Devexpress Winform MVVM
归纳总结备忘
前言
MVVM
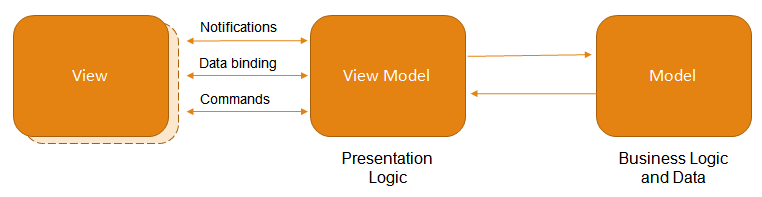
MVVM是Model-View-ViewModel,是一种专为WPF开发而设计的架构设计模式,类似MVC。MVVM 就是将其中的View 的状态和行为抽象化,让我们将视图 UI 和业务逻辑分开。 ViewModel 根据databindings,commond,notification等与view层连接,可以取出 Model 的数据同时帮忙处理 View 中由于需要展示内容而涉及的业务逻辑,充当视图层与数据层的通信桥梁。
好处:
- 逻辑低耦合
- 可重用性
- 方便单元测试
Devexpress
DevExpress全称Developer Express,是全球著名的控件开发公司,其.NET界面控件DXperience Universal Suite(Dev宇宙版)全球知名,获奖无数。DevExpress控件以界面美观和功能强大著称,拥有大量的示例和帮助文档,开发者能够快速上手。在国内,DevExpress亦拥有大量的用户,资料比较完善,交流方便。DevExpress广泛应用于ECM企业内容管理、 成本管控、进程监督、生产调度,在企业/政务信息化管理中占据一席重要之地。
官网:https://www.devexpress.com/
如上所说,mvvm专为WPF设计,而没有第三方MVVM框架的 winform平台缺乏灵活的绑定以及绑定commad等基本特性,必须手动实现,而devexpress为这些特性提供了完整支持,是开发更关心本身业务逻辑。
正文
databindings及 UI Triggers
在devexpress中viewModel所有的 virtual 属性都将是可绑定的,在更改值时会自动传递PropertyChanged消息(在未有devexpress的winform程序类必须继承 INotifyPropertyChanged并实现该接口才能实现双向绑定),当没有virtual属性时,只有主动调用 this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.你的属性)才会向视图层传递PropertyChanged消息。
下面例子:
viewmodel
public class ViewModel {
public virtual string Test {get;private set ; }//标准
[Bindable(false)]
public virtual string Test1 {get; private set ; } //取消 bindable property generation支持
string testCore;
[BindableProperty] //带backing field的属性将被忽略,使用该显示标记以使该属性支持databinding
public virtual string Test2
{
get { return testCore; }
set { testCore = value; }
}
}view层
TextEdit editor = new TextEdit();
editor.Parent = this;
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModel);
// Data binding for the Title property (via MVVMContext API)
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();//支持 fluentAPI特性
fluentAPI.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, x => x.Test);//双向绑定
fluentAPI.SetTrigger(x => x.Test, (active) =>
{
label.Text = active; //UI Triggers 单向绑定
});
Command
委托Command
MVVMContext mvvmContext = new MVVMContext();
mvvmContext.ContainerControl = this;
SimpleButton commandButton = new SimpleButton();
commandButton.Parent = this;
Func<int, bool> canExecute = (p) => (2 + 2 == p);
// This command is created as parameterized and with `canExecute` parameter.
