Spring Cloud 系列之 Netflix Hystrix 服务容错(一)
什么是 Hystrix

Hystrix 源自 Netflix 团队于 2011 年开始研发。2012年 Hystrix 不断发展和成熟,Netflix 内部的许多团队都采用了它。如今,每天在 Netflix 上通过 Hystrix 执行数百亿个线程隔离和数千亿个信号量隔离的调用。极大地提高了系统的稳定性。
在分布式环境中,不可避免地会有许多服务依赖项中的某些服务失败而导致雪崩效应。Hystrix 是一个库,可通过添加等待时间容限和容错逻辑来帮助您控制这些分布式服务之间的交互。Hystrix 通过隔离服务之间的访问点,停止服务之间的级联故障并提供后备选项来实现此目的,所有这些都可以提高系统的整体稳定性。
雪崩效应
在微服务架构中,一个请求需要调用多个服务是非常常见的。如客户端访问 A 服务,而 A 服务需要调用 B 服务,B 服务需要调用 C 服务,由于网络原因或者自身的原因,如果 B 服务或者 C 服务不能及时响应,A 服务将处于阻塞状态,直到 B 服务 C 服务响应。此时若有大量的请求涌入,容器的线程资源会被消耗完毕,导致服务瘫痪。服务与服务之间的依赖性,故障会传播,造成连锁反应,会对整个微服务系统造成灾难性的严重后果,这就是服务故障的“雪崩”效应。以下图示完美解释了什么是雪崩效应。
当一切服务正常时,请求看起来是这样的:
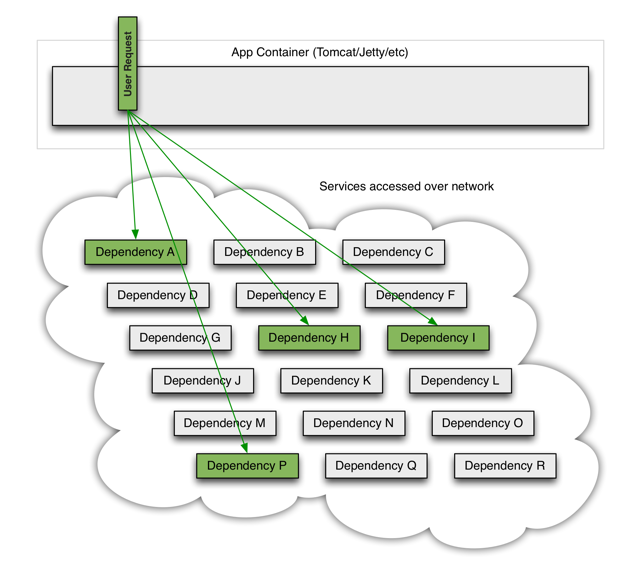
当其中一个服务有延迟时,它可能阻塞整个用户请求:
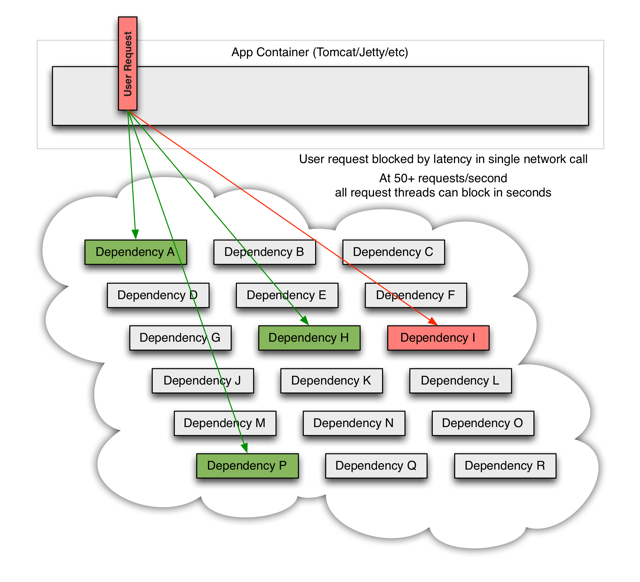
在高并发的情况下,一个服务的延迟可能导致所有服务器上的所有资源在数秒内饱和。比起服务故障,更糟糕的是这些应用程序还可能导致服务之间的延迟增加,从而备份队列,线程和其他系统资源,从而导致整个系统出现更多级联故障。
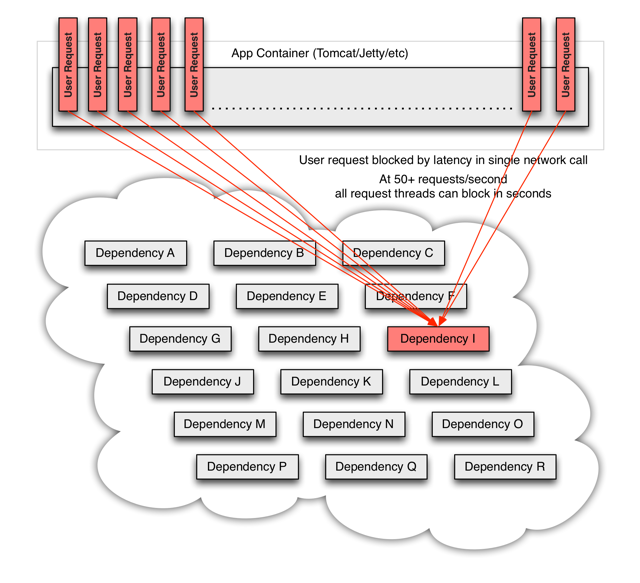
总结
造成雪崩的原因可以归结为以下三点:
- 服务提供者不可用(硬件故障,程序 BUG,缓存击穿,用户大量请求等)
- 重试加大流量(用户重试,代码逻辑重试)
- 服务消费者不可用(同步等待造成的资源耗尽)
最终的结果就是:一个服务不可用,导致一系列服务的不可用。
解决方案
雪崩是系统中的蝴蝶效应导致,其发生的原因多种多样,从源头我们无法完全杜绝雪崩的发生,但是雪崩的根本原因来源于服务之间的强依赖,所以我们可以提前评估做好服务容错。解决方案大概可以分为以下几种:
- 请求缓存:支持将一个请求与返回结果做缓存处理;
- 请求合并:将相同的请求进行合并然后调用批处理接口;
- 服务隔离:限制调用分布式服务的资源,某一个调用的服务出现问题不会影响其他服务调用;
- 服务熔断:牺牲局部服务,保全整体系统稳定性的措施;
- 服务降级:服务熔断以后,客户端调用自己本地方法返回缺省值。
环境准备
hystrix-demo 聚合工程。SpringBoot 2.2.4.RELEASE、Spring Cloud Hoxton.SR1。
eureka-server:注册中心eureka-server02:注册中心product-service:商品服务,提供了/product/{id}接口,/product/list接口,/product/listByIds接口order-service-rest:订单服务,基于Ribbon通过RestTemplate调用商品服务order-server-feign:订单服务,基于Feign通过声明式服务调用商品服务

模拟高并发场景
服务提供者接口添加 Thread.sleep(2000),模拟服务处理时长。
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.pojo.Product;
