vue-router 的基本使用
路由:指向的意思,也可以说是一种映射(一对一)。
例如:点击+页面上的home按钮,页面中展示home的内容。点击detail按钮,页面中展示detail内容。
如何正确的对应显示,这就要在js文件中配置路由,路由中有三个基本概念route,routes,router.
1.route,是一条路由 ,一个局部对象。
2.routes,是一组路由,多个局部对象。
3.router,是一个机制,相当于管理者--->管理路由,全局的对象。因为routes定义了一组路由,当有交互事件发生时,router就会到routes中去查找对应的路由。
4.客户端的路由,实际上就是dom元素的显示和隐藏,当页面中显示home内容的时候,detail中的内容就全部隐藏,反之也是一样。
客户端路由有两种实现方式:基于hash和基于html5 history api
在vue中使用vue-router
在vue中页面中所有内容都是组件化的,我们只要把路径和组件对应起来,然后在页面中把组件渲染出来
html模板中
在vue-router中,定义了两个标签<router-link>和<router-view>来对应点击和显示部分。<router-link>定义页面中的点击部分,<router-view>定义显示部分,就是点击后匹配的内容显示在什么地方。
<router-link>有一个非常重要的属性to,定义点击之后要到哪里去。<router-link to='/home'>Home</router-link>
js中配置路由
1.一条路由,是一个对象,由两部分组成:path和component,path指路径,component指的是组件 。例如:{path:'/home',component: home}
2.多条路由组成一个routes
const routes = { {path:'/home',component: home} {path:'/detail',component: detail} }
3.通过构造函数new vueRouter()创建router对路由进行管理,接受routes参数
const router = new VueRouter({ routes ( routes: routes 的简写) })
配置完成之后,把route实例注入到vue根实例中,就可以使用路由了

执行过程:当用户点击 router-link 标签时,会去寻找它的 to 属性, 它的 to 属性和 js 中配置的路径{ path: '/home', component: Home} path 一 一对应,从而找到了匹配的组件, 最后把组件渲染到 <router-view> 标签所在的地方。所有的这些实现才是基于hash 实现的。
vue-cli 创建一个项目体验一下, 当然不要忘记安装vue-router
1.在src 目录下新建两个组件,home.vue 和 about.vue
//home.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>home</h1>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
msg: "我是home 组件"
}
}
}
</script>
// about.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>about</h1>
<p>{{aboutMsg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
aboutMsg: '我是about组件'
}
}
}
</script>
2. 在 App.vue中 定义<router-link > 和 </router-view>
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<header>
<!-- router-link 定义点击后导航到哪个路径下 -->
<router-link to="/home">Home</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>
</header>
<!-- 对应的组件内容渲染到router-view中 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
3.在 src目录下再新建一个router.js 定义router, 就是定义 路径到 组件的 映射。
import Vue from "vue";
import VueRouter from "vue-router";
// 引入组件
import home from "./home.vue";
import about from "./about.vue";
// 要告诉 vue 使用 vueRouter
Vue.use(VueRouter);
const routes = [
{
path:"/home",
component: home
},
{
path: "/about",
component: about
}
]
var router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router;
4.把路由注入到根实例中,启动路由。在main.js中引入路由,注入到根实例中。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 引入路由
import router from "./router.js" // import router 的router 一定要小写, 不要写成Router, 否则报 can't match的报错
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router, // 注入到根实例中
render: h => h(App)
})
5. 这时点击页面上的home 和about 可以看到组件来回切换。但是有一个问题,当首次进入页面的时候,页面中并没有显示任何内容。
这是因为首次进入页面时,它的路径是 '/',我们并没有给这个路径做相应的配置。一般,页面一加载进来都会显示home页面,我们也要把这个路径指向home组件。
但是如果我们写{ path: '/', component: Home },vue 会报错,因为两条路径却指向同一个方向。这怎么办?
