U-Boot命令使用
帮助命令
help
所有命令提示:
h
?
help
某一条命令提示:
? 命令名
help 命令名
信息查询命令
bdinfo
查看板子信息:
=> bdinfo
arch_number = 0x00000000
boot_params = 0x80000100 #启动参数保存地址
DRAM bank = 0x00000000
-> start = 0x80000000 #DRAM起始地址
-> size = 0x20000000 #DRAM大小,512M
eth0name = FEC1
ethaddr = 00:04:9f:04:d2:35
current eth = FEC1
ip_addr = 192.168.1.27
baudrate = 115200 bps
TLB addr = 0x9FFF0000
relocaddr = 0x9FF56000
reloc off = 0x18756000
irq_sp = 0x9EF53EA0
sp start = 0x9EF53E90 #堆栈指针起始地址
printenv
查看环境变量信息:
=> printenv
[-f]=name
baudrate=115200
board_name=EVK
board_rev=14X14
boot_fdt=try
bootcmd=console=ttymxc0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblkp2 rootwait rw
bootcmd_mfg=run mfgtool_args;bootz ${loadaddr} ${initrd_addr} ${fdt_addr};
bootdelay=5 #uboot启动延时
bootscript=echo Running bootscript from mmc ...; source
console=ttymxc0
ethact=FEC1
ethaddr=00:04:9f:04:d2:35
ethprime=FEC
fdt_addr=0x83000000
version
查看uboot版本号:
=> version
U-Boot 2016.03 (Mar 08 2022 - 22:32:31 +0800)
arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc (Sourcery CodeBench Lite 2014.05-29) 4.8.3 20140320 (prerelease)
GNU ld (Sourcery CodeBench Lite 2014.05-29) 2.24.51.20140217
环境变量操作
环境变量的操作涉及到两个命令:setenv 和 saveenv,命令 setenv 用于设置或者修改环境变
量的值。命令 saveenv 用于保存修改后的环境变量,一般环境变量是存放在外部 flash 中的,
uboot 启动的时候会将环境变量从 flash 读取到 DRAM 中。
setenv & saveenv
(1)修改和保存环境变量:
=> setenv bootdelay 3
=> printenv bootdelay
bootdelay=3
=> saveenv
Saving Environment to MMC...
Writing to MMC(1)... done #保存在MMC(1)中,当前也就是EMMC
(2)修改环境变量如果带空格,需要使用单引号括起来:
=> setenv bootargs 'console=ttymxc0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblklp2 rootwait rw'
=> saveenv
(3)新建环境变量
=> setenv author grace
=> saveenv
Saving Environment to MMC...
Writing to MMC(1)... done
=> printenv author
author=grace
(4)删除环境变量,对环境变量赋空值
=> setenv author
=> saveenv
=> printenv author
## Error: "author" not defined
内存相关命令
uboot 命令中的数字都是十六进制的!不是十进制的。
内存操作命令就是用于直接对 DRAM 进行读写操作的,常用的内存操作命令有 md、nm、
mm、mw、cp 和 cmp。
md
md命令:显示内存值
=> help md
md - memory display
Usage:
md [.b, .w, .l] address [# of objects]
# b:byte(1字节) w:word(2字节) l:long(4字节)
# address: 内存起始地址
# [# of objects]: 查看的数据长度,多少个单位,十六进制格式
=> md.b 800000000 14 #从0x80000000开始读取20个bytes
00000000: 1c f0 9f e5 1c f0 9f e5 1c f0 9f e5 1c f0 9f e5 ................
00000010: 1c f0 9f e5 ....
=> md.w 800000000 14 #从0x80000000开始读取20个words
00000000: f01c e59f f01c e59f f01c e59f f01c e59f ................
00000010: f01c e59f f01c e59f f01c e59f f01c e59f ................
00000020: f01c e59f f9bc 0000 ........
=> md.l 800000000 14 #从0x80000000开始读取20个long
00000000: e59ff01c e59ff01c e59ff01c e59ff01c ................
00000010: e59ff01c e59ff01c e59ff01c e59ff01c ................
00000020: e59ff01c 0000f9bc 0091ffbc 0091ffc0 ................
00000030: 0091ffc4 0091ffc8 0091ffcc 0091ffd0 ................
