StaticFileMiddleware 解析
说明:由于部分产品没有静态资源的管理,我突然想到能不能用现有的静态文件中间件的功能调整一下实现多组织件上传文件的隔离呢?那第一步先看懂 StaticFileMiddleware做了什么吧。
PS:本文不解释中间件原理。
第一步 方法源码
using System;using System.IO;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using Microsoft.Extensions.Options; namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.StaticFiles { /// <summary> /// 这个就是静态文件中间件的核心代码 /// </summary> public class StaticFileMiddleware { /// <summary> /// 构造函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="next">The next middleware in the pipeline.</param> /// <param name="hostingEnv">The used by this middleware.</param> /// <param name="options">The configuration options.</param> /// <param name="loggerFactory">An instance used to create loggers.</param> public StaticFileMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IHostingEnvironment hostingEnv, IOptions<StaticFileOptions> options, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { if (next == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("next"); } if (hostingEnv == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("hostingEnv"); } if (options == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("options"); } if (loggerFactory == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("loggerFactory"); } this._next = next; this._options = options.Value; this._contentTypeProvider = (options.Value.ContentTypeProvider ?? new FileExtensionContentTypeProvider()); this._fileProvider = (this._options.FileProvider ?? Helpers.ResolveFileProvider(hostingEnv)); this._matchUrl = this._options.RequestPath; this._logger = LoggerFactoryExtensions.CreateLogger<StaticFileMiddleware>(loggerFactory); } /// <summary> /// 这里才是静态文件处理的业务方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="context"></param> /// <returns></returns> public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) {
StaticFileContext fileContext = new StaticFileContext(context, this._options, this._matchUrl, this._logger, this._fileProvider, this._contentTypeProvider);
//验证请求方法 if (!fileContext.ValidateMethod()) { this._logger.LogRequestMethodNotSupported(context.Request.Method); }
//验证路径
else if (!fileContext.ValidatePath()) { this._logger.LogPathMismatch(fileContext.SubPath); }
//验证文件类型系统是否识别 else if (!fileContext.LookupContentType()) { this._logger.LogFileTypeNotSupported(fileContext.SubPath); } else {
//尝试读取文件信息 if (fileContext.LookupFileInfo()) {
// fileContext.ComprehendRequestHeaders(); switch (fileContext.GetPreconditionState()) {
//访问成功了 case StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.Unspecified: case StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.ShouldProcess:
//如果是head请求,直接范围200,不返回请求体 if (fileContext.IsHeadMethod) { await fileContext.SendStatusAsync(200); return; } try {
//请求包含Range if (fileContext.IsRangeRequest) { await fileContext.SendRangeAsync(); return; }
//这个默认无参的时候是200 await fileContext.SendAsync(); this._logger.LogFileServed(fileContext.SubPath, fileContext.PhysicalPath); return; } catch (FileNotFoundException) { ResponseExtensions.Clear(context.Response); goto IL_3E2; } break;