import com.example.service.ProductService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
/**
* 查询商品列表
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<Product> selectProductList() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return productService.selectProductList();
}
/**
* 根据多个主键查询商品
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/listByIds")
public List<Product> selectProductListByIds(@RequestParam("id") List<Integer> ids) {
return productService.selectProductListByIds(ids);
}
/**
* 根据主键查询商品
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Product selectProductById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return productService.selectProductById(id);
}
}
服务消费者降低 Tomcat 最大线程数方便模拟高并发。
server:
port: 8080
tomcat:
max-threads: 10 # 降低最大线程数方便模拟高并发
JMeter
点击链接观看:JMeter 视频(获取更多请关注公众号「哈喽沃德先生」)

Apache JMeter 应用程序是开源软件,100% 纯 Java 应用而设计的负载测试功能行为和测量性能。它最初是为测试 Web 应用程序而设计的,但此后已扩展到其他测试功能。
Apache JMeter 可用于测试静态和动态资源,Web 动态应用程序的性能。它可用于模拟服务器,服务器组,网络或对象上的繁重负载,以测试其强度或分析不同负载类型下的整体性能。
安装
官网:https://jmeter.apache.org/ 本文安装 Windows 版本。


解压 apache-jmeter-5.2.1.zip,进入 bin 目录运行 jmeter.bat 即可。不过运行之前我们先来修改一下配置文件,方便大家更友好的使用。
修改配置
进入 bin 目录编辑 jmeter.properties 文件,修改 37 行和 1085 行两处代码(不同的电脑可能行数不一致,不过上下差距不大)。
language=zh_CN界面显示中文sampleresult.default.encoding=UTF-8编码字符集使用 UTF-8
#language=en
language=zh_CN
#sampleresult.default.encoding=ISO-8859-1
sampleresult.default.encoding=UTF-8
运行
运行 bin/jmeter.bat 文件,界面显示如下。
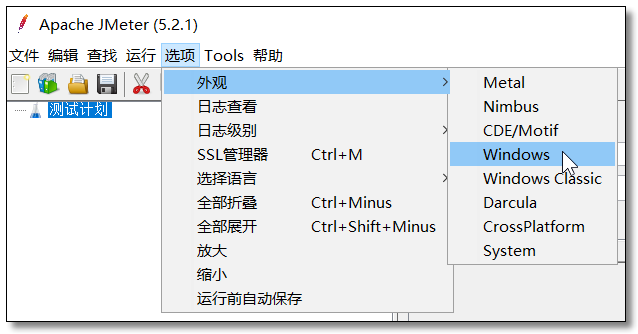
大家可以通过 选项 → 外观 选择自己喜欢的界面风格。
基本使用
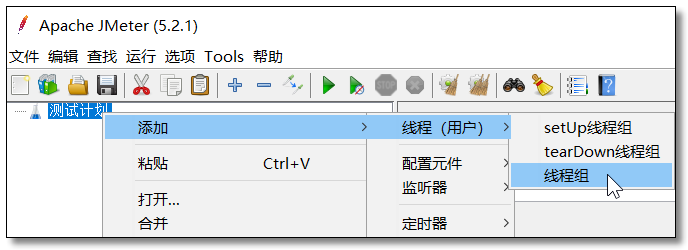
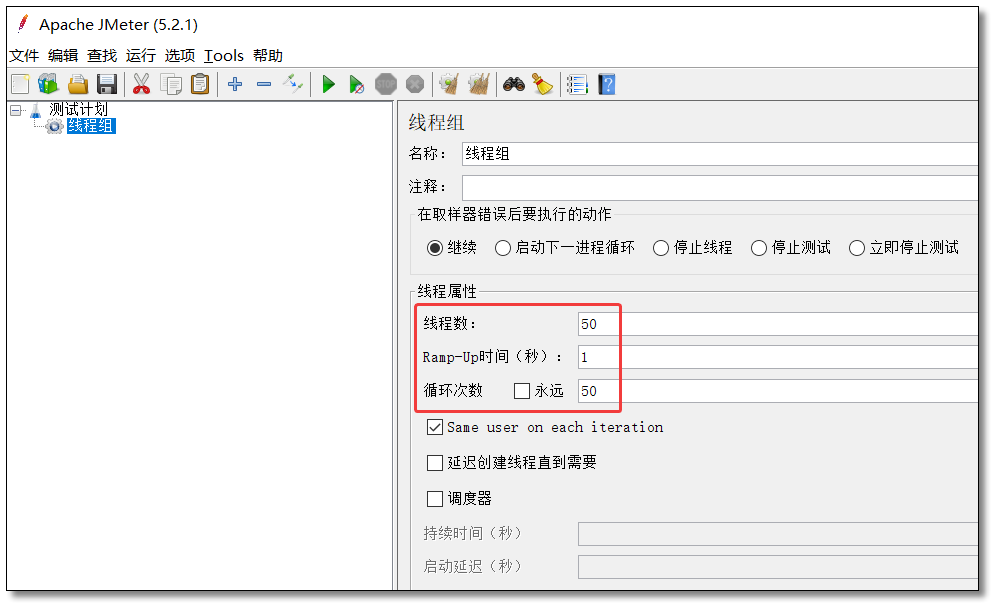
添加线程组
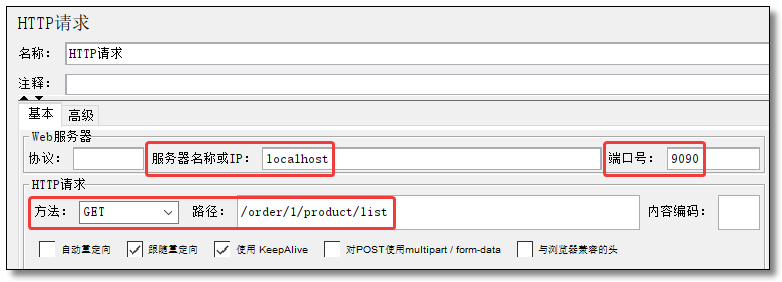
添加 HTTP 请求
