多线程的使用
通过NSThread方式开辟线程三种方式
//1.alloc init,手动开启|能够对线程进行更加详细的设置 -(void)createNewThread1 { //1.创建线程 /* 第一个参数:目标对象 self 第二个参数:要调用的方法的名称 第三个参数:要调用方法需要传递的参数<最多传递一个参数,不传nil */ MSHThread *threadA = [[MSHThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(task) object:nil]; //设置线程的属性 threadA.name = @"线程A"; //设置线程的名称 threadA.threadPriority = 1.0; //设置线程的优先级,优先级取值范围为0.0~1.0 最高为1.0 //2.启动线程 [threadA start]; self.threadA = threadA; /////////在创建两条线程//////////// MSHThread *threadB = [[MSHThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(task) object:nil]; threadB.name = @"线程B"; [threadB start]; MSHThread *threadC = [[MSHThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(task) object:nil]; threadC.name = @"线程C"; threadC.threadPriority = 0.1; [threadC start]; } 分离方式创建线程 //2.分离出一条新的线程,自动开启|不能够对线程进行更加详细的设置 -(void)createNewThread2 { //分离出一条新的线程 /* 第一个参数:要调用的方法 第二个参数:目标对象 self 第三个参数:要调用方法需要传递的参数 */ [NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(run:) toTarget:self withObject:@"分离出一条新的线程"]; } //3.开启一条后台线程,自动开启|不能够对线程进行更加详细的设置 -(void)createNewThread3 { //开启一条后台线程 开后台线程的方式 [self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(run:) withObject:@"开启一条后台线程"]; } //线程生命周期:当任务执行完毕之后,线程对象会被销毁 -(void)task { 耗时操作放进线程 for (NSInteger i =0; i<100; i++) { NSLog(@"%zd---task----%@",i,[NSThread currentThread].name); } } -(void)run:(NSString *)param { NSLog(@"run---%@---%@",[NSThread currentThread],param); }
线程的状态接创建跟跟销毁
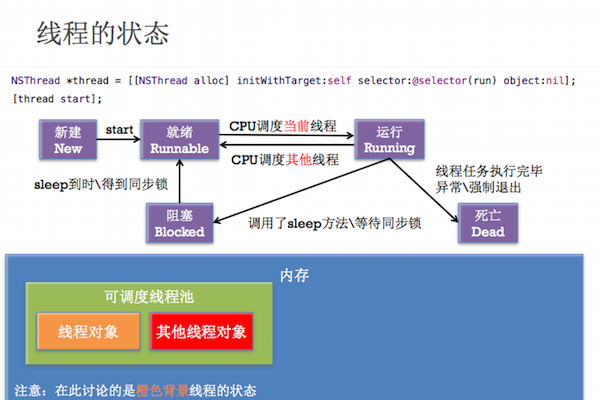
启动线程 - (void)start; // 进入就绪状态 -> 运行状态。当线程任务执行完毕,自动进入死亡状态 阻塞(暂停)线程 + (void)sleepUntilDate:(NSDate *)date; + (void)sleepForTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)ti; // 进入阻塞状态 强制停止线程 + (void)exit; // 进入死亡状态 注意:一旦线程停止(死亡)了,就不能再次开启任务
线程安全
#import "ViewController.h" @interface ViewController () /** 售票员A*/ @property (nonatomic ,strong)NSThread *threadA; /** 售票员B*/ @property (nonatomic ,strong)NSThread *threadB; /** 售票员C*/ @property (nonatomic ,strong)NSThread *threadC; /** 总票数*/ @property (nonatomic ,assign)NSInteger totalTickets; @end @implementation ViewController -(void)viewDidLoad { self.threadA = [[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sale) object:nil]; self.threadA.name = @"售票员A"; self.threadB = [[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sale) object:nil]; self.threadB.name = @"售票员B"; self.threadC = [[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sale) object:nil]; self.threadC.name = @"售票员C"; //设置100 self.totalTickets = 100; } -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { [self.threadA start]; [self.threadB start]; [self.threadC start]; } -(void)sale { //int i = 0; //查看余票的数量,如有有name就卖出去一张,如果没有就告诉用户今年别回家了 while (1) {
// 多条线程访问一个资源,此处加锁 @synchronized(self) { //锁对象:要求时唯一的 NSInteger count = self.totalTickets; if (count >0) { [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:0.01]; self.totalTickets = count - 1; NSLog(@"%@卖出去了一张票,还剩下%zd张票",[NSThread currentThread].name,self.totalTickets); }else { NSLog(@"今年别回家了"); break; } } } }
多线程的安全隐患
l资源共享
p1块资源可能会被多个线程共享,也就是多个线程可能会访问同一块资源
p比如多个线程访问同一个对象、同一个变量、同一个文件
l当多个线程访问同一块资源时,很容易引发数据错乱和数据安全问题
解决的方案
l互斥锁使用格式
@synchronized(锁对象) { // 需要锁定的代码 }
注意:锁定1份代码只用1把锁,用多把锁是无效的
l互斥锁的优缺点
p优点:能有效防止因多线程抢夺资源造成的数据安全问题
p缺点:需要消耗大量的CPU资源
p
l互斥锁的使用前提:多条线程抢夺同一块资源
p
l相关专业术语:线程同步
p线程同步的意思是:多条线程在同一条线上执行(按顺序地执行任务)
p互斥锁,就是使用了线程同步技术
原子和非原子属性
lOC在定义属性时有nonatomic和atomic两种选择
patomic:原子属性,为setter方法加锁(默认就是atomic)
pnonatomic:非原子属性,不会为setter方法加锁
线程之间通信
//演示线程间通信 -(void)download3 { //1.获得下载图片的url 在子线程方法中进行耗时操作 NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://g.hiphotos.baidu.com/zhidao/pic/item/42166d224f4a20a4884b622491529822730ed0f8.jpg"]; //2.下载图片的二进制数据到本地 NSData *imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url]; //3.把二进制数据转换为image UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:imageData]; NSLog(@"下载图片---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); //4.回到主线程刷新UI /* 第一个参数:要调用的方法 第二个参数:要传递的参数 第三个参数:要不要继续等到调用方法执行完毕 */回主线程的三种方式 //[self performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(showImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO]; //[self performSelector:@selector(showImage:) onThread:[NSThread mainThread] withObject:image waitUntilDone:YES]; //线程间通信的简便方法 [self.imageView performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(setImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:YES]; NSLog(@"---------"); } -(void)showImage:(UIImage *)image { 刷新UI // [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2.0]; NSLog(@"刷新UI---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); self.imageView.image = image; }
通过GDC方式开辟线程(C语言)