DelegateCommand<int> command = new DelegateCommand<int>((v) => {
XtraMessageBox.Show(string.Format(
"Hello! The parameter passed to command is {0}." + Environment.NewLine +
"And I'm running, because the `canExecute` condition is `True` for this parameter." + Environment.NewLine +
"Try to change this parameter!", v));
}, canExecute);
//
int parameter = 4;
// UI binding for button with the `queryParameter` function
commandButton.BindCommand(command, () => parameter);
POCO Commands
viewmodel
public class ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand { //viewmodel
// A parameterized POCO-command will be created from this method.
public void DoSomething(int p) {
XtraMessageBox.Show(string.Format(
"Hello! The parameter passed to command is {0}." + Environment.NewLine +
"And I'm running, because the `canExecute` condition is `True` for this parameter." + Environment.NewLine +
"Try to change this parameter!", p));
}
// A parameterized `CanExecute` method for the `Say` command.
public bool CanDoSomething(int p) {
return (2 + 2) == p; //自行修改条件
}
}view
MVVMContext mvvmContext = new MVVMContext();
mvvmContext.ContainerControl = this;
SimpleButton commandButton = new SimpleButton();
commandButton.Text = "Execute Command";
commandButton.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
commandButton.Parent = this;
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand);
//
int parameter = 4;
// UI binding for button with the `queryParameter` function
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand>();
fluentAPI.BindCommand(commandButton, (x, p) => x.DoSomething(p), x => parameter);异步command
两个按钮控制进度条滚动开始停止
viewmodel
public class ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation {
// An asynchronous POCO-command will be created from this method.
public Task DoSomethingAsynchronously() {
return Task.Factory.StartNew(() => {
var asyncCommand = this.GetAsyncCommand(x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
if (asyncCommand.IsCancellationRequested) // cancellation check
break;
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(25); // do some work here
UpdateProgressOnUIThread(i);
}
UpdateProgressOnUIThread(0);
});
}
// Property for progress
public int Progress { get; private set; }
protected IDispatcherService DispatcherService {
get { return this.GetService<IDispatcherService>(); }
}
void UpdateProgressOnUIThread(int progress) {
DispatcherService.BeginInvoke(() => {
Progress = progress;
this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.Progress);
});
}
}view
MVVMContext mvvmContext = new MVVMContext();
mvvmContext.ContainerControl = this;
ProgressBarControl progressBar = new ProgressBarControl();
progressBar.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
SimpleButton commandButton = new SimpleButton();
commandButton.Text = "Start Command Execution";
commandButton.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
SimpleButton cancelButton = new SimpleButton();
cancelButton.Text = "Cancel Command Execution";
cancelButton.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
cancelButton.Parent = this;
commandButton.Parent = this;
progressBar.Parent = this;
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation);
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation>();
// UI binding for the button
fluentAPI.BindCommand(commandButton, x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
// UI binding for cancelation
fluentAPI.BindCancelCommand(cancelButton, x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
// UI binding for progress
fluentAPI.SetBinding(progressBar, p => p.EditValue, x => x.Progress);WithCommand extension
四种常见使用情况
viewmodel
public class ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation {
// An asynchronous POCO-command will be created from this method.
public Task DoSomethingAsynchronously() {
return Task.Factory.StartNew(() => {
var asyncCommand = this.GetAsyncCommand(x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
if (asyncCommand.IsCancellationRequested) // cancellation check
break;
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(25); // do some work here
UpdateProgressOnUIThread(i);
}
UpdateProgressOnUIThread(0);
});
}
// Property for progress
public int Progress { get; private set; }
protected IDispatcherService DispatcherService {
get { return this.GetService<IDispatcherService>(); }
}
void UpdateProgressOnUIThread(int progress) {
DispatcherService.BeginInvoke(() => {
Progress = progress;
this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.Progress);
});
}
}view
MVVMContext mvvmContext = new MVVMContext();
mvvmContext.ContainerControl = this;
ProgressBarControl progressBar = new ProgressBarControl();
progressBar.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
SimpleButton commandButton2 = new SimpleButton();
commandButton2.Text = "Execute Command 2";
commandButton2.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
commandButton2.Parent = this;
commandButton2.Visible = false;
SimpleButton commandButton1 = new SimpleButton();
commandButton1.Text = "Execute Command 1";
commandButton1.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
commandButton1.Parent = this;
SimpleButton commandButton = new SimpleButton();
commandButton.Text = "Start Command Execution";
commandButton.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
SimpleButton cancelButton = new SimpleButton();
cancelButton.Text = "Cancel Command Execution";
cancelButton.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
cancelButton.Parent = this;
commandButton.Parent = this;
progressBar.Parent = this;
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation);
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation>();
// UI binding for buttons
fluentAPI.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously()) //功能如上一例子
.Bind(commandButton)
.BindCancel(cancelButton);
fluentAPI.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething()) //多控件绑定一command
.Bind(commandButton1)
.Bind(commandButton2);
fluentAPI.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething()) //单绑定
.Bind(commandButton1);
fluentAPI.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething())//OnCanExecuteChanged,Before,After 三种command triggers
.OnCanExecuteChanged(() => XtraMessageBox.Show("The CanExecute condition has changed"));
// .Before(() => XtraMessageBox.Show("The target command is about to be executed"));
// .After(() => XtraMessageBox.Show("The target command has been executed"));
// UI binding for progress
fluentAPI.SetBinding(progressBar, p => p.EditValue, x => x.Progress);Attaching Behaviors
Confirmation behavior.
