URLDNS链分析
URLDNS 是ysoserial中利用链的一个名字,通常用于检测是否存在Java反序列化漏洞。该利用链具有如下特点:
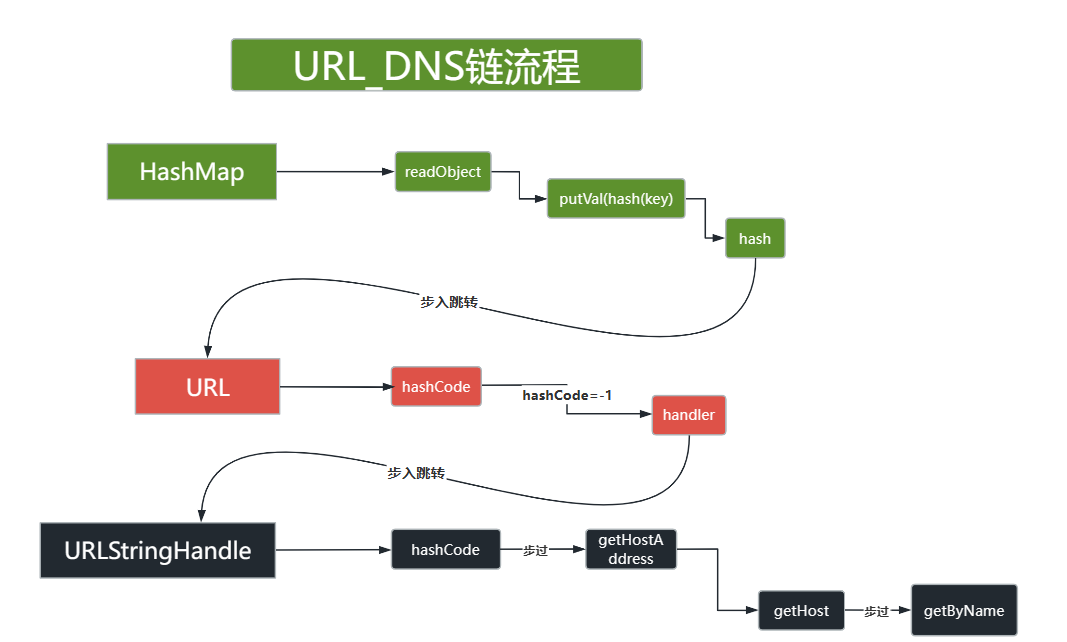
java.util.HashMap 重写了 readObject, 在反序列化时会调用 hash 函数计算 key 的 hashCode.而 java.net.URL 的 hashCode 在计算时会调用 getHostAddress 来解析域名, 从而发出 DNS 请求.
调试到断点位置,步入此步,进入HashMap.readObject
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}关注putVal方法,putVal是往HashMap中放入键值对的方法,这里调用了hash方法来处理key,跟进hash方法(步入putVal后,单击hash):
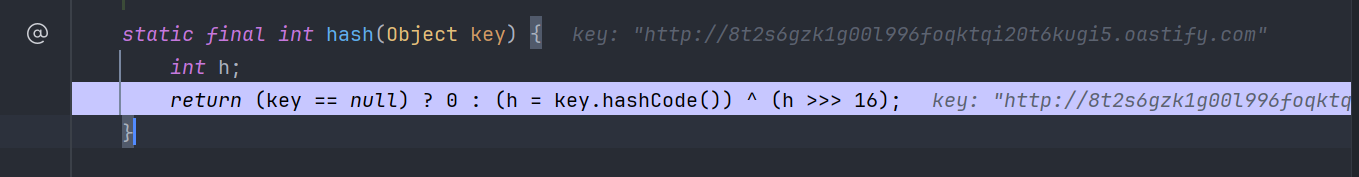
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}这里又调用了key.hashcode方法,而key此时是我们传入的 java.net.URL 对象,那么跟进到这个类的hashCode()方法看下
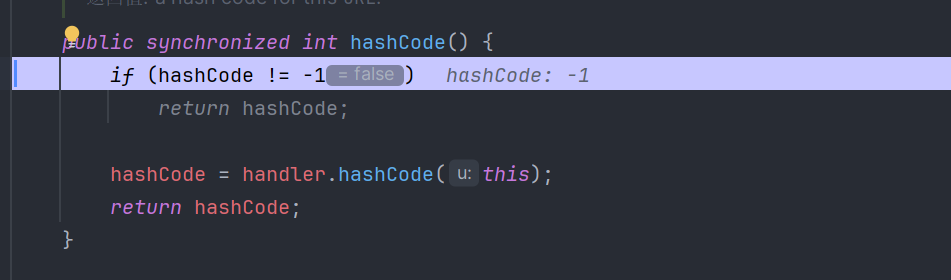
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}当hashCode字段等于-1时会进行handler.hashCode(this)计算,跟进handler发现,定义是
transient URLStreamHandler handler; // transient 关键字,修饰Java序列化对象时,不需要序列化的属性
跟进java.net.URLStreamHandler#hashCode()
4、java.net.URLStreamHandler#hashCode()