#import "ViewController.h" @interface ViewController () @end @implementation ViewController -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { //[self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(syncMain) withObject:nil]; [self asyncConcurrent]; } 异步:只决定具有开辟线程
同步:不具备开辟线程的能力
串行:队列里的任务是有顺序的执行
并行:队列里的任务是并发执行,没有循序
注意:并行队列只在异步函数中有效 //异步函数+并发队列:会开线程,开多条线程,任务并发执行 -(void)asyncConcurrent { //创建队列,保持任务,安排|调度任务 /* 第一个参数:C语言的字符串,设置队列的标签 第二个参数:队列的类型 DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL:串行队列 DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT:并发队列 */ dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("download", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT); NSLog(@"---start----"); //异步函数,封装任务,添加任务到队列中 //异步函数:不需要等待当前代码执行完毕,就可以执行后面的代码 //同步函数:要等到当前代码执行完毕,才能继续往下执行 /* 第一个参数:队列 第二个参数: */ dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 1---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 2---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 3---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 4---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"---end----"); } //异步函数+串行队列:会开线程,1条线程,任务串行执行 -(void)asyncSerial { //创建队列,保持任务,安排|调度任务 /* 第一个参数:C语言的字符串,设置队列的标签 第二个参数:队列的类型 DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL:串行队列 DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT:并发队列 */ dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("download", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); //异步函数,封装任务,添加任务到队列中 /* 第一个参数:队列 第二个参数: */ dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 1---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 2---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 3---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); } //同步函数+并发队列:不会开线程,任务串行执行的 -(void)syncConcurrent { //创建队列,保持任务,安排|调度任务 /* 第一个参数:C语言的字符串,设置队列的标签 第二个参数:队列的类型 DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL:串行队列 DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT:并发队列 */ // dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("download", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT); //获得全局并发队列,默认存在,特殊的并发队列 //第一个参数:队列的优先级 DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT == 0 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0); NSLog(@"---start----"); //同步函数,封装任务,添加任务到队列中 /* 第一个参数:队列 第二个参数: */ dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 1---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 2---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 3---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"---end----"); } //同步函数+串行队列:不会开线程,任务串行执行的 -(void)syncSerial { //创建队列,保持任务,安排|调度任务 /* 第一个参数:C语言的字符串,设置队列的标签 第二个参数:队列的类型 DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL:串行队列 DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT:并发队列 */ dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("download", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); //同步函数,封装任务,添加任务到队列中 /* 第一个参数:队列 第二个参数: */ dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 1---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 2---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 3---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); } //异步函数+主队列:不会开线程,任务串行执行的 -(void)asyncMain { //1.获得主队列 //特点:凡是放在主队列中的任务都在主线程中执行 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_main_queue(); //2.异步函数,封装任务,添加任务到队列中 dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 1---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 2---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 3---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); } //同步函数+主队列:死锁 //主队列特点:如果发现主线程当前正在执行代码(任务),那么主队列将不会调度队列里的任务,直到主线程的任务执行完毕 -(void)syncMain { //1.获得主队列 //特点:凡是放在主队列中的任务都在主线程中执行
// 全局主队列队列
都会在主线程中执行,有序的,不能用同步函数执行 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_main_queue(); NSLog(@"------start----"); //2.同步函数,封装任务,添加任务到队列中 dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 1---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 2---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download 3---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"------end----"); }
CDG中线程的同步
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0); //使用异步函数+并发队列开线程现在图片 dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"download----%@",[NSThread currentThread]); NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.chinanews.com/cr/2014/0108/1576296051.jpg"]; NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url]; UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data]; //回到主线程刷新UI dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ NSLog(@"UI----%@",[NSThread currentThread]); self.imageView.image = image; }); }); }