00000040: 0091ffd4 0091ffd8 00000000 00000000 ................
nm
nm命令:修改指定地址的内存值,修改内存的时候地址不会自增
=> help nm
nm - memory modify (constant address)
Usage:
nm [.b, .w, .l] address
# b:byte(1字节) w:word(2字节) l:long(4字节)
# address: 内存起始地址
=> nm.b 80000000 #byte为单位修改0x80000000地址内存值
80000000: ff ? 12 #修改为0x12
80000000: 12 ? q #保存退出
=> nm.w 80000000
80000000: ff12 ? 5678
80000000: 5678 ? q
=> nm.l 80000000
80000000: efff5678 ? 12345678
80000000: 12345678 ? q
=> md.l 80000000 1
80000000: 12345678 xV4.
mm
mm命令:修改指定地址的内存值,修改内存的时候地址会自增
=> help mm
mm - memory modify (auto-incrementing address)
Usage:
mm [.b, .w, .l] address
# b:byte(1字节) w:word(2字节) l:long(4字节)
# address: 内存起始地址
=> mm.l 80000000
80000000: 12345611 ? 5a5a5a5a
80000004: ffffffff ? 88888888
80000008: ffffffff ? 0a0a0a0a
8000000c: f7bfffff ? q
=> md.l 80000000 3
80000000: 5a5a5a5a 88888888 0a0a0a0a ZZZZ........
mw
mw命令:使用一个指定的数据填充一段内存
=> mw
mw - memory write (fill)
Usage:
mw [.b, .w, .l] address value [count]
# b:byte(1字节) w:word(2字节) l:long(4字节)
# address: 内存起始地址
# value: 填充的值
# count: 填充的单位个数
=> mw.l 80000000 0a0a0a0a 10
=> md.l 80000000 10
80000000: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000010: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000020: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000030: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
cp
cp命令:将DRAM中的数据从一段内存拷贝到另一段内存中,或者FLASH中的数据拷贝到DRAM中
=> help cp
cp - memory copy
Usage:
cp [.b, .w, .l] source target count
# b:byte(1字节) w:word(2字节) l:long(4字节)
# source: 起始地址
# target: 目的地址
# count: 拷贝的单位个数
=> cp.l 80000000 80000100 10
=> md.l 80000000 10
80000000: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000010: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000020: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000030: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
=> md.l 80000100 10
80000100: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000110: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000120: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
80000130: 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a 0a0a0a0a ................
cmp
cmp命令:比较内存值
=> help cmp
cmp - memory compare
Usage:
cmp [.b, .w, .l] addr1 addr2 count
# b:byte(1字节) w:word(2字节) l:long(4字节)
# addr1: 第一段地址
# addr2: 第二段地址
# count: 比较的单位个数
=> cmp.l 80000000 80000100 10
Total of 16 word(s) were the same
=> cmp.l 80000000 80000100 12
word at 0x80000040 (0xffffffff) != word at 0x80000140 (0xfdffffff)
Total of 16 word(s) were the same
网络相关命令
配置前需要先将开发板和路由器或者电脑连接起来,当前测试是开发板和路由器相连接的。
路由器、开发板、笔记本之间的网络关系如下,笔记本作为服务器:
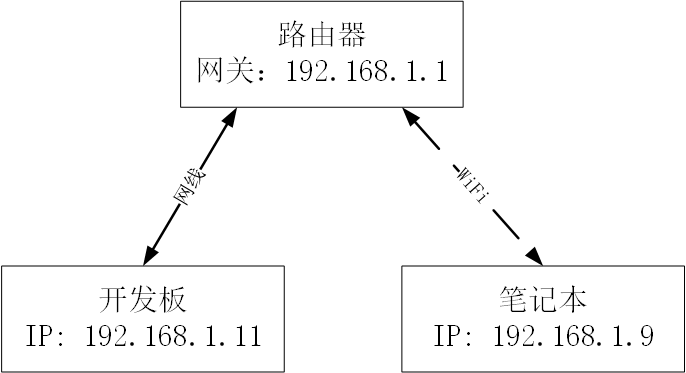
配置命令
开发板主要需要配置如下变量:
=> setenv ipaddr 192.168.1.11 #配置开发板IP
=> setenv ethaddr 00:04:9f:04:d2:35 #配置开发板MAC地址
=> setenv gatewayip 192.168.1.1 #配置网关地址
=> setenv netmask 255.255.255.0 #配置子网掩码
=> setenv serverip 192.168.1.9 #配置服务器IP地址
=> saveenv
需要注意以下几点:
1、开发板和服务器IP需要在同一个网段内;
2、MAC地址必须配置,并且同一个网段内不能存在相同的地址。
ping
ping命令:IP配置好之后,可以通过该命令测试网络是否正常
=> ping 192.168.1.1
FEC1 Waiting for PHY auto negotiation to complete.... done
Using FEC1 device
host 192.168.1.1 is alive
如果服务器不能ping通,也是正常的,可能笔记本防火墙没关。
=> ping 192.168.1.9
Using FEC1 device
ping failed; host 192.168.1.9 is not alive
注意:不能ping uboot,uboot没有对ping处理
DHCP
DHCP命令:从路由器获取IP地址
=> dhcp
BOOTP broadcast 1
BOOTP broadcast 2
BOOTP broadcast 3
BOOTP broadcast 4
*** Unhandled DHCP Option in OFFER/ACK: 125
*** Unhandled DHCP Option in OFFER/ACK: 125
DHCP client bound to address 192.168.1.11 (2204 ms)
*** Warning: no boot file name; using 'C0A8010B.img'
Using FEC1 device
TFTP from server 192.168.1.9; our IP address is 192.168.1.11
Filename 'C0A8010B.img'.
