前言
基于深度学习的人脸识别系统,一共用到了5个开源库:OpenCV(计算机视觉库)、Caffe(深度学习库)、Dlib(机器学习库)、libfacedetection(人脸检测库)、cudnn(gpu加速库)。
用到了一个开源的深度学习模型:VGG model。
最终的效果是很赞的,识别一张人脸的速度是0.039秒,而且最重要的是:精度高啊!!!
CPU:intel i5-4590
GPU:GTX 980
系统:Win 10
OpenCV版本:3.1(这个无所谓)
Caffe版本:Microsoft caffe (微软编译的Caffe,安装方便,在这里安利一波)
Dlib版本:19.0(也无所谓
CUDA版本:7.5
cudnn版本:4
libfacedetection:6月份之后的(这个有所谓,6月后出了64位版本的)
这个系列纯C++构成,有问题的各位朋同学可以直接在博客下留言,我们互相交流学习。
====================================================================
本篇是该系列的第五篇博客,介绍设计一个人脸识别的注册类与识别类用于具体的识别任务。
思路
回顾一下这个系列的前四篇博文,把人脸识别的整个任务剖析为了一个个的小任务。我们现在希望用我们定义的这些接口能够非常方便的进行人脸识别的任务,而且可以实现很短的时间内就匹配一个人脸。我们现在希望,可以将其用于一个具体的分类任务中。
我们可以自己来定义这个任务:假设我有20个人要进行人脸识别,我们希望通过我们设计的代码来实现这个任务。如何方便而又快捷的进行实现呢?
这里考虑设计两个类:Register与Recognition。当有人需要注册时,其信息会添加入Register类中的某个成员空间,这里我们用到的信息可以稍微简单一点:
姓名、注册图片、人脸空间。
其中姓名、注册图片是必须要的,而这个人脸空间的意思就是:我们可以实现很多不同场景下的人脸识别。比如在考勤方面,学校想要人脸识别时,受限于人脸数目众多,不可能把所有的人都放在一个数据库里。这个时候我们可以某个信息来区分他们,比如说:课程。 课程这个信息就可以算作一个人脸空间。当我们进行具体的识别时,只会在相应的人脸空间内进行匹配,而不会在其他的人脸空间内匹配。
由于在上一篇博客我们介绍了如何使用CUBLAS来进行人脸向量的运算,那么我们需要对代码进行一些修改,将其换为二维数组。
修改
ExtractFeature.h:
#include <opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
float* ExtractFeature_(Mat FaceROI);//添加一个提取特征的函数
vector<float> ExtractFeature(Mat FaceROI);
void Caffe_Predefine();在这里面添加相应的函数ExtractFeature.cpp:
float* ExtractFeature_(Mat FaceROI)
{
caffe::Caffe::set_mode(caffe::Caffe::GPU);
std::vector<Mat> test;
std::vector<int> testLabel;
test.push_back(FaceROI);
testLabel.push_back(0);
memory_layer->AddMatVector(test, testLabel);// memory_layer and net , must be define be a global variable.
test.clear();
testLabel.clear();
std::vector<caffe::Blob<float>*> input_vec;
net->Forward(input_vec);
boost::shared_ptr<caffe::Blob<float>> fc8 = net->blob_by_name("fc8");
int test_num = 0;
float FaceVector[2622];
while (test_num < 2622)
{
FaceVector[test_num] = (fc8->data_at(0, test_num, 1, 1));
test_num++;
}
return FaceVector;
}实现
我们希望整个类能够具有这样一些功能:可以新加入人脸到某个人脸空间中,可以将人脸空间中的人脸提取出来保存到一个矩阵当中(很多个向量组成的矩阵),可以把提取出来的矩阵和人脸的名字都保存起来以便于下一次的读取。
SaveVector.h:
#include <opencv.hpp>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void SaveNameVector(vector<string> &NameVector, string filename);//保存姓名,需要输入
vector<string> LoadNameVector(vector<string> &NameVector, string filename);
void SaveFaceMatrix(float **FaceMatrix, string filename, int rows);//用于保存提取出来特征的人脸矩阵,需要输入:人脸矩阵、保存的文件名,矩阵的行数(列均为2622维)
Mat LoadMat(string file);//将xml文件提取出来转换为OpenCV的Mat类
float** MatToVector2d(Mat &FaceMatrix_mat);//将Mat类转换为二维数组SaveVector.cpp:
#include <SaveVector.h>
Mat Vector2dToMat(float **FaceMatrix,int rows)
{
//know FaceMatrix's col and row.