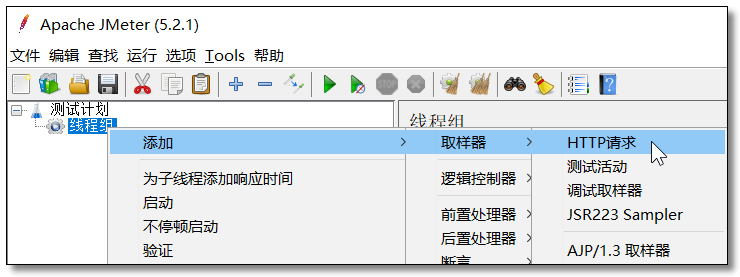
HTTP 请求配置为服务消费者的 http://localhost:9090/order/1/product/list
添加结果数
我们可以添加结果数来查看请求响应的结果数据。
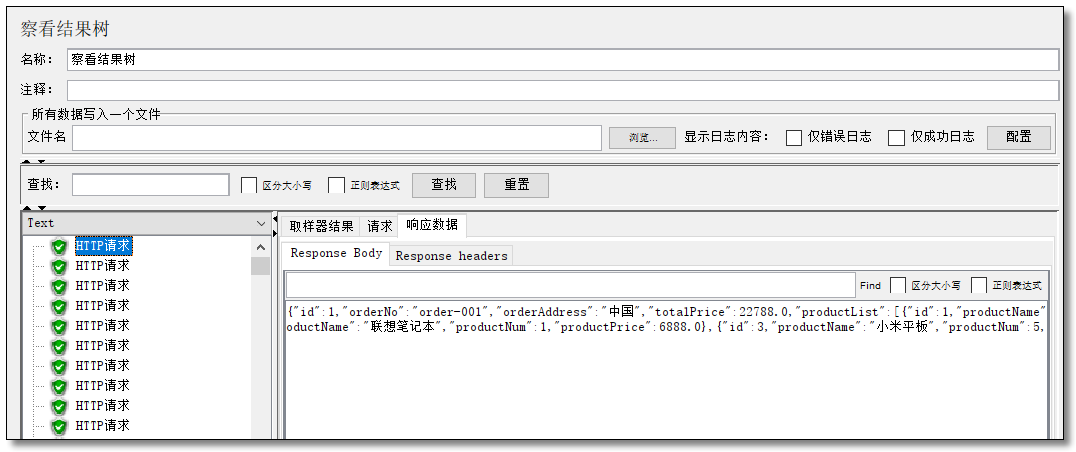
下图是执行请求以后所显示的效果。
执行请求
如下图所示,点击启动按钮即可开始执行请求。STOP 按钮则为停止请求。
测试请求
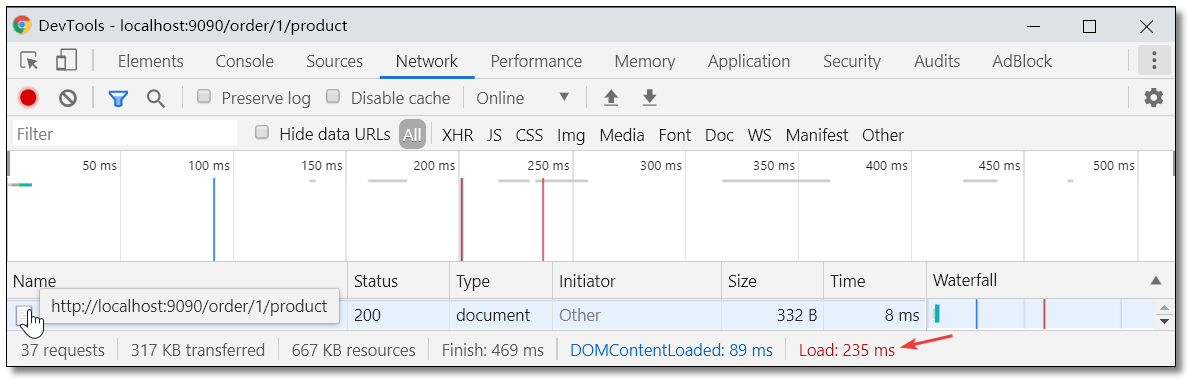
浏览器请求 http://localhost:9090/order/1/product 统计耗时如下。请求耗时:235ms
通过 JMeter 开启 50 线程循环 50 次请求服务消费者 http://localhost:9090/order/1/product/list 然后浏览器再次请求 http://localhost:9090/order/1/product 统计耗时如下。请求耗时:9.12s
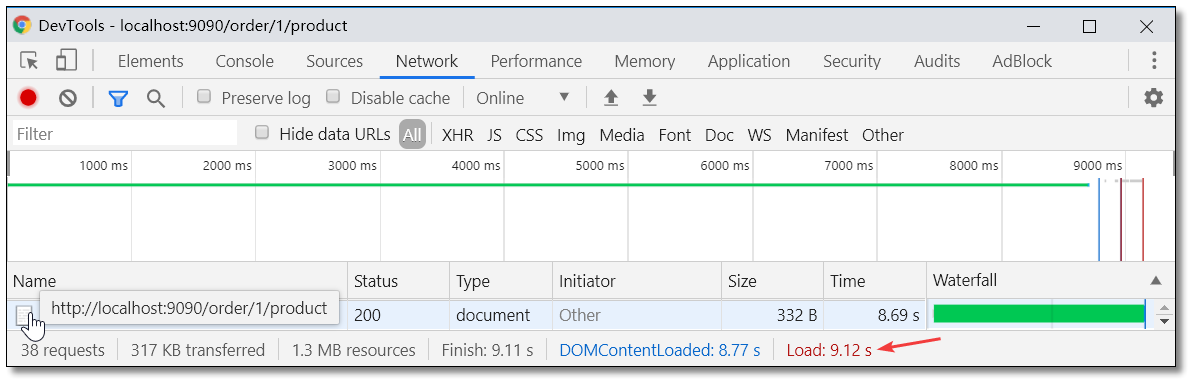
通过以上测试我们可以发现,/product/list 服务如果出现故障或延迟整个系统的资源会被耗尽从而导致影响其他服务的正常使用,这种情况在微服务项目中是非常常见的,所以我们需要对服务做出容错处理。接下来我们就一个个学习服务容错的解决方案。
请求缓存
点击链接观看:请求缓存视频(获取更多请关注公众号「哈喽沃德先生」)
Hystrix 为了降低访问服务的频率,支持将一个请求与返回结果做缓存处理。如果再次请求的 URL 没有变化,那么 Hystrix 不会请求服务,而是直接从缓存中将结果返回。这样可以大大降低访问服务的压力。
安装 Redis
Hystrix 自带缓存有两个缺点:
- 本地缓存,集群情况下缓存无法同步。
- 不支持第三方缓存容器,如:Redis,MemCache。
本文使用 Spring 的缓存集成方案,NoSql 使用 Redis 来实现,Redis 使用的是 5.0.7 版本。
添加依赖
服务消费者 pom.xml 添加 redis 和 commons-pool2 依赖。
<!-- spring boot data redis 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- commons-pool2 对象池依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件
服务消费者 application.yml 配置 Redis 缓存。
spring:
# redis 缓存
redis:
timeout: 10000 # 连接超时时间
host: 192.168.10.101 # Redis服务器地址
port: 6379 # Redis服务器端口
password: root # Redis服务器密码
database: 0 # 选择哪个库,默认0库
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 1024 # 最大连接数,默认 8
max-wait: 10000 # 最大连接阻塞等待时间,单位毫秒,默认 -1
max-idle: 200 # 最大空闲连接,默认 8
min-idle: 5 # 最小空闲连接,默认 0
配置类
添加 Redis 配置类重写序列化规则。
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheWriter;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* Redis 配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