Load address: 0x80800000
Loading: T T T T T T T T T T
Retry count exceeded; starting again
TFTP
TFTP命令:通过TFTP服务从网络下载文件到DRAM中
这里在笔记本上使用IPOP作为TFTP服务器,uboot从TFTP上下载zImage来进行实验。
=> help tftp
tftpboot - boot image via network using TFTP protocol
Usage:
tftpboot [loadAddress] [[hostIPaddr:]bootfilename]
# loadAddress: 文件存放在DRAM中的地址
# hostIPaddr: TFTP服务器的地址
# bootfilename: 下载文件名
=> tftp 80800000 zImage
Using FEC1 device
TFTP from server 192.168.1.9; our IP address is 192.168.1.11
Filename 'zImage'.
Load address: 0x80800000
Loading: #################################################################
########################################################
211.9 KiB/s
done
Bytes transferred = 5607728 (559130 hex)
MMC操作命令
uboot支持EMMC、SD卡、NAND FLASH等,当前使用的是EMMC进行实验。
查看MMC相关命令:
=> help mmc
mmc - MMC sub system
Usage:
mmc info - display info of the current MMC device
mmc read addr blk# cnt
mmc write addr blk# cnt
mmc erase blk# cnt
mmc rescan
mmc part - lists available partition on current mmc device
mmc dev [dev] [part] - show or set current mmc device [partition]
mmc list - lists available devices
mmc hwpartition [args...] - does hardware partitioning
arguments (sizes in 512-byte blocks):
[user [enh start cnt] [wrrel {on|off}]] - sets user data area attributes
[gp1|gp2|gp3|gp4 cnt [enh] [wrrel {on|off}]] - general purpose partition
[check|set|complete] - mode, complete set partitioning completed
WARNING: Partitioning is a write-once setting once it is set to complete.
Power cycling is required to initialize partitions after set to complete.
mmc bootbus dev boot_bus_width reset_boot_bus_width boot_mode
- Set the BOOT_BUS_WIDTH field of the specified device
mmc bootpart-resize <dev> <boot part size MB> <RPMB part size MB>
- Change sizes of boot and RPMB partitions of specified device
mmc partconf dev boot_ack boot_partition partition_access
- Change the bits of the PARTITION_CONFIG field of the specified device
mmc rst-function dev value
- Change the RST_n_FUNCTION field of the specified device
WARNING: This is a write-once field and 0 / 1 / 2 are the only valid values.
mmc setdsr <value> - set DSR register value
mmc info
mmc info:输出MMC设备信息
=> mmc info
Device: FSL_SDHC
Manufacturer ID: 15
OEM: 100
Name: 8GTF4
Tran Speed: 52000000 #速度52MHz
Rd Block Len: 512
MMC version 4.0
High Capacity: Yes
Capacity: 7.3 GiB
Bus Width: 8-bit #总线位宽
Erase Group Size: 512 KiB
mmc rescan
mmc rescan:扫描板子上的所有MMC设备
=> mmc rescan
mmc list
mmc list:查看当前有几个MMC设备
=> mmc list
FSL_SDHC: 0
FSL_SDHC: 1 (eMMC)
mmc dev
mmc dev:切换当前MMC设备
# mmc dev [dev] [part] - show or set current mmc device [partition]
=> mmc dev 0 # 当前板子没有MMC 0设备
Card did not respond to voltage select!