//请求没有变更,这之后跳出switch,反回304 case StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.NotModified: break; case StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.PreconditionFailed: this._logger.LogPreconditionFailed(fileContext.SubPath);
//请求不匹配 await fileContext.SendStatusAsync(412); return; default: throw new NotImplementedException(fileContext.GetPreconditionState().ToString()); } this._logger.LogPathNotModified(fileContext.SubPath); await fileContext.SendStatusAsync(304); return; }
this._logger.LogFileNotFound(fileContext.SubPath); }
//不符合静态资源的要求,走下一个中间件(通常是MVC中间件) IL_3E2: await this._next.Invoke(context); } // Token: 0x04000048 RID: 72 private readonly StaticFileOptions _options; // Token: 0x04000049 RID: 73 private readonly PathString _matchUrl; // Token: 0x0400004A RID: 74 private readonly RequestDelegate _next; // Token: 0x0400004B RID: 75 private readonly ILogger _logger; // Token: 0x0400004C RID: 76 private readonly IFileProvider _fileProvider; // Token: 0x0400004D RID: 77 private readonly IContentTypeProvider _contentTypeProvider; } }
第二步 方法解析
1 ValidateMethod 验证请求方式
public bool ValidateMethod() { this._method = this._request.Method; this._isGet = HttpMethods.IsGet(this._method); this._isHead = HttpMethods.IsHead(this._method); return this._isGet || this._isHead; }
这个函数从字面上看就是判断当前静态资源的请求方式是不是get 和head,只要是其中一种就是可以的。
get请求方式就不说吗了,head请求方式的解释如下:
HEAD方法与GET方法的行为很类似,但服务器在响应中只返回首部。不会反回实体的主体部分。这就允许客户端在未获取实际资源的情况下,对资源的首部进行检查。一般应用于在不获取资源的情况下了解资源情况。
2 ValidatePath 验证路径
public bool ValidatePath() { return Helpers.TryMatchPath(this._context, this._matchUrl, false, out this._subPath); } internal static bool TryMatchPath(HttpContext context, PathString matchUrl, bool forDirectory, out PathString subpath) { PathString pathString = context.Request.Path; if (forDirectory && !Helpers.PathEndsInSlash(pathString)) { pathString += new PathString("/"); } return pathString.StartsWithSegments(matchUrl, ref subpath); }
internal static bool PathEndsInSlash(PathString path)
{
return path.Value.EndsWith("/", StringComparison.Ordinal);
}
这个验证其实就是验证请求文件的路径前缀是否和你系统设置的是否一致。matchUrl这个参数可以在Startup.cs中在静态文件中间件中作为参数传递进去。如图所示
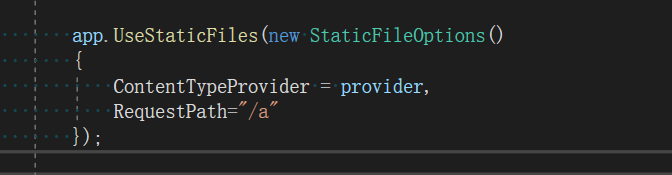
如上所述,现在系统只能请求/a开头的文件了(路径开头,不是文件名称开头)。
具体匹配逻辑可以看Path 的StartsWithSegments的实现。
3 LookupContentType 文件类型验证
if (this._contentTypeProvider.TryGetContentType(this._subPath.Value, out this._contentType)) { return true; } if (this._options.ServeUnknownFileTypes) { this._contentType = this._options.DefaultContentType; return true; } return false;
这个验证就是检验拓展名的。可以结合一下实例查看

首先判断请求文件的拓展名在FileExtensionContentTypeProvider中是否存在(FileExtensionContentTypeProvider原本就会有很多拓展类型,截图中我们认为的添加上了image和log的拓展格式)
系统先去判断拓展格式是否存在,如果存在则连带的把反馈类型也返回出来。
如果不存在就去判断是否设置了允许未知的拓展出。例如我有一个拓展名叫做 .alex,然后我们希望系统可以将其以txt的格式反馈,那么就需要如下操作:
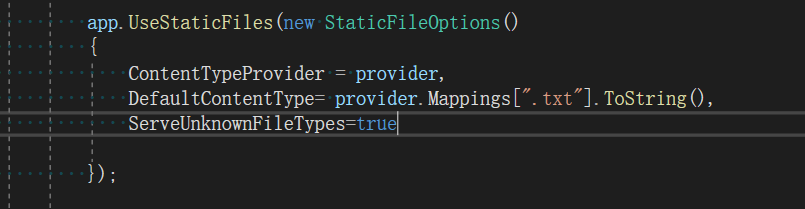
4 LookupFileInfo 文件信息验证
public bool LookupFileInfo() { this._fileInfo = this._fileProvider.GetFileInfo(this._subPath.Value); if (this._fileInfo.Exists) { this._length = this._fileInfo.Length; DateTimeOffset lastModified = this._fileInfo.LastModified; this._lastModified = new DateTimeOffset(lastModified.Year, lastModified.Month, lastModified.Day, lastModified.Hour, lastModified.Minute, lastModified.Second, lastModified.Offset).ToUniversalTime(); long value = this._lastModified.ToFileTime() ^ this._length; this._etag = new EntityTagHeaderValue("\"" + Convert.ToString(value, 16) + "\""); } return this._fileInfo.Exists; }