checkBox修改的再确认
view
MVVMContext mvvmContext = new MVVMContext();
mvvmContext.ContainerControl = this;
CheckEdit editor = new CheckEdit();
editor.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
editor.Text = "Please, try to change checked state of this editor";
editor.Parent = this;
#endregion SetUp
#region #confirmationBehaviorFluentAPI
// UI binding for the generic ConfirmationBehavior behavior with some specific parameters
mvvmContext.WithEvent<ChangingEventArgs>(editor, "EditValueChanging")
.Confirmation(behavior =>
{
behavior.Caption = "CheckEdit State changing";
behavior.Text = "This checkEdit's checked-state is about to be changed. Are you sure?";
});Event To Command.
事件转命令,效果与POCO Commands例子一致
viewmodel
public class ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand { //viewmodel
// A parameterized POCO-command will be created from this method.
public void DoSomething(int p) {
XtraMessageBox.Show(string.Format(
"Hello! The parameter passed to command is {0}." + Environment.NewLine +
"And I'm running, because the `canExecute` condition is `True` for this parameter." + Environment.NewLine +
"Try to change this parameter!", p));
}
// A parameterized `CanExecute` method for the `Say` command.
public bool CanDoSomething(int p) {
return (2 + 2) == p; //自行修改条件
}
}view
MVVMContext mvvmContext = new MVVMContext();
mvvmContext.ContainerControl = this;
SimpleButton commandButton = new SimpleButton();
commandButton.Text = "Execute Command";
commandButton.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
commandButton.Parent = this;
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand);
//
int parameter = 4;
// UI binding for button with the `queryParameter` function
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand>();
fluentAPI.WithEvent(commandButton, "Click")
.EventToCommand((x) => x.DoSomething(new int()), x => parameter);Key(s)-To-Command
按键转命令
viewModel
public class KeyAwareViewModel {
protected IMessageBoxService MessageBoxService {
get { return this.GetService<IMessageBoxService>(); }
}
public void OnAKey() {
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Key Command: A");
}
public void OnAltAKey() {
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Key Command: Alt+A");
}
public void OnKey(Keys keys) {
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Key Command: " + keys.ToString());
}
public void OnKeyArgs(KeyEventArgs args) {
string message = string.Join(", ",
"KeyValue: " + args.KeyValue.ToString(),
"KeyData: " + args.KeyData.ToString(),
"KeyCode: " + args.KeyCode.ToString(),
"Modifiers: " + args.Modifiers.ToString());
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Args = {" + message + "}");
}
}view
MVVMContext mvvmContext = new MVVMContext();
mvvmContext.ContainerControl = this;
UserControl panel = new UserControl();
panel.Dock = DockStyle.Top;
panel.Parent = this;
MemoEdit memo = new MemoEdit();
