代码块
定义在方法或语句中,用{}来划清界限
分类:
局部代码块,构造代码块,静态代码块
1.局部代码块:定义在方法或者是语句里面
特点: 用 { } 来划定代码的区域
方法和类都是用代码块的方式划定边界的
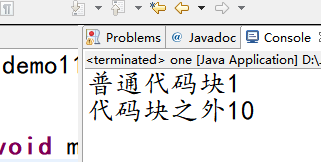
package com.oracle.demo11; public class one { public static void main(String[] args) { { int a=1; System.out.println("普通代码块"+a); } int a=10; System.out.println("代码块之外"+a); } }
2.构造代码块:
定义在类的成员(成员变量,成员方法)位置的代码块
特点:
优先于构造方法执行,用于所有对象的初始化动作
每创建一个新的对象都会执行一次构造代码块
package com.oracle.demo11; public class three { String name; int age; { System.out.println("这是构造代码块"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("吃饭"); } }
package com.oracle.demo11; public class two { public static void main(String[] args) { three th=new three(); th.eat(); three th2=new three(); th2.eat(); three th3=new three(); th3.eat(); } }

3.静态代码块:
定义在成员位置,使用static修饰的代码块
特点:
优于主方法和构造方法执行,当以任意的形式使用到该类的时候执行一次
该类不管创建多少对象,都只执行一次
可以给静态变量赋值,用来初始化类
package com.oracle.demo11; public class four { int age; String name; static{ System.out.println("静态构造方法"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println(age+"的"+name+"吃饭"); } }
package com.oracle.demo11; public class five { public static void main(String[] args) { four fo=new four(); fo.name="小刘"; fo.age=18; fo.eat(); four fo1=new four(); fo1.name="小孙"; fo1.age=18; fo1.eat(); } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号