//FaceVector->Mat
Mat T(rows, 2622, CV_32F);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 2622; j++)
{
T.at<float>(i, j) = FaceMatrix[i][j];
}
return T;
}
void SaveMat(Mat &FaceMatrix_,string filename)
{
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "FaceMatrix" << FaceMatrix_;
fs.release();
}
Mat LoadMat(string file)//文件名
{
FileStorage fs(file, FileStorage::READ);
Mat FaceMatrix_;
fs["FaceMatrix"] >> FaceMatrix_;
return FaceMatrix_;
}
float** MatToVector2d(Mat &FaceMatrix_mat)
{
float **array2d = new float*[FaceMatrix_mat.rows];
for (int i = 0; i<FaceMatrix_mat.rows; ++i)
array2d[i] = new float[FaceMatrix_mat.cols];
for (int i = 0; i<FaceMatrix_mat.rows; ++i)
array2d[i] = FaceMatrix_mat.ptr<float>(i);
return array2d;
}
void SaveFaceMatrix(float *FaceMatrix[], string filename,int rows)
{
Mat T = Vector2dToMat(FaceMatrix, rows);
if (!T.empty())
SaveMat(T, filename);
else
{
cout << "Please check out your the matrix and the file.We can not read any information." << endl;
exit(0);
}
}
//存储姓名
void SaveNameVector(vector<string> &NameVector, string filename){
int Num = 0;
ofstream NameSaveFile(filename, ios::app);
while (Num < NameVector.size())
NameSaveFile << NameVector[Num++] << endl;
NameSaveFile.clear();
}
vector<string> LoadNameVector(vector<string> &NameVector_, string filename)
{
ifstream in(filename);
int Num = 0;
string line;
if (in){
while (getline(in, line))
{
NameVector_.push_back(line);
}
}
in.clear();
return NameVector_;
}这里在存储时,先将二维数组转换为OpenCV的Mat类型,再使用FileStorage将其序列化。当然,你也可以使用boost库来做这个事情。
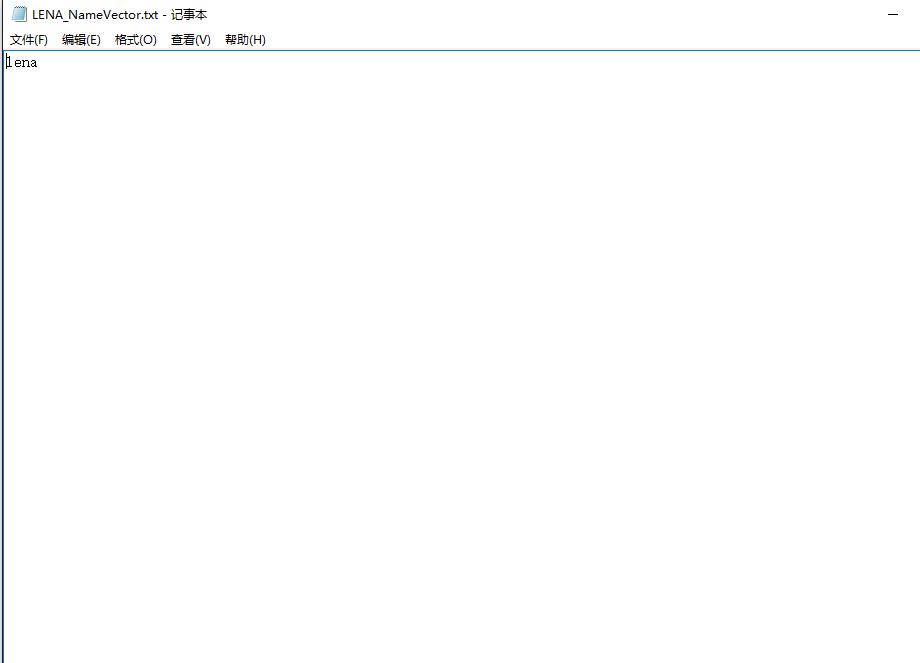
存储的结果是这样的(一个人):

然后我们再来实现类:
Register.h:
//define a register
#include <opencv.hpp>
#include <SaveVector.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
class Register
{
public:
string FaceSpace;//The name of FaceSpace
vector<string> FaceName;//People's name ,the same as FaceNumber
//float *
float* MatToVector_(Mat TrainMat);//将Mat在人脸识别、预处理后转换为一个向量
float *FaceMatrix[20];//20个人
void JoinFaceSpace_(Mat newFace, string FaceSpace, string FaceName);//join the new face to FaceSpace
float** LoadVector_(string FaceSpace);//读入数据
Mat FaceMatrix_mat;//临时存储读取的Mat类型
private:
void SaveVector_(float *FaceMatrix_[], vector<string> FaceName_, string FaceSpace_) // save the people's face vector
{
//使用xml来存储数据
if (!(FaceMatrix_ == NULL) && !FaceName_.empty())
{
SaveFaceMatrix(FaceMatrix_, "data/" + FaceSpace_ + "_FaceMatrix.xml", FaceName_.size());
SaveNameVector(FaceName, "data/" + FaceSpace_ + "_NameVector.txt");
}
else { cout << "Sorry.There are some problems while saving your face and name. please try again" << endl; }
}
};Register.cpp:
#include <Register.h>
#include <FaceDetect.h>
#include <ComputeDistance.h>
#include <ExtractFeature_.h>
float* Register::MatToVector_(Mat TrainMat)
{
Mat TrainMat_ROI = Facedetect(TrainMat);
if (!TrainMat_ROI.empty())
return ExtractFeature_(TrainMat_ROI);
else return NULL;
}
void arrayJoinArray2d(float *feature, float *FaceMatrix[], int i)//实现人脸向量加入人脸矩阵
{
FaceMatrix[i] = feature;
}
void Register::JoinFaceSpace_(Mat newFace, string FaceSpace, string Name)
{
float *FaceVector = MatToVector_(newFace);
if (FaceVector!=NULL)//如果不为空,即存在人脸
{
//加入两个数据表
arrayJoinArray2d(FaceVector, FaceMatrix, FaceName.size());
FaceName.push_back(Name);
//保存这两个数据表
//格式为:矩阵类型;向量类型
//下次可直接读入
SaveVector_(FaceMatrix, FaceName, FaceSpace);
}
else
{
cout << "Please try again,We can not find your face." << endl;
}
}
float** Register::LoadVector_(string FaceSpace) // start load the features.
