python-组合类型【集合、文件、字典】
一、集合类型
1、{}
2、元素为不可变数据类型【列表就不行】
2、集合中元素唯一,不存在相同元素
3、集合中元素无序
4、建立集合{} 或 set(),建立空集合只能用set()
a = {1,334,'dcs',(2,'ffd')}
print(a) #{'dcs', 1, (2, 'ffd'), 334} ,无序
b = set('拉拉链')
print(b) #{'链', '拉'} ## 元素无序且不重复
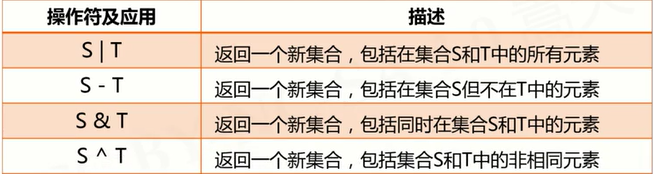
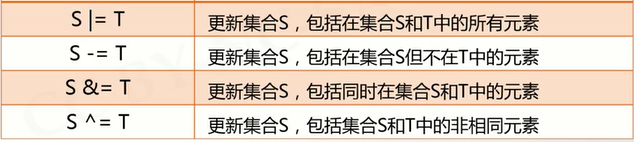
5、集合操作符
一、文件
1、常用编码
①ASCII码--表示英文字母的二进制编码
print(ord('a')) ##97,字符转二进制
print(chr(65)) ##A,二进制转字符
②Unicode
多语言
③UTF-8
可变长的Unicode
④编码 encode()
解码decode()
⑤GBK编码--汉字编码
2、文件数据
(1)文本文件 :数字、字符(ASCII码)
\n 换行符
(2)二进制文件
3、文件基本处理
(1)文件打开
<variable> = open(<文件名>,<打开模式>)

(2)文件读取
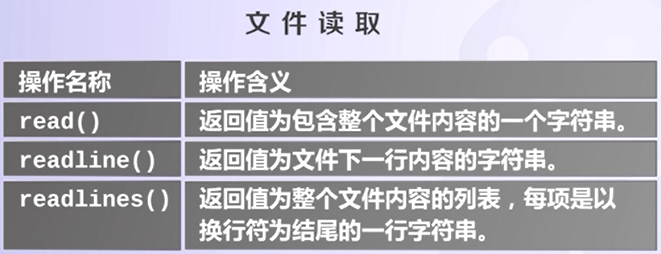
read()
def main():
fname = input('请输入文件名:')
infile = open(fname,'r',encoding='utf-8')
data = infile.read() ##读取整个文件内容
print(data)
main()
readline()
##读取前五行
infile = open('数中','r',encoding='UTF-8')
for i in range(5):
line = infile.readline()
print(line[:-1]) ##去掉每行最后的换行符\n,不然输出每行之间会有一行空行
(3)文件写入

##若test文件不存在,python会创建一个test文件;
##若test文件存在,python会删掉已存在的test文件,重新创建一个test文件;
outfile = open('test','w',encoding='UTF-8')
outfile.writelines('Hello world!')
outfile.close()
infile = open('test','r',encoding='UTF-8')
print(infile.read())
(4)文件遍历
文件遍历框架模板
file = open('文件名','r',encoding='UTF-8')
for line in file:
##处理一行文件内容
file.close()
实例一:文件拷贝
##文件拷贝
def main():
#用户输入文件名
f1 = input('输入一个源文件名:').strip() ##strip()函数是删除字符串首尾的空格
f2 = input('输入拷贝的文件名:').strip()
#打开文件
infile = open(f1,'r',encoding='UTF-8')
outfile = open(f2,'w',encoding='UTF-8')
#拷贝数据
countLines = countCharts = 0
for line in infile:
countLines +=1
countCharts += len(line)
outfile.write(line)
print(countLines,'行中的',countCharts,'字符,已经被复制')
infile.close()
outfile.close()
main()
实例二:多文件合并成一个文件
 +
+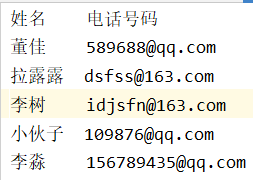 --------->>>>
--------->>>>
## 两个文件合并成一个
###利用字符串和列表将两个通讯录文本合并为一个文本
def main():
f1 = open('Tele','r',encoding='UTF-8')
f2 = open('Email','r',encoding='UTF-8')
f1.readline()#跳过第一行
f2.readline()
line1 = f1.readlines()
line2 = f2.readlines()
list1_name = []
list1_tele = []
list2_name = []
list2_email = []
for line in line1: ##获取第1个文件中的姓名和电话
elements = line.split() ##split()按空格进行切片
list1_name.append(str(elements[0]))
list1_tele.append(str(elements[1]))
for line in line2: ##获取第2个文件中的姓名和电话
elements = line.split() ##split()按空格进行切片
list2_name.append(str(elements[0]))
list2_email.append(str(elements[1]))
###开始处理
lines = []
lines.append('姓名\t 电话 \t 邮箱\n')
##按索引方式遍历姓名列表1 list1_name
for i in range(len(list1_name)):
s = ''
if list1_name[i] in list2_name:
j = list2_name.index(list1_name[i])##找到list1_name对应list2_name的姓名的索引位置
s = '\t'.join([list1_name[i],list1_tele[i],list2_email[j]])
s += '\n'
else:
s = '\t'.join([list1_name[i],list1_tele[i],str(' ----- ')])
