【转】【Java/Android】Intent的简介以及属性的详解
一.Intent的介绍
Intent的中文意思是“意图,意向”,在Android中提供了Intent机制来协助应用间的交互与通讯,Intent负责对应用中一次操作的动作、动作涉及数据、附加数据进行描述,Android则根据此Intent的描述,负责找到对应的组件,将 Intent传递给调用的组件,并完成组件的调用。Intent不仅可用于应用程序之间,也可用于应用程序内部的Activity/Service之间的交互。因此,可以将Intent理解为不同组件之间通信的“媒介”专门提供组件互相调用的相关信息。
二.Inten启动组件的方法
Intent可以启动一个Activity,也可以启动一个Service,还可以发起一个广播Broadcasts。具体方法如下:
|
组件名称 |
方法名称 |
|
Activity |
startActvity( ) startActivity( ) |
|
Service |
startService( ) bindService( ) |
|
Broadcasts |
sendBroadcasts( ) sendOrderedBroadcasts( ) sendStickyBroadcasts( ) |
三.Intent的属性
Intent有以下几个属性:
动作(Action),数据(Data),分类(Category),类型(Type),组件(Compent)以及扩展信(Extra)。其中最常用的是Action属性和Data属性。
1.Intent的Action属性
Action是指Intent要完成的动作,是一个字符串常量。SDK中定义了一些标准的Action常量如下表所示。
|
Constant |
Target component |
Action |
|
ACTION_CALL |
activity |
Initiate a phone call. |
|
ACTION_EDIT |
activity |
Display data for the user to edit. |
|
ACTION_MAIN |
activity |
Start up as the initial activity of a task, with no data input and no returned output. |
|
ACTION_SYNC |
activity |
Synchronize data on a server with data on the mobile device. |
|
ACTION_BATTERY_LOW |
broadcast receiver |
A warning that the battery is low. |
|
ACTION_HEADSET_PLUG |
broadcast receiver |
A headset has been plugged into the device, or unplugged from it. |
|
ACTION_SCREEN_ON |
broadcast receiver |
The screen has been turned on. |
|
ACTION_TIMEZONE_CHANGED |
broadcast receiver |
The setting for the time zone has changed. |
下面是一个测试Action常量的例子:
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" /> <Button android:text="测试Action属性" android:id="@+id/getBtn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
strings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">测试Action属性</string> <string name="app_name">IntentActionDemo</string> </resources>
MainActivity.java
package com.android.action.activity; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private Button getBtn; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); getBtn=(Button)findViewById(R.id.getBtn); getBtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);// 设置Intent Action属性 intent.setType("vnd.android.cursor.item/phone");// 设置Intent Type 属性 //主要是获取通讯录的内容 startActivity(intent); // 启动Activity } }); } }
效果图:

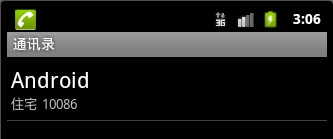
2.Intent的Data属性
Intent的Data属性是执行动作的URI和MIME类型,不同的Action有不同的Data数据指定。比如:ACTION_EDIT Action应该和要编辑的文档URI Data匹配,ACTION_VIEW应用应该和要显示的URI匹配。
3.Intent的Category属性
Intent中的Category属性是一个执行动作Action的附加信息。比如:CATEGORY_HOME则表示放回到Home界面,ALTERNATIVE_CATEGORY表示当前的Intent是一系列的可选动作中的一个。下表是SDK文档中关于Category的信息。
|
Constant |
Meaning |
|
CATEGORY_BROWSABLE |
The target activity can be safely invoked by the browser to display data referenced by a link — for example, an image or an e-mail message. |
|
CATEGORY_GADGET |
The activity can be embedded inside of another activity that hosts gadgets. |
|
CATEGORY_HOME |
The activity displays the home screen, the first screen the user sees when the device is turned on or when the HOME key is pressed. |
|
CATEGORY_LAUNCHER |
The activity can be the initial activity of a task and is listed in the top-level application launcher. |
|
CATEGORY_PREFERENCE |
The target activity is a preference panel. |
下面是一个回到Home界面的例子:
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="测试Intent Category" /> <Button android:id="@+id/Button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="转到Home界面" /> </LinearLayout>
strings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello World, MainActivity!</string> <string name="app_name">IntentCategoryDemo</string> </resources>
MainActivity.java
package com.android.category.activity; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends Activity { private Button btn; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.Button1); btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_MAIN);// 添加Action属性 intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);// 添加Category属性 startActivity(intent);// 启动Activity } }); } }