// 重写 RedisTemplate 序列化
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 为 String 类型 key 设置序列化器
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 为 String 类型 value 设置序列化器
template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 为 Hash 类型 key 设置序列化器
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 为 Hash 类型 value 设置序列化器
template.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
// 重写 Cache 序列化
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
RedisCacheWriter redisCacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory());
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
// 设置默认过期时间 30 min
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30))
// 设置 key 和 value 的序列化
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisTemplate.getKeySerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisTemplate.getValueSerializer()));
return new RedisCacheManager(redisCacheWriter, redisCacheConfiguration);
}
}
启动类
服务消费者启动类开启缓存注解
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
// 开启缓存注解
@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceRestApplication {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceRestApplication.class, args);
}
}
业务层
服务消费者业务层代码添加缓存规则。
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.example.pojo.Product;
import com.example.service.ProductService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.core.ParameterizedTypeReference;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
/**
* 查询商品列表
*
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "orderService:product:list")
@Override
public List<Product> selectProductList() {
// ResponseEntity: 封装了返回数据
return restTemplate.exchange(
"http://product-service/product/list",
HttpMethod.GET,
null,
new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<Product>>() {
}).getBody();
}
/**
* 根据主键查询商品
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "orderService:product:single", key = "#id")
@Override
public Product selectProductById(Integer id) {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://product-service/product/" + id, Product.class);
}
}
测试
为了方便查看效果我们在服务提供者对应接口中添加打印语句。
访问:http://localhost:9090/order/1/product/list 和 http://localhost:9090/order/1/product 效果如下。
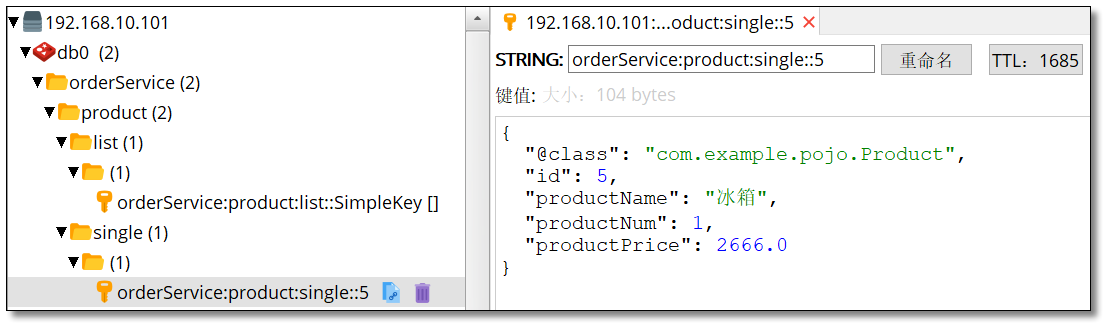
当我们请求相同服务时,服务提供者也不再打印语句说明服务消费者的请求直接获取了缓存的数据。
JMeter 开启 50 线程循环 50 次请求 http://localhost:9090/order/1/product/list
浏览器请求 http://localhost:9090/order/1/product,结果如下:
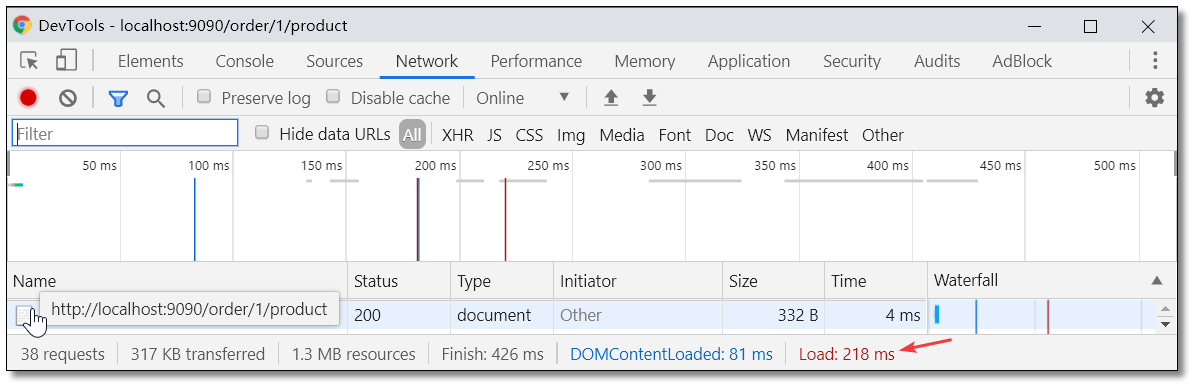
从结果可以看出请求缓存已解决之前服务响应速度过慢的问题。
请求合并
在微服务架构中,我们将一个项目拆分成很多个独立的模块,这些独立的模块通过远程调用来互相配合工作,但是,在高并发情况下,通信次数的增加会导致总的通信时间增加,同时,线程池的资源也是有限的,高并发环境会导致有大量的线程处于等待状态,进而导致响应延迟,为了解决这些问题,我们需要来了解 Hystrix 的请求合并。
请求合并的缺点
设置请求合并之后,本来一个请求可能 5ms 就搞定了,但是现在必须再等 10ms 看看还有没有其他的请求一起,这样一个请求的耗时就从 5ms 增加到 15ms 了。
如果我们要发起的命令本身就是一个高延迟的命令,那么这个时候就可以使用请求合并了,因为这个时候时间消耗就显得微不足道了,另外高并发也是请求合并的一个非常重要的场景。
添加依赖
服务消费者 pom.xml 添加 hystrix 依赖。
<!-- spring-cloud netflix hystrix 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
业务层
服务消费者业务层代码添加请求合并规则。
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.example.pojo.Product;
import com.example.service.ProductService;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCollapser;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixCommand;
import com.netflix.hystrix.contrib.javanica.annotation.HystrixProperty;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.ParameterizedTypeReference;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@Service