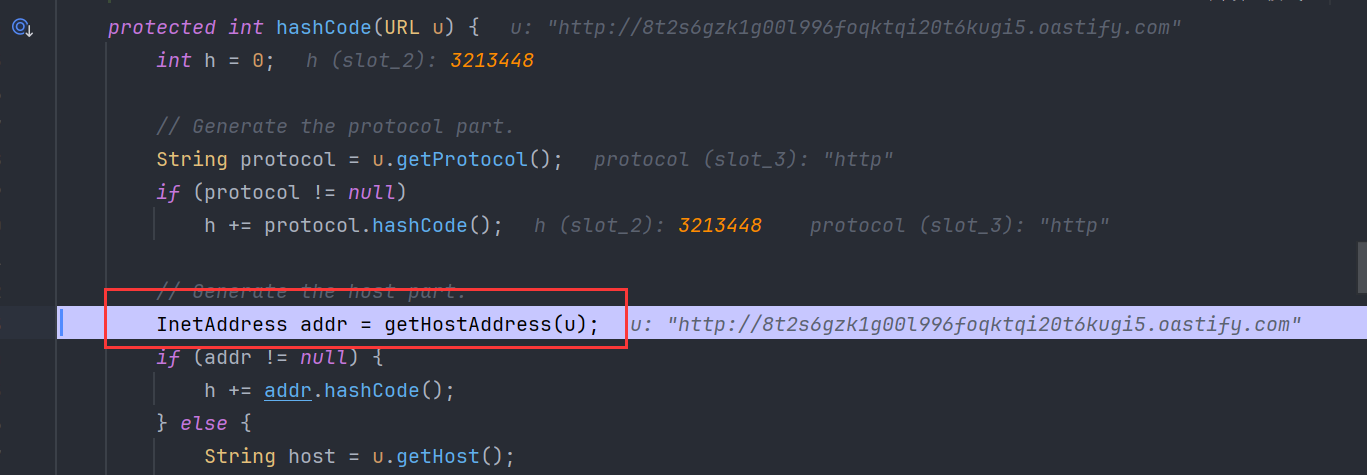
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
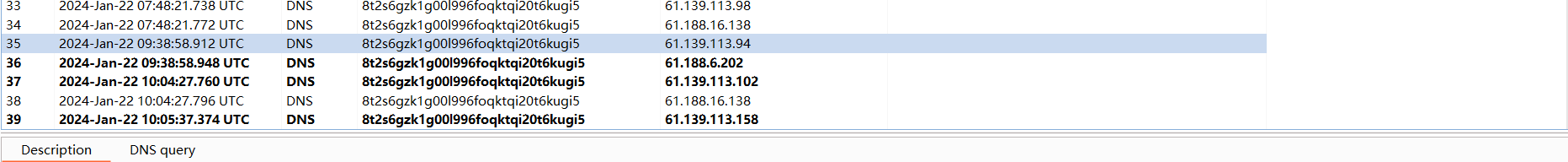
}u 是我们传入的url,在调用getHostAddress方法时,会进行dns查询。
package com.mzy.URLDNS;
import java.io.*;
public class Serializable {
public static void serializable(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("mzy.ser"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Student student = new Student("mzy",21);
serializable(student);
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------
运行此程序会在当前目录生成一个mm.ser的序列化文件package com.mzy.URLDNS;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class unSerializable {
public static Object unserializable(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj= ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Student stu = (Student) unserializable("mm.ser");
System.out.println(stu);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号