这个验证首先是验证文件是否存在,之后会做一系列的计算操作。这一步会获取两个值
_lastModified:文件最后操作日期
_etag :等效算法,通过文件大小、最后操作日期来生成的一个数据值。上述两个值可以通过浏览器查看如下:
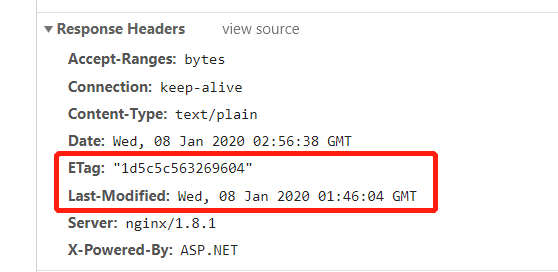
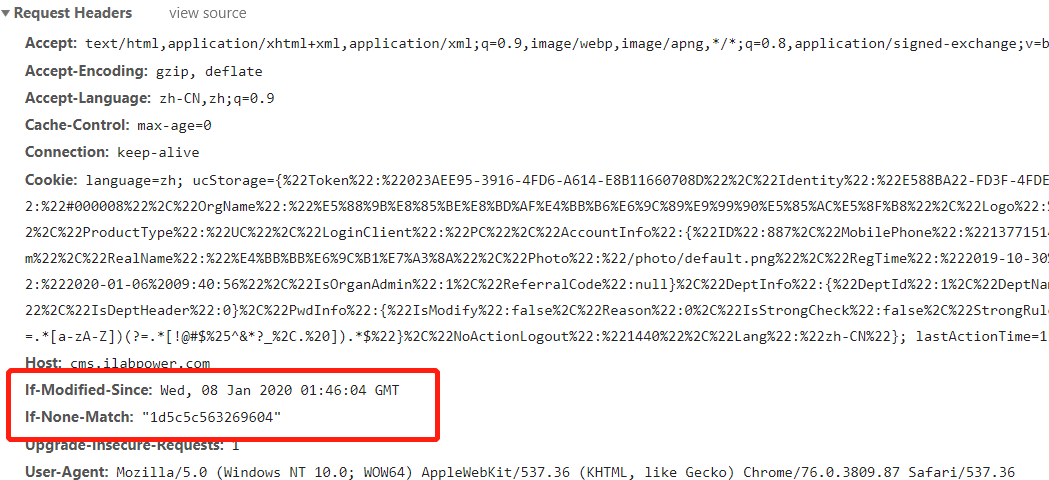
这两个值其实就是判断文件缓存的,具体分析可以参看以下文章:
https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/5986339.html
5 ComprehendRequestHeaders 请求头验证
public void ComprehendRequestHeaders() { this.ComputeIfMatch(); this.ComputeIfModifiedSince(); this.ComputeRange(); this.ComputeIfRange(); }
这一段就用到了上一个验证的时候生成的_lastModified和_etag来计算缓存问题,故不再赘述了。逻辑代码如下:
private void ComputeIfMatch() { IList<EntityTagHeaderValue> ifMatch = this._requestHeaders.IfMatch; if (ifMatch != null && ifMatch.Any<EntityTagHeaderValue>()) { this._ifMatchState = StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.PreconditionFailed; foreach (EntityTagHeaderValue entityTagHeaderValue in ifMatch) { if (entityTagHeaderValue.Equals(EntityTagHeaderValue.Any) || entityTagHeaderValue.Compare(this._etag, true)) { this._ifMatchState = StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.ShouldProcess; break; } } } IList<EntityTagHeaderValue> ifNoneMatch = this._requestHeaders.IfNoneMatch; if (ifNoneMatch != null && ifNoneMatch.Any<EntityTagHeaderValue>()) { this._ifNoneMatchState = StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.ShouldProcess; foreach (EntityTagHeaderValue entityTagHeaderValue2 in ifNoneMatch) { if (entityTagHeaderValue2.Equals(EntityTagHeaderValue.Any) || entityTagHeaderValue2.Compare(this._etag, true)) { this._ifNoneMatchState = StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.NotModified; break; } } } } // Token: 0x0600006C RID: 108 RVA: 0x00004CE8 File Offset: 0x00002EE8 private void ComputeIfModifiedSince() { DateTimeOffset utcNow = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow; DateTimeOffset? ifModifiedSince = this._requestHeaders.IfModifiedSince; if (ifModifiedSince != null && ifModifiedSince <= utcNow) { this._ifModifiedSinceState = ((ifModifiedSince < this._lastModified) ? StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.ShouldProcess : StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.NotModified); } DateTimeOffset? ifUnmodifiedSince = this._requestHeaders.IfUnmodifiedSince; if (ifUnmodifiedSince != null && ifUnmodifiedSince <= utcNow) { this._ifUnmodifiedSinceState = ((ifUnmodifiedSince >= this._lastModified) ? StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.ShouldProcess : StaticFileContext.PreconditionState.PreconditionFailed); } }
后面几个方法,this.ComputeRange();和this.ComputeIfRange();
可以参考一下文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/shuimuniao/article/details/8086438
总结
静态资源中间件的逻辑可以简单的归纳如下:
1、判断是否是静态资源请求方式(Head或者Get)
2、判断请求连接是否符合设置UrlMatch(RequestPath配置)
3、判断文件拓展名是否存在或者启动未知拓展名服务(DefaultContentType、ServeUnknownFileTypes)
4、判断文件是否存在,计算文件_lastModified和_etag
5、如果上述4点判断都失败了,则认为不是静态资源请求,走下一个中间件
6、根据请求头和请求资源的数据判断以下几种反馈请求
- 请求类型是Head ,返回 200 但是没有请求体
- 请求If-Range不匹配,反馈412
- 请求的缓存匹配,反馈 304
- 请求成功,反馈200及请求体。