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
/**
* 根据多个主键查询商品
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
// 声明需要服务容错的方法
@HystrixCommand
@Override
public List<Product> selectProductListByIds(List<Integer> ids) {
System.out.println("-----orderService-----selectProductListByIds-----");
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
ids.forEach(id -> sb.append("id=" + id + "&"));
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://product-service/product/listByIds?" + sb.toString(), List.class);
}
/**
* 根据主键查询商品
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
// 处理请求合并的方法一定要支持异步,返回值必须是 Future<T>
// 合并请求
@HystrixCollapser(batchMethod = "selectProductListByIds", // 合并请求方法
scope = com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCollapser.Scope.GLOBAL, // 请求方式
collapserProperties = {
// 间隔多久的请求会进行合并,默认 10ms
@HystrixProperty(name = "timerDelayInMilliseconds", value = "20"),
// 批处理之前,批处理中允许的最大请求数
@HystrixProperty(name = "maxRequestsInBatch", value = "200")
})
@Override
public Future<Product> selectProductById(Integer id) {
System.out.println("-----orderService-----selectProductById-----");
return null;
}
}
@HystrixCollapser 注解各项参数说明如下:

服务消费者模拟同一时间用户发起多个请求。
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.example.pojo.Order;
import com.example.pojo.Product;
import com.example.service.OrderService;
import com.example.service.ProductService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
/**
* 根据主键查询订单
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Override
public Order searchOrderById(Integer id) {