memo.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
memo.ReadOnly = true;
memo.MinimumSize = new Size(0, 100);
memo.Parent = panel;
memo.Text = "Click here and press the A or Alt+A keys to execute a command";
//
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(KeyAwareViewModel);
// UI binding for the KeyToCommand behavior
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKey(memo, Keys.A) //单按键
.KeyToCommand(x => x.OnAKey());
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKey(memo, Keys.A | Keys.Alt) // 使用|代表复选
.KeyToCommand(x => x.OnAltAKey());
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKeys(memo, new Keys[] { Keys.A, Keys.B, Keys.C }) //多选择单按键
.KeysToCommand(x => x.OnKey(Keys.None), args => args.KeyCode);
// UI binding for the KeysToCommand behavior
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKeys(memo, new Keys[] { Keys.Shift | Keys.A, Keys.Shift | Keys.B, Keys.Shift | Keys.C })//多选择多按键
.KeysToCommand(x => x.OnKeyArgs((KeyEventArgs)null), args => (KeyEventArgs)args);
出处:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43862847/article/details/86750608
ViewModel中的代码
public void KeyDown(System.Windows.Forms.KeyEventArgs args) { if (args.KeyCode == System.Windows.Forms.Keys.Enter) { args.Handled = true; //将Handled设置为true,指示已经处理过KeyPress事件 Login(); } }
View中的代码
//fluent.WithEvent<KeyEventArgs>(textEdit2, "KeyDown").EventToCommand(vm => vm.KeyDown(new KeyEventArgs(Keys.Enter)));//① //fluent.WithEvent<KeyEventArgs>(textEdit2, "KeyDown").EventToCommand(vm => vm.KeyDown((KeyEventArgs)null));//② fluent.WithKeys(textEdit2, new Keys[] { Keys.Shift | Keys.A, Keys.Shift | Keys.B, Keys.Shift | Keys.C })//多选择多按键 //③ .KeysToCommand(x => x.KeyDown((KeyEventArgs)null), args => (KeyEventArgs)args);
以上三种方式,你都可以使用,具体自己看着办。
第①和②二种方式效果一样,当光标在textEdit2中的时候,按任何键盘都会进入KeyDown的方法中
第③种方式,则是必须满足: new Keys[] 中设置的按键才会触发KeyDown的方法
多说一句
1)在设置为窗体的事件的时候,需要设置窗体的KeyPreview属性为true
2)在Event To Command的时候,需要注意:我们平常使用的是:private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) 注意的方法签名,而在ViewModel的时候只有private void button1_Click(EventArgs e) 就可以了,调用:fluentAPI.WithEvent(commandButton, "Click").EventToCommand((x) => x.DoSomething(null));
如果,您希望更容易地发现我的新博客,不妨点击一下绿色通道的【关注我】。(●'◡'●)
因为,我的写作热情也离不开您的肯定与支持,感谢您的阅读,我是【Jack_孟】!
本文来自博客园,作者:jack_Meng,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/mq0036/p/10573440.html
【免责声明】本文来自源于网络,如涉及版权或侵权问题,请及时联系我们,我们将第一时间删除或更改!
posted on 2019-03-21 18:06 jack_Meng 阅读(4205) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报






【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 一个奇形怪状的面试题:Bean中的CHM要不要加volatile?
· [.NET]调用本地 Deepseek 模型
· 一个费力不讨好的项目,让我损失了近一半的绩效!
· .NET Core 托管堆内存泄露/CPU异常的常见思路
· DeepSeek “源神”启动!「GitHub 热点速览」
· 微软正式发布.NET 10 Preview 1:开启下一代开发框架新篇章
· C# 集成 DeepSeek 模型实现 AI 私有化(本地部署与 API 调用教程)
· DeepSeek R1 简明指南:架构、训练、本地部署及硬件要求
· NetPad:一个.NET开源、跨平台的C#编辑器
2018-03-21 win7上搭建Android环境及调试
2017-03-21 提高开发水平的方法