效果图:


4.Intent的Type属性
Intent的Type属性显式指定Intent的数据类型(MIME)。一般Intent的数据类型能够根据数据本身进行判定,但是通过设置这个属性,可以强制采用显式指定的类型而不再进行推导。
5.Intent的Compent属性
Intent的Compent属性指定Intent的的目标组件的类名称。通常 Android会根据Intent 中包含的其它属性的信息,比如action、data/type、category进行查找,最终找到一个与之匹配的目标组件。但是,如果 component这个属性有指定的话,将直接使用它指定的组件,而不再执行上述查找过程。指定了这个属性以后,Intent的其它所有属性都是可选的。
6.Intent的Extra属性
Intent的Extra属性是添加一些组件的附加信息。比如,如果我们要通过一个Activity来发送一个Email,就可以通过Extra属性来添加subject和body。
下面的例子在第一个Activity的EditText输入用户名,该年龄保存在Intent的Extras属性中。当单击Button时,会在第二个Activity中显示用户名。
first.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="请输入用户名" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/EditText1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:id="@+id/Button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="测试Extras属性" /> </LinearLayout>
second.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:id="@+id/TextView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
strings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello World, FirstActivity!</string> <string name="app_name">IntentExtrasDemo</string> </resources>
FirstActivity.java
package com.android.extras.activity; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; public class FirstActivity extends Activity { private Button btn; private EditText etx; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.first); btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.Button1); etx = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.EditText1); btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(); //设置Intent的class属性,跳转到SecondActivity intent.setClass(FirstActivity.this, SecondActivity.class); //为intent添加额外的信息 intent.putExtra("useName", etx.getText().toString()); //启动Activity startActivity(intent); } }); } }
SecondActivity.java
package com.android.extras.activity; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.TextView; public class SecondActivity extends Activity { private TextView tv; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //设置当前的Activity的界面布局 setContentView(R.layout.second); //获得Intent Intent intent = this.getIntent(); tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.TextView1); //从Intent获得额外信息,设置为TextView的文本 tv.setText(intent.getStringExtra("useName")); } }
注意:在添加第二个Activity SecondActivity的时候,要在AndroidManifest.xml里面添加上SecondActivity,具体如下,即是在15行</activity>的后面添加上16~18行的代码。如果不这样做,就会在模拟器上出现错误。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.android.extras.activity" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0"> <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="10" /> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name"> <activity android:name=".FirstActivity" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".SecondActivity" android:label="@string/app_name"> </activity> </application> </manifest>
效果图:

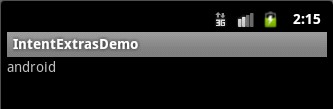
补充:
返回上一个 Activity
Intent intent=new Intent(SecondActivity.this,MainActivity.class); intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_REORDER_TO_FRONT); startActivity(intent); finish();
参数介绍:
FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT
这个标志一般不是由程序代码设置的,如在launchMode中设置singleTask模式时系统帮你设定。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP
如果设置,并且这个Activity已经在当前的Task中运行,因此,不再是重新启动一个这个Activity的实例,而是在这个Activity上方的所有Activity都将关闭,然后这个Intent会作为一个新的Intent投递到老的Activity(现在位于顶端)中。 例如,假设一个Task中包含这些Activity:A,B,C,D。如果D调用了startActivity(),并且包含一个指向Activity B的Intent,那么,C和D都将结束,然后B接收到这个Intent,因此,目前stack的状况是:A,B。 上例中正在运行的Activity B既可以在onNewIntent()中接收到这个新的Intent,也可以把自己关闭然后重新启动来接收这个Intent。如果它的启动模式声明为“multiple”(默认值),并且你没有在这个Intent中设置FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP标志,那么它将关闭然后重新创建;对于其它的启动模式,或者在这个Intent中设置FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP标志,都将把这个Intent投递到当前这个实例的onNewIntent()中。 这个启动模式还可以与FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK结合起来使用:用于启动一个Task中的根Activity,它会把那个Task中任何运行的实例带入前台,然后清除它直到根Activity。这非常有用,例如,当从Notification Manager处启动一个Activity。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_WHEN_TASK_RESET