// 模拟同一时间用户发起多个请求。
Future<Product> p1 = productService.selectProductById(1);
Future<Product> p2 = productService.selectProductById(2);
Future<Product> p3 = productService.selectProductById(3);
Future<Product> p4 = productService.selectProductById(4);
Future<Product> p5 = productService.selectProductById(5);
try {
System.out.println(p1.get());
System.out.println(p2.get());
System.out.println(p3.get());
System.out.println(p4.get());
System.out.println(p5.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new Order(id, "order-003", "中国", 29000D, null);
}
}
启动类
服务消费者启动类开启熔断器注解。
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
// 开启熔断器注解 2 选 1,@EnableHystrix 封装了 @EnableCircuitBreaker
// @EnableHystrix
@EnableCircuitBreaker
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceRestApplication {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceRestApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试
访问:http://localhost:9090/order/1/product 控制台打印结果如下:
-----orderService-----selectProductListByIds-----
{id=1, productName=电视机1, productNum=1, productPrice=5800.0}
{id=2, productName=电视机2, productNum=1, productPrice=5800.0}
{id=3, productName=电视机3, productNum=1, productPrice=5800.0}
{id=4, productName=电视机4, productNum=1, productPrice=5800.0}
{id=5, productName=电视机5, productNum=1, productPrice=5800.0}
根据结果得知,请求本来调用的是单个商品查询,请求合并以后只请求了一次批处理查询。
下一篇我们讲解 Hystrix 服务隔离中的线程池隔离与信号量隔离,记得关注噢~

本文采用 知识共享「署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际」许可协议。
大家可以通过 分类 查看更多关于 Spring Cloud 的文章。
🤗 您的点赞和转发是对我最大的支持。
📢 扫码关注 哈喽沃德先生「文档 + 视频」每篇文章都配有专门视频讲解,学习更轻松噢 ~
https://mrhelloworld.com


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号