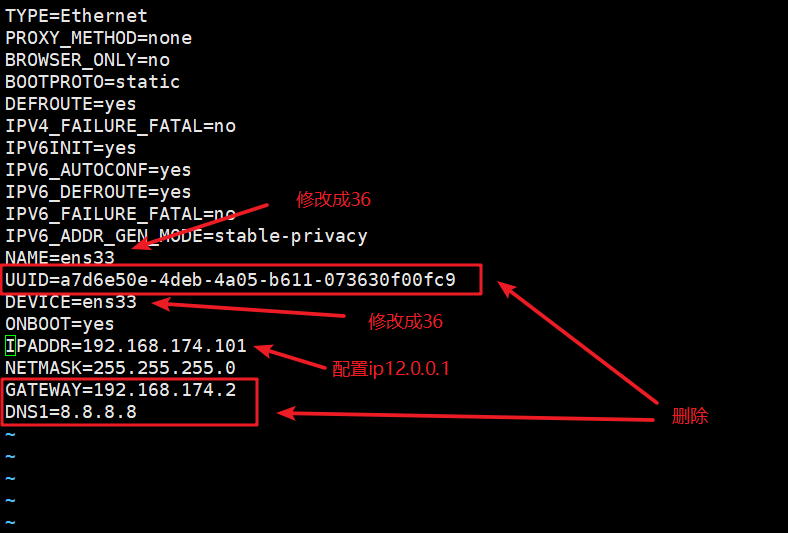
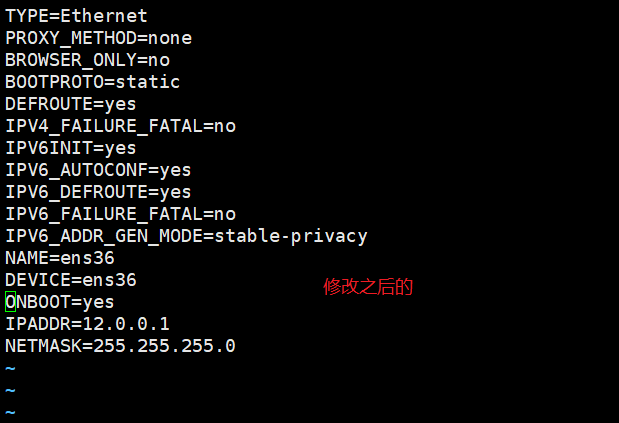
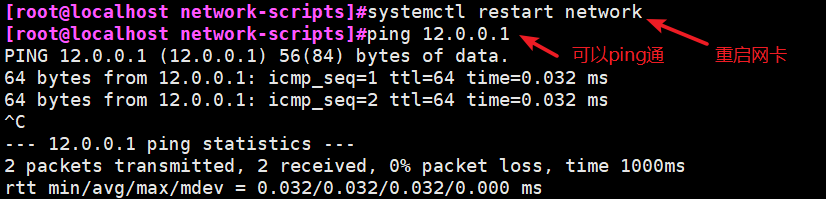
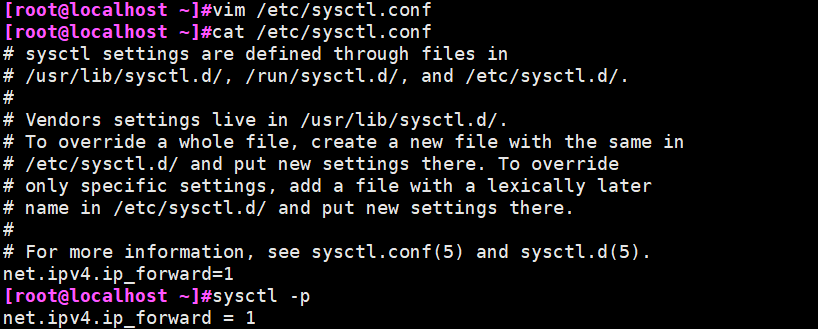
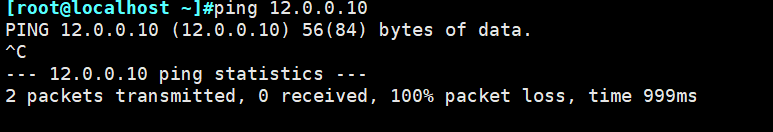

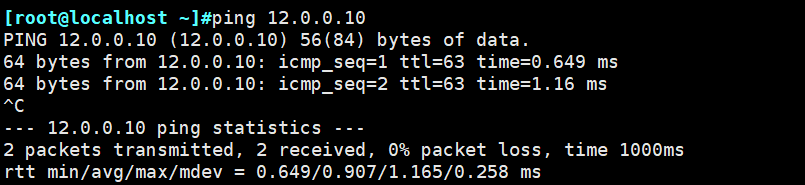

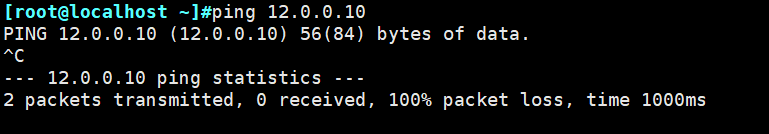

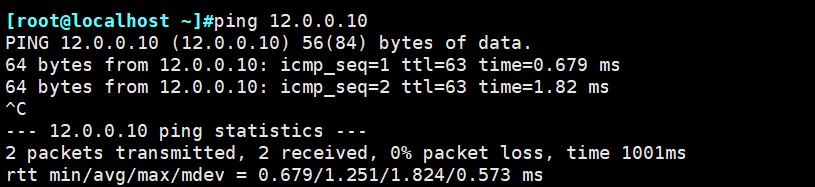
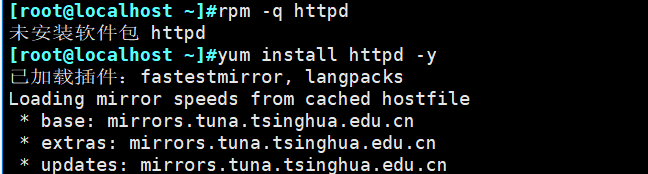
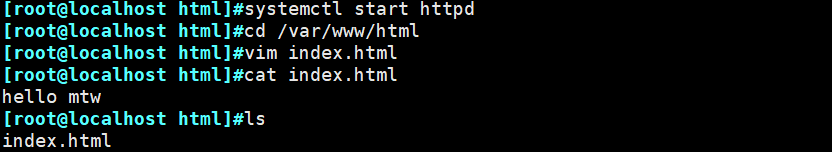



本文作者:德国南部之星
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/mtwm/p/17636921.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步