GCD中常用的函数
#pragma mark ---------------------- #pragma mark Events -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { [self apply]; // MSHPerson *p1 = [[MSHPerson alloc]init]; // MSHPerson *p2 = [[MSHPerson alloc]init]; // NSLog(@"%@---%@",p1.books,p2.books); } #pragma mark ---------------------- #pragma Methods //延迟执行 -(void)delay { NSLog(@"---start---"); //延迟执行 //[NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:2.0 target:self selector:@selector(task) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; //[self performSelector:@selector(task) withObject:nil afterDelay:3.0]; dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0); //GCD延迟执行 /* 第一个参数:表示从什么时候开始计时 DISPATCH_TIME_NOW:现在 第二个参数:间隔的时间 第三个参数:队列,决定block在哪个线程中调用,只有当队列是主队列的时候才在主线程调用 第四个参数: */ dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(2.0 * NSEC_PER_SEC)), queue, ^{ NSLog(@"----GCD---%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }); } //栅栏函数 -(void)barrier { //1.创建并发队列 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("www.520it", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT); //2.使用异步函数添加任务 dispatch_async(queue, ^{ for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10; i++) { NSLog(@"download 1--%zd-%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]); } }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10; i++) { NSLog(@"download 2--%zd-%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]); } }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10; i++) { NSLog(@"download 3--%zd-%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]); } }); //栅栏函数:控制队列中任务的执行顺序,前面的所有任务执行完毕之后执行栅栏函数,自己执行完毕之后再之后后面的任务 dispatch_barrier_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"++++++++++++++++++++++++++"); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10; i++) { NSLog(@"download 4--%zd-%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]); } }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10; i++) { NSLog(@"download 5--%zd-%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]); } }); } //一次性代码 /*保证在整个程序运行过程中执行一次*/ -(void)once { static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ NSLog(@"---once---"); }); } //普通遍历和快速迭代比较 -(void)forAndApply { // for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10; i++) { // NSLog(@"%zd----%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]); // } //1.创建并发队列 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("www.520it", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT); /* 第一个参数:遍历的次数 第二个参数:队列,决定block在哪个线程调用,并发队列 第三个参数:索引 */ dispatch_apply(10, queue, ^(size_t index) { NSLog(@"%zd----%@",index,[NSThread currentThread]); }); } //普通遍历剪切文件 -(void)moveFile { //1.拿到文件夹的路径 NSString *from = @"/Users/xmg/Desktop/from"; //2.拿到目标文件夹的路径 NSString *to = @"/Users/xmg/Desktop/to"; //3.拿到该文件夹下面所有的文件 NSArray *subPaths = [[NSFileManager defaultManager] subpathsAtPath:from]; // NSLog(@"%@",subPaths); NSInteger count = subPaths.count; //4.遍历数组 for (NSInteger i = 0; i<count; i++) { //4.0 获得文件的名称 NSString *fileName = subPaths[i]; //4.1 拼接文件的全路径 //stringByAppendingPathComponent:在拼接之前添加/ NSString *fromFullPath = [from stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName]; //4.2 剪切到什么地方 NSString *toFullPath = [to stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName]; NSLog(@"%@---%@---%@",fromFullPath,toFullPath,[NSThread currentThread]); //4.3 执行剪切操作 /* 第一个参数:文件的路径 第二个参数:目标路径 第三个参数: */ NSError *error = nil; [[NSFileManager defaultManager] moveItemAtPath:fromFullPath toPath:toFullPath error:&error]; } } //快速迭代剪切文件 -(void)apply { //1.拿到文件夹的路径 NSString *from = @"/Users/xmg/Desktop/from"; //2.拿到目标文件夹的路径 NSString *to = @"/Users/xmg/Desktop/to"; //3.拿到该文件夹下面所有的文件 NSArray *subPaths = [[NSFileManager defaultManager] subpathsAtPath:from]; // NSLog(@"%@",subPaths); NSInteger count = subPaths.count; //4.遍历数组 dispatch_apply(count, dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^(size_t index) { //4.0 获得文件的名称 NSString *fileName = subPaths[index]; //4.1 拼接文件的全路径 //stringByAppendingPathComponent:在拼接之前添加/ NSString *fromFullPath = [from stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName]; //4.2 剪切到什么地方 NSString *toFullPath = [to stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName]; NSLog(@"%@---%@---%@",fromFullPath,toFullPath,[NSThread currentThread]); //4.3 执行剪切操作 /* 第一个参数:文件的路径 第二个参数:目标路径 第三个参数: */ NSError *error = nil; [[NSFileManager defaultManager] moveItemAtPath:fromFullPath toPath:toFullPath error:&error]; }); } //延迟执行的测试方法 -(void)task { NSLog(@"---%s",__func__); } @end