=> mmc dev 1
switch to partitions #0, OK
mmc1(part 0) is current device
mmc part
mmc part:查看MMC分区
=> mmc part
Partition Map for MMC device 1 -- Partition Type: DOS
Part Start Sector Num Sectors UUID Type
1 20480 262144 6101e345-01 0c
2 282624 14987264 6101e345-02 83
#编号 起始扇区 扇区个数
#如果EMMC烧写了系统,则会存在3个分区:第 0 个分区存放 uboot,第 1 个分区存放Linux 镜像文件和设备树,第 2 个分区存放根文件系统。
=> mmc dev 1 2 #切换第二个分区为当前MMC设备
switch to partitions #2, OK
mmc1(part 2) is current device
mmc read
mmc read:读取mmc设备的数据
# mmc read addr blk# cnt
# addr: 数据读取到DRAM的地址
# blk: 读取的块起始地址,一个块512字节
# cnt: 读取的块数量
=> mmc read 80800000 600 10
MMC read: dev # 1, block # 1536, count 16 ... 16 blocks read: OK
mmc write
mmc write:将数据写到MMC设备
# mmc write addr blk# cnt
# addr: 写入MMC中的数据在DRAM中的起始地址
# blk: 写入的块起始地址,一个块512字节
# cnt: 写入的块数量
可使用MMC设备来升级uboot,在uboot中更新uboot。实现方式:通过tftp将新的uboot下载到DRAM中,在使用mmc write将其写入MMC设备中。
=> version
U-Boot 2016.03 (Mar 08 2022 - 22:32:31 +0800)
arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc (Sourcery CodeBench Lite 2014.05-29) 4.8.3 20140320 (prerelease)
GNU ld (Sourcery CodeBench Lite 2014.05-29) 2.24.51.20140217
=> tftp 80800000 u-boot.imx
Using FEC1 device
TFTP from server 192.168.1.9; our IP address is 192.168.1.11
Filename 'u-boot.imx'.
Load address: 0x80800000
Loading: #################################################################
#######
347.7 KiB/s
done
Bytes transferred = 363520 (58c00 hex)
=> mmc dev 1 1
switch to partitions #0, OK
mmc1(part 0) is current device
=> mmc write 80800000 2 32E
MMC write: dev # 1, block # 2, count 814 ... 814 blocks written: OK
=> reset
resetting ...
U-Boot 2016.03 (Mar 11 2022 - 22:18:24 +0800)
CPU: Freescale i.MX6ULL rev1.1 792 MHz (running at 396 MHz)
CPU: Industrial temperature grade (-40C to 105C) at 49C
Reset cause: WDOG
Board: I.MX6U ALPHA|MINI
I2C: ready
DRAM: 512 MiB
MMC: FSL_SDHC: 0, FSL_SDHC: 1
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
switch to partitions #0, OK
mmc1(part 0) is current device
Net: FEC1
Normal Boot
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
需要注意以下几点:
1)写多少个块,可计算得到,比如u-boot大小为363520,则需要写:363520/512=710(2c6)
2)千万不要写 SD 卡或者 EMMC 的前两个块(扇区),里面保存着分区表!
(8)mmc erase:擦除MMC设备的指定块(尽量不要使用)
# mmc erase blk# cnt
# blk: 擦除的起始块
# cnt: 擦除的数量
FAT格式文件系统操作
对EMMC或其它FLASH中的文件进行操作时,需要用到文件操作相关命令。这里说的仅支持FAT格式的文件系统。
fatfifo
fatfifo:查询执行MMC设备分区的文件系统信息
=> help fatinfo
fatinfo - print information about filesystem
Usage:
fatinfo <interface> [<dev[:part]>]
- print information about filesystem from 'dev' on 'interface'
# interface: 接口,比如mmc
# dev: 查询的设备号
# part: 查询的分区
=> fatinfo mmc 1:1 # EMMC分区1的文件系统信息
Interface: MMC
Device 1: Vendor: Man 000015 Snr 56cf8d2d Rev: 0.6 Prod: 8GTF4R
Type: Removable Hard Disk
Capacity: 7456.0 MB = 7.2 GB (15269888 x 512)
Filesystem: FAT32 "NO NAME " # 文件系统格式为FAT32
fatls
fatls:查看FAT格式设备的目录和文件信息
=> help fatls
fatls - list files in a directory (default /)
Usage:
fatls <interface> [<dev[:part]>] [directory]
- list files from 'dev' on 'interface' in a 'directory'
# interface: 接口,比如mmc
# dev: 查询的设备号
# part: 查询的分区
# directory: 查询的目录
=> fatls mmc 1:1
6785360 zimage
39323 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-4.3-480x272-c.dtb
39323 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-4.3-800x480-c.dtb
39323 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-7-800x480-c.dtb
39323 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-7-1024x600-c.dtb
39323 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-10.1-1280x800-c.dtb
40159 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-hdmi.dtb
40067 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-vga.dtb
8 file(s), 0 dir(s)
fstype
fstype:查看MMC设备某个分区的文件系统格式
=> help fstype
fstype - Look up a filesystem type
Usage:
fstype <interface> <dev>:<part>
- print filesystem type
fstype <interface> <dev>:<part> <varname>
- set environment variable to filesystem type
# interface: 接口,比如mmc
# dev: 查询的设备号
# part: 查询的分区
=> fstype mmc 1:0
Failed to mount ext2 filesystem...