如果设置,这将在Task的Activity stack中设置一个还原点,当Task恢复时,需要清理Activity。也就是说,下一次Task带着FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED标记进入前台时(典型的操作是用户在主画面重启它),这个Activity和它之上的都将关闭,以至于用户不能再返回到它们,但是可以回到之前的Activity。 这在你的程序有分割点的时候很有用。例如,一个e-mail应用程序可能有一个操作是查看一个附件,需要启动图片浏览Activity来显示。这个Activity应该作为e-mail应用程序Task的一部分,因为这是用户在这个Task中触发的操作。然而,当用户离开这个Task,然后从主画面选择e-mail app,我们可能希望回到查看的会话中,但不是查看图片附件,因为这让人困惑。通过在启动图片浏览时设定这个标志,浏览及其它启动的Activity在下次用户返回到mail程序时都将全部清除。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS
如果设置,新的Activity不会在最近启动的Activity的列表中保存。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT
如果设置,并且这个Intent用于从一个存在的Activity启动一个新的Activity,那么,这个作为答复目标的Activity将会传到这个新的Activity中。这种方式下,新的Activity可以调用setResult(int),并且这个结果值将发送给那个作为答复目标的Activity。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_LAUNCHED_FROM_HISTORY
这个标志一般不由应用程序代码设置,如果这个Activity是从历史记录里启动的(常按HOME键),那么,系统会帮你设定。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK
不要使用这个标志,除非你自己实现了应用程序启动器。与FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK结合起来使用,可以禁用把已存的Task送入前台的行为。当设置时,新的Task总是会启动来处理Intent,而不管这是是否已经有一个Task可以处理相同的事情。 由于默认的系统不包含图形Task管理功能,因此,你不应该使用这个标志,除非你提供给用户一种方式可以返回到已经启动的Task。 如果FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK标志没有设置,这个标志被忽略。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK
如果设置,这个Activity会成为历史stack中一个新Task的开始。一个Task(从启动它的Activity到下一个Task中的Activity)定义了用户可以迁移的Activity原子组。Task可以移动到前台和后台;在某个特定Task中的所有Activity总是保持相同的次序。 这个标志一般用于呈现“启动”类型的行为:它们提供用户一系列可以单独完成的事情,与启动它们的Activity完全无关。 使用这个标志,如果正在启动的Activity的Task已经在运行的话,那么,新的Activity将不会启动;代替的,当前Task会简单的移入前台。参考FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK标志,可以禁用这一行为。 这个标志不能用于调用方对已经启动的Activity请求结果。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_ANIMATION
如果在Intent中设置,并传递给Context.startActivity()的话,这个标志将阻止系统进入下一个Activity时应用Acitivity迁移动画。这并不意味着动画将永不运行——如果另一个Activity在启动显示之前,没有指定这个标志,那么,动画将被应用。这个标志可以很好的用于执行一连串的操作,而动画被看作是更高一级的事件的驱动。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_HISTORY
如果设置,新的Activity将不再历史stack中保留。用户一离开它,这个Activity就关闭了。这也可以通过设置noHistory特性。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_USER_ACTION
如果设置,作为新启动的Activity进入前台时,这个标志将在Activity暂停之前阻止从最前方的Activity回调的onUserLeaveHint()。 典型的,一个Activity可以依赖这个回调指明显式的用户动作引起的Activity移出后台。这个回调在Activity的生命周期中标记一个合适的点,并关闭一些Notification。 如果一个Activity通过非用户驱动的事件,如来电或闹钟,启动的,这个标志也应该传递给Context.startActivity,保证暂停的Activity不认为用户已经知晓其Notification。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_PREVIOUS_IS_TOP
If set and this intent is being used to launch a new activity from an existing one, the current activity will not be counted as the top activity for deciding whether the new intent should be delivered to the top instead of starting a new one. The previous activity will be used as the top, with the assumption being that the current activity will finish itself immediately.
FLAG_ACTIVITY_REORDER_TO_FRONT
如果在Intent中设置,并传递给Context.startActivity(),这个标志将引发已经运行的Activity移动到历史stack的顶端。 例如,假设一个Task由四个Activity组成:A,B,C,D。如果D调用startActivity()来启动Activity B,那么,B会移动到历史stack的顶端,现在的次序变成A,C,D,B。如果FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP标志也设置的话,那么这个标志将被忽略。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED
If set, and this activity is either being started in a new task or bringing to the top an existing task, then it will be launched as the front door of the task. This will result in the application of any affinities needed to have that task in the proper state (either moving activities to or from it), or simply resetting that task to its initial state if needed.
FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP
如果设置,当这个Activity位于历史stack的顶端运行时,不再启动一个新的。
原文地址:http://liangruijun.blog.51cto.com/3061169/634411/





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义