{
string FaceVectorRoad = "data/" + FaceSpace + "_FaceMatrix.xml";
string NameVectorRoad = "data/" + FaceSpace + "_NameVector.txt";
vector<string> NameVector;
NameVector=LoadNameVector(NameVector, NameVectorRoad);
if ( !NameVector.empty())
{
FaceName = NameVector;
FaceMatrix_mat = LoadMat(FaceVectorRoad);
if (!FaceMatrix_mat.empty())
{
float** a = MatToVector2d(FaceMatrix_mat);
cout << "Sucessfully read the FaceSpace:" + FaceSpace + "'s data!" << endl;
return a;
}
}
else { cout << "There is no data in this FaceSpace:" + FaceSpace + ",Please input ." << endl; }
}这样一来,我们在main函数里就可以非常方便的调用。比如我们要提取一张人脸的图片(这个人的名字叫lena),将其保存在LLEENNAA这个人脸空间中:
#include <Register.h>
#include <FaceDetect.h>
#include <ExtractFeature_.h>
int main()
{
Caffe_Predefine();
Dlib_Predefine();
Register train;
Mat lena = imread("lena.jpg");
train.JoinFaceSpace_(lena,"LLEENNAA","lena");
}即可。
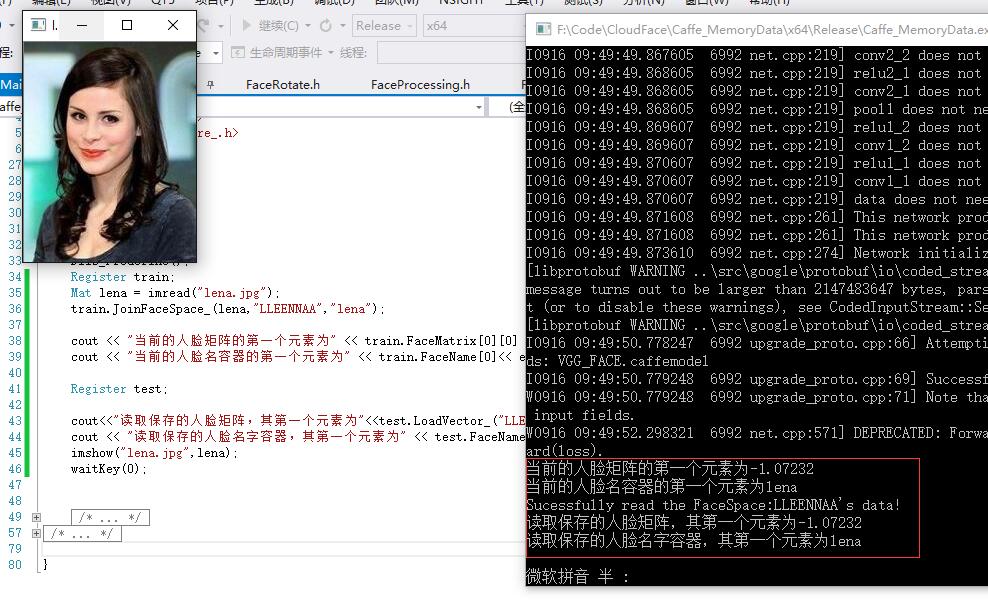
我们可以做个试验,看看程序的正确性。在执行train.JoinFaceSpace_(lena,”LLEENNAA”,”lena”)后,Register里的FaceMatrix会相应增加,并且也会保存为xml和txt。我们再读取这个xml和txt来看看。
#include <Register.h>
#include <FaceDetect.h>
#include <ExtractFeature_.h>
int main()
{
Caffe_Predefine();
Dlib_Predefine();
Register train;
Mat lena = imread("lena.jpg");
train.JoinFaceSpace_(lena,"LLEENNAA","lena");
cout << "当前的人脸矩阵的第一个元素为" << train.FaceMatrix[0][0] << endl;
cout << "当前的人脸名容器的第一个元素为" << train.FaceName[0]<< endl;
Register test;
cout<<"读取保存的人脸矩阵,其第一个元素为"<<test.LoadVector_("LLEENNAA")[0][0]<<endl;
cout << "读取保存的人脸名字容器,其第一个元素为" << test.FaceName[0]<<endl;
imshow("lena.jpg",lena);
waitKey(0);
}程序显示完全一致,表示正确:
=================================================================



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号