** Unrecognized filesystem type **
=> fstype mmc 1:1
fat
=> fstype mmc 1:2
ext4
# 分区 0 格式未知,因为分区 0 存放的 uboot,并且分区 0 没有格式化,所以文件系统格式未知。分区 1 的格式为 fat,分区 1 用于存放 linux 镜像和设备树。分区 2 的格式为 ext4,用于存放 Linux 的根文件系统(rootfs)。
fatload
fatload:将指定的文件读取到DRAM中
=> help fatload
fatload - load binary file from a dos filesystem
Usage:
fatload <interface> [<dev[:part]> [<addr> [<filename> [bytes [pos]]]]]
- Load binary file 'filename' from 'dev' on 'interface'
to address 'addr' from dos filesystem.
'pos' gives the file position to start loading from.
If 'pos' is omitted, 0 is used. 'pos' requires 'bytes'.
'bytes' gives the size to load. If 'bytes' is 0 or omitted,
the load stops on end of file.
If either 'pos' or 'bytes' are not aligned to
ARCH_DMA_MINALIGN then a misaligned buffer warning will
be printed and performance will suffer for the load.
# interface: 接口,比如mmc
# dev: 读取的设备号
# part: 读取的分区
# addr: 保存在DRAM的起始地址
# filename: 读取的文件名字
# bytes: 读取多少字节的数据,为0或省略则读取整个文件
# pos: 要读取的文件相对于文件首地址的偏移,为0或省略则从文件首地址读取
=> fatload mmc 1:1 80800000 zImage #将EMMC分区1的zImage读取到DRAM的80800000地址
reading zImage
6785360 bytes read in 222 ms (29.1 MiB/s)
fatwrite
fatwrite:将DRAM中的数据写入到MMC设备中
=> help fatwrite
fatwrite - write file into a dos filesystem
Usage:
fatwrite <interface> <dev[:part]> <addr> <filename> <bytes>
- write file 'filename' from the address 'addr' in RAM
to 'dev' on 'interface'
# interface: 接口,比如mmc
# dev: 写入的设备号
# part: 写入的分区
# addr: 写入的数据在DRAM的起始地址
# filename: 写入的文件名字
# bytes: 写入多少字节的数据
EXT格式文件系统操作
uboot 有ext2和ext4这两种格式的文件系统的操作命令,常用的就四个命令,分别为:ext2load、ext2ls、ext4load、ext4ls 和 ext4write。这些命令的含义和使用与 fatload、fatls 和 fatwrite一样,只是 ext2 和 ext4 都是针对 ext 文件系统的。比如 ext4ls 命令,EMMC 的分区2就是 ext4格式的,使用 ext4ls 就可以查询 EMMC 的分区 2 中的文件和目录。
=> ext4ls mmc 1:2
<DIR> 4096 .
<DIR> 4096 ..
<DIR> 16384 lost+found
<DIR> 4096 bin
<DIR> 4096 boot
<DIR> 4096 dev
<DIR> 4096 etc
<DIR> 4096 home
<DIR> 4096 lib
<DIR> 4096 media
<DIR> 4096 mnt
<DIR> 4096 opt
<DIR> 4096 proc
<DIR> 4096 run
<DIR> 4096 sbin
<DIR> 4096 sys
<SYM> 8 tmp
<DIR> 4096 usr
<DIR> 4096 var
<DIR> 4096 .cache
<DIR> 4096 .local
<DIR> 4096 .config
BOOT操作命令(重要)
uboot 的本质工作是引导 Linux,所以 uboot 肯定有相关的 boot(引导)命令来启动 Linux。
常用的跟 boot 有关的命令有:bootz、bootm 和 boot。
bootz
bootz:启动zImage镜像文件
要启动 Linux,需要先将 Linux 镜像文件拷贝到 DRAM 中,如果用到了设备树,也需要拷贝到DRAM中。
常见的拷贝方式:从 EMMC 或者 NAND 等存储设备中将 Linux 镜像和设备树文件拷贝到 DRAM;通过 nfs 或者 tftp 将 Linux 镜像文件和设备树文件下载到 DRAM 中。
=> help bootz
bootz - boot Linux zImage image from memory
Usage:
bootz [addr [initrd[:size]] [fdt]]
- boot Linux zImage stored in memory
The argument 'initrd' is optional and specifies the address
of the initrd in memory. The optional argument ':size' allows
specifying the size of RAW initrd.