s +='\n'
lines.append(s)
#处理list2中没有匹配到的姓名
for i in range(len(list2_name)):
s = ''
if list2_name[i] not in list1_name:
s = '\t'.join([list2_name[i], str(' ----- '), list2_email[i]])
s += '\n'
lines.append(s)
f3 = open('Address','w',encoding='UTF-8')
f3.writelines(lines)
f1.close()
f2.close()
f3.close()
main()
二、字典(dict)
(1)字典中的元素是无序排列的
d1 = {'r':21,'b':78}
d2 = {'b':78,'r':21}
print(d1==d2) ##True
(2)字典元素增删改
students = {'201901':'叽叽','201902':'线线'}
#访问字典元素
print(students['201902']) ##线线
#增加字典元素
students['201903']='赞赞'
print(students) ##{'201901': '叽叽', '201902': '线线', '201903': '赞赞'}
#删除字典中的元素
del students['201901']
(3)字典的遍历
students = {'201901':'叽叽','201902':'线线'}
#字典的遍历,默认遍历字典的键key
for key in students:
print(key + ':' +str(students[key]))
#201901:叽叽
#201902:线线
#遍历字典的值value
for value in students.values():
print(value)
#遍历字典的项
for item in students.items():
print(item)
#('201901', '叽叽')
#('201902', '线线')
#遍历字典的key-value
for key,value in students.items():
print(key,value)
#201901 叽叽
#201902 线线
(4)判断一个元素是否在字典中
in not in
(5)字典的标准操作符
-,<,>,<=,>=,==,!=,and,or,not
(6)字典方法
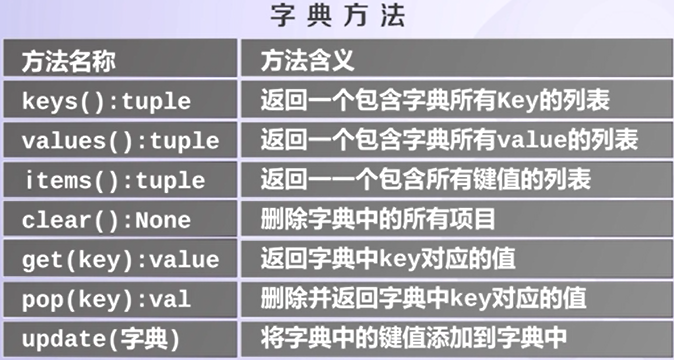
#字典转列表
students = {'201901':'叽叽','201902':'线线'}
li = list(students.items())
print(li)#[('201901', '叽叽'), ('201902', '线线')] 列表内的元素是tuple
print(li[0]) #('201901', '叽叽')
print(li[0][0]) #201901
实例一:统计词频(英文)【中文需要引入分词】
import turtle
##全局变量##
#词频排列显示个数
count = 10
#单词频率数组-作为y轴数据
data = []
#单词数组-作为x轴数据
words = []
#y轴显示放大倍数-可以根据词频数量进行调节
yScale = 6
#x轴显示放大倍数-可以根据count数量进行调节
xScale = 30
################# Turtle Start ####################
# 从点(x1,y1)到(x2,y2)绘制线段
def drawLine(t, x1, y1, x2, y2):
t.penup()
t.goto(x1, y1)
t.pendown()
t.goto(x2, y2)
# 在坐标(x,y)处写文字
def drawText(t, x, y, text):
t.penup()
t.goto(x, y)
t.pendown()
t.write(text)
def drawGraph(t):
# 绘制x/y轴线
drawLine(t, 0, 0, 360, 0)
drawLine(t, 0, 300, 0, 0)
# x轴: 坐标及描述
for x in range(count):
x = x + 1 # 向右移一位,为了不画在原点上
drawText(t, x * xScale - 4, -20, (words[x - 1]))
drawText(t, x * xScale - 4, data[x - 1] * yScale + 10, data[x - 1])
drawBar(t)
# 绘制一个柱体
def drawRectangle(t, x, y):
x = x * xScale
y = y * yScale # 放大倍数显示
drawLine(t, x - 5, 0, x - 5, y)
drawLine(t, x - 5, y, x + 5, y)
drawLine(t, x + 5, y, x + 5, 0)
drawLine(t, x + 5, 0, x - 5, 0)
# 绘制多个柱体
def drawBar(t):
for i in range(count):
drawRectangle(t, i + 1, data[i])
################# Turtle End ####################
##计算一行文本的词频
def processLine(line,wordCounts):
#用空格替换标点符号
line = replacePunctuations(line)
#从每一行获取每个词
words = line.split() ##按空格分割字符串,返回列表
for word in words:
if word in wordCounts: #wordCounts字典{'word':出现次数}
wordCounts[word] += 1 #若该word已在字典中,则为次数+1
else:
wordCounts[word] = 1 #否则新建一项
#用空格替换标点符号
