- feature learning:也叫 representation learning,表示学习;
- deep learning:deep structural learning,deep machine learning;
- hierarchical
- neuron: nerve cell,神经细胞的别称;
0. concepts
机器学习的分类:
- 预测(predicative),被称为 supervised learning
- 如果输出为 categorical,问题又可称为 分类或者模式识别;
- 如果输出为实数(real-valued),问题则被称为回归型问题;
- 描述(descriptive ),则被称为 unsupervised learning,也称为知识发现(knowledge discovery)
- 预测(predicative),被称为 supervised learning
可见节点,不可见结点;
- visible neurons:输入层,输出层;
- invisible neurons:隐层;
- linear or non-linear:
aℓ=σ(wℓ⋅aℓ−1+bℓ) (线性变换,非线性激励)wℓ⋅aℓ−1+bℓ 线性变换,自然是线性的;σ(zℓ) :因为 S 型函数的定义所在,这一步转换又是非线性的;
1. retina layer、receptive fields
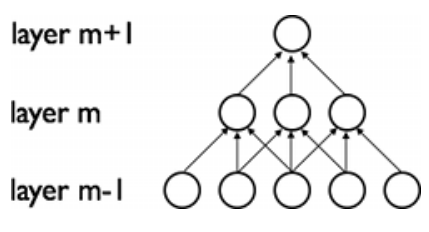
- m-1 层,也即最开始的层,代表 retina layer 视网膜层(表示整个网络结构的输入)
- m 层,具有宽度为 3 的 receptive fields,也因此 m 层的神经元只连接着其邻接层(retina layer,m-1 层)中的 3 个神经元;
- m+1 层具有同 m 层一样的连接性质,其上的 receptive fields 也是 3,但第 m+1 层关于输入层(m-1)层更大,是 5,
- 参照其英文表述,their(m+1)receptive field with respect to the layer below(m 层)is 3,but their(m+1)receptive field with respect to the input (m-1) is larger(5)。
2. end-to-end
端到端,更直观地说,对应着输入到输出(输入层到输出层),对于语音识别(speech recognition)的问题:
- audio(
X )⇒ phonemes ⇒ transcript (Y )((X,Y) ) - audio ⇒ transcript
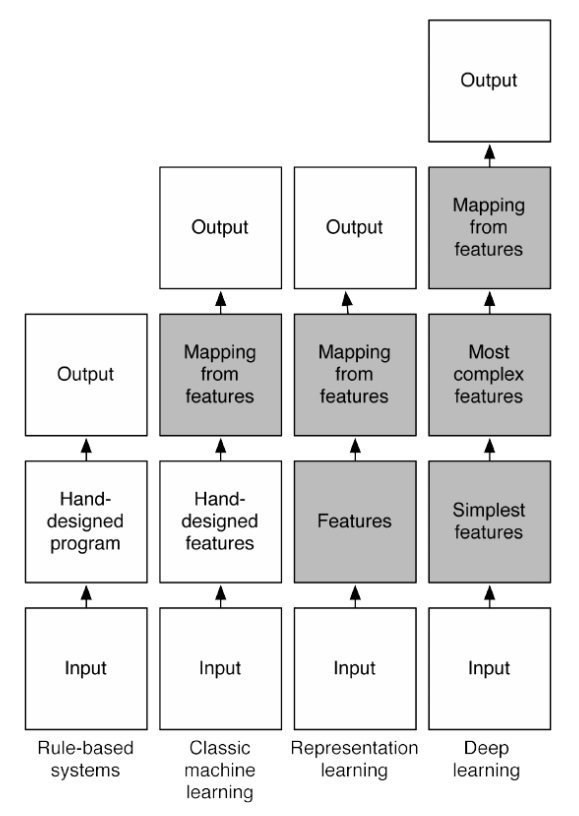
经典机器学习方式是以人类的先验知识将 raw 数据预处理成 feature,然后对feature 进行分类。分类结果取决于 feature 的好坏。所以过去的机器学习专家将大部分时间花费在设计 feature 上。那时的机器学习有个更合适的名字叫 feature engineering。
利用神经网络,让网络自己学习如何抓取 feature 效果更佳。于是兴起了representation learning。这种方式对数据的拟合更加灵活。
网络进一步加深,多层次概念的 representation learning (也就是著名的 deep learning)将识别率达到了另一个新高度。
end to end的好处:通过缩减人工预处理和后续处理,尽可能使模型从原始输入到最终输出,给模型更多可以根据数据自动调节的空间,增加模型的整体契合度。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号