When booting a Linux kernel which requires a flat device-tree
a third argument is required which is the address of the
device-tree blob. To boot that kernel without an initrd image,
use a '-' for the second argument. If you do not pass a third
a bd_info struct will be passed instead
# addr: Linux镜像文件在DRAM中的位置
# initrd: initrd文件在DRAM中的位置,不使用则使用'-'代替
# fdt: 设备树在DRAM中的位置
# 使用TFTP从网络下载镜像和设备树,然后启动
=> tftp 80800000 zImage
=> tftp 83000000 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-4.3-480x272-c.dtb
=> bootz 80800000 - 83000000
bootm
bootm:用于启动uImage镜像
=> help bootm
bootm - boot application image from memory
Usage:
bootm [addr [arg ...]]
- boot application image stored in memory
passing arguments 'arg ...'; when booting a Linux kernel,
'arg' can be the address of an initrd image
When booting a Linux kernel which requires a flat device-tree
a third argument is required which is the address of the
device-tree blob. To boot that kernel without an initrd image,
use a '-' for the second argument. If you do not pass a third
a bd_info struct will be passed instead
# add: uImage镜像在DRAM中的地址
Sub-commands to do part of the bootm sequence. The sub-commands must be
issued in the order below (it's ok to not issue all sub-commands):
start [addr [arg ...]]
loados - load OS image
ramdisk - relocate initrd, set env initrd_start/initrd_end
fdt - relocate flat device tree
cmdline - OS specific command line processing/setup
bdt - OS specific bd_t processing
prep - OS specific prep before relocation or go
go - start OS
boot
boot:用于启动Linux内核,通过读取环境变量bootcmd来启动系统。
bootcmd是非常重要的环境变量,保存着引导命令,具体的引导命令是可以修改的。
=> help boot
boot - boot default, i.e., run 'bootcmd'
Usage:
boot
=> print bootcmd
bootcmd=console=ttymxc0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblkp2 rootwait rw
# 使用TFTP从网络下载镜像和设备树,然后启动
=> setenv bootcmd 'tftp 80800000 zImage;tftp 83000000 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-4.3-480x272-c.dtb; bootz 80800000 - 83000000'
=> saveenv
Saving Environment to MMC...
Writing to MMC(1)... done
=> boot
# 从MMC设备拷贝镜像和设备树到DRAM中,然后运行
=> setenv bootcmd 'fatload mmc 1:1 80800000 zImage; fatload mmc 1:1 83000000 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-4.3-480x272-c.dtb; bootz 80800000 - 83000000'
=> saveenv
Saving Environment to MMC...
Writing to MMC(1)... done
=> boot
其它命令
reset
reset:复位重启
=> reset
resetting ...
go
go:跳转到指定的DRAM地址执行,比如测试裸机程序的时候就可以这样测试。
=> help go
go - start application at address 'addr'
Usage:
go addr [arg ...]
- start application at address 'addr'
passing 'arg' as arguments
=> tftp 87800000 led.bin
=> go 87800000
## Starting application at 0x87800000 ...
run
run:运行环境变量中定义的命令,可以运行我们自定义的环境变量。
=> setenv mybootnet 'tftp 80800000 zImage;tftp 83000000 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-4.3-480x272-c.dtb; bootz 80800000 - 83000000'
=>
=> setenv mybootemmc 'fatload mmc 1:1 80800000 zImage; fatload mmc 1:1 83000000 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-4.3-480x272-c.dtb; bootz 80800000 - 83000000'
=> saveenv
Saving Environment to MMC...
Writing to MMC(1)... done
=> run mybootemmc
reading zImage
mtset
mtest:简单的内存读写测试命令。
=> help mtest
mtest - simple RAM read/write test
Usage:
mtest [start [end [pattern [iterations]]]]
# start: 测试起始地址
# end: 测试结束地址