def replacePunctuations(line):
for ch in line:
if ch in "~@#$%^&*()_-+=<>?/,.:;{}[]|\'""":
line = line.replace(ch,'')
return line
def main():
#用户输入文件名
filename = input('请输入文件名:').strip() ##strip()删除首位空格
infile = open(filename,'r',encoding='UTF-8')
#建立用于计算词频的空字典
wordCounts = {}
for line in infile:
processLine(line.lower(),wordCounts)
#从字典中获取数据对
pairs = list(wordCounts.items()) #字典转成列表
#列表中数据交换位置,数据对排序
items = [[x,y]for [y,x] in pairs]
items.sort()
# 输出count个数词频结果
print('词\t词频')
for i in range(len(items) - 1, len(items) - count - 1, -1): ##倒序输出
print(items[i][1] + "\t" + str(items[i][0]))
data.append(items[i][0])
words.append(items[i][1])
infile.close()
#根据词频结果绘制柱状图
turtle.title('词频结果柱状图')
turtle.setup(900,750,0,0) #设置图形窗口
t = turtle.Turtle() #初始化画笔
t.hideturtle()
t.width(3)
drawGraph(t)
turtle.done()
main()
输出
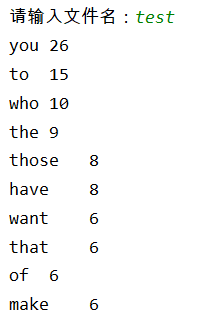
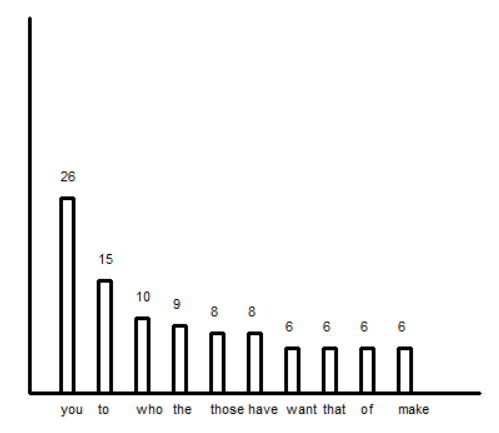
词频统计二
def getText():
txt = open('test','r',encoding='UTF-8').read()
txt = txt.lower()
for ch in "~@#$%^&*()_-+=<>?/,.:;{}[]|\'""":
txt =txt.replace(ch,'')
return txt
testTxt = getText()
words = testTxt.split()
file = open('excludes','r',encoding='UTF-8').read()
excludes = file.split()
counts = {}
for word in words:
if word not in excludes: ##排除excludes里面的词
counts[word] = counts.get(word, 0) + 1
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True) ##排序
for i in range(10):
word , count = items[i]
print("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word,count))
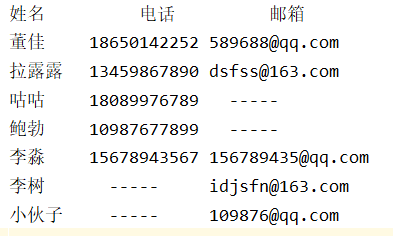
案例二:使用字典合并两个文件
## 两个文件合并成一个
###利用字符串和列表将两个通讯录文本合并为一个文本
def main():
f1 = open('Tele','r',encoding='UTF-8')
f2 = open('Email','r',encoding='UTF-8')
f1.readline()#跳过第一行
f2.readline()
line1 = f1.readlines()
line2 = f2.readlines()
#字典方式保存
dict1={}
dict2={}
for line in line1: ##获取第1个文件中的姓名和电话
elements = line.split() ##split()按空格进行切片
dict1[elements[0]] = str(elements[1]) ##elements[0]为字典的键key,elements[1]为字典的值value
for line in line2: ##获取第2个文件中的姓名和电话
elements = line.split() ##split()按空格进行切片
dict2[elements[0]] = str(elements[1])
###开始处理
lines = []
lines.append('姓名\t 电话 \t 邮箱\n')
for key in dict1:
s = ''
if key in dict2:
s = '\t'.join([key,dict1[key],dict2[key]])
s += '\n'
else:
s = '\t'.join([key, dict1[key], str(' ----- ')])
s += '\n'
lines.append(s)
for key in dict2:
s = ''
if key not in dict1:
s = '\t'.join([key, str(' ----- '), dict2[key]])
s += '\n'
lines.append(s)
f3 = open('Address','w',encoding='UTF-8')
f3.writelines(lines)
f1.close()
f2.close()
f3.close()
main()
※※※中文分词
jieba库

import jieba
print(jieba.lcut('中国是一个伟大的国家!'))
#['中国', '是', '一个', '伟大', '的', '国家', '!']##返回字符串分词后的列表



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号