这需要重定向,所谓重定向,就是重新给它指定一个方向,它本来是访问 / 路径,我们重新指向‘/home’, 它就相当于访问 '/home', 相应地, home组件就会显示到页面上。vueRouter中用 redirect 来定义重定向。
const routes = [
{
path:"/home",
component: home
},
{
path: "/about",
component: about
},
// 重定向
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/home'
}
]
现在页面正常了,首次进入显示home, 并且点击也可以看到内容的切换。
6.最后,我们看一下路由是怎么实现的
打开浏览器控制台,首先看到 router-link 标签渲染成了 a 标签,to 属性变成了a 标签的 href 属性,这时就明白了点击跳转的意思。
router-view 标签渲染成了我们定义的组件,其实它就是一个占位符,它在什么地方,匹配路径的组件就在什么地方,所以 router-link 和router-view 标签一 一对应,成对出现。
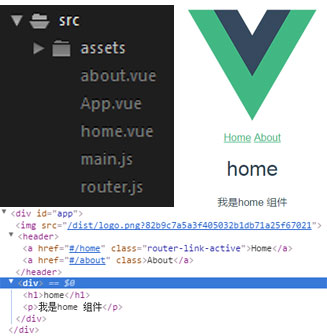
这里还看到,当点击Home和About 来回切换时,a 标签有一个样式类 .router-link-active 也在来回切换, 原来这是当router-link 处于选中状态时,vueRouter 会自动添加这个类,因此我们也可以利用这个类来改变选中时的状态,如选中时,让它变成红色。
但当设置 .router-link-active {color: red;},它并没有生效,这时还要在类前面加一个a, a.router-link-active {color: red;}, 这样就没有问题了。
未处于选中状态的router-link, 我们也想给它更改样式,怎么办? 直接给它添加一个 class 就可以了, <router-link class="red">Home</router-link>
7.动态路由
上面我们定义的路由,都是严格匹配的,只有router-link 中的to属性和 js 中一条路由route中 path 一模一样,才能显示相应的组件component. 但有时现实却不是这样的,当我们去访问网站并登录成功后,它会显示 欢迎你,+ 你的名字。不同的用户登录,
只是显示“你的名字” 部分不同,其它部分是一样的。这就表示,它是一个组件,假设是user组件。不同的用户(就是用户的id不同),它都会导航到同一个user 组件中。
这样我们在配置路由的时候,就不能写死, 就是路由中的path属性,不能写死,那要怎么设置? 导航到 user 组件,路径中肯定有user, id 不同,那就给路径一个动态部分来匹配不同的id. 在vue-router中,动态部分 以 : 开头,那么路径就变成了 /user/:id, 这条路由就可以这么写: { path:"/user/:id", component: user }.
我们定义一个user组件(自己随便写一个就好了),页面中再添加两个router-link 用于导航, 最后router.js中添加路由配置,来体验一下
app.vue 中添加两个router-link:
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<header>
<router-link to="/home">Home</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>
<!-- 增加两个到user组件的导航,可以看到这里使用了不同的to属性 -->
<router-link to="/user/123">User123</router-link>
<router-link to="/user/456">User456</router-link>
</header>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
router.js 配置user动态路由:
const routes = [
{
path:"/home",
component: home
},
{
path: "/about",
component: about
},
/*新增user路径,配置了动态的id*/
{
path: "/user/:id",
component: user
},
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/home'
}
]
user组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>User</h1>
<div>我是user组件</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
这时在页面中点击user123 和user456, 可以看到它们都导航到user组件,配置正确。
在动态路由中,怎么获取到动态部分? 因为在组件中是可以显示不同部分的,就是上面提到的“你的名字”。其实,当整个vue-router 注入到根实例后,在组件的内部,可以通过this.$route 来获取到 router 实例。
它有一个params 属性,就是来获得这个动态部分的。它是一个对象,属性名,就是路径中定义的动态部分 id, 属性值就是router-link中to 属性中的动态部分,如123。
使用vuex时,组件中想要获取到state 中的状态,是用computed 属性,在这里也是一样,在组件中,定义一个computed 属性dynamicSegment, user 组件修改如下:
<template>
<div>
<h1>User</h1>
<div>我是user组件, 动态部分是{{dynamicSegment}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed: {
dynamicSegment () {
return this.$route.params.id
}
}
}
</script>
这里还有最后一个问题,就是动态路由在来回切换时,由于它们都是指向同一组件,vue不会销毁再创建这个组件,而是复用这个组件,就是当第一次点击(如:user123)的时候,vue 把对应的组件渲染出来,但在user123, user456点击来回切换的时候,这个组件就不会发生变化了,组件的生命周期不管用了。
这时如果想要在组件来回切换的时候做点事情,那么只能在组件内部(user.vue中)利用watch 来监听$route 的变化。把上面的代码用监听$route 实现
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
dynamicSegment: ''
}
},
watch: {
$route (to,from){
// to表示的是你要去的那个组件,from 表示的是你从哪个组件过来的,它们是两个对象,你可以把它打印出来,它们也有一个param 属性
console.log(to);
console.log(from);
this.dynamicSegment = to.params.id
}
}
}
</script>
8.嵌套路由
嵌套路由,主要是由我们的页面结构所决定的。当我们进入到home页面的时候,它下面还有分类,如手机系列,平板系列,电脑系列。当我们点击各个分类的时候,它还是需要路由到各个部分,如点击手机,它肯定到对应到手机的部分。
在路由的设计上,首先进入到 home ,然后才能进入到phone, tablet, computer. Phone, tablet, compute 就相当于进入到了home的子元素。所以vue 提供了childrens 属性,它也是一组路由,相当于我们所写的routes。
首先,在home页面上定义三个router-link 标签用于导航,然后再定义一个router-view标签,用于渲染对应的组件。router-link 和router-view 标签要一一对应。
home.vue 组件修改如下:
<template>
<div>
<h1>home</h1>
<!-- router-link 的to属性要注意,路由是先进入到home,然后才进入相应的子路由如 phone,所以书写时要把 home 带上 -->
<p>
<router-link to="/home/phone">手机</router-link>
<router-link to="/home/tablet">平板</router-link>
<router-link to="/home/computer">电脑</router-link>
</p>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
router.js 配置路由,修改如下:
const routes = [
{
path:"/home",
// 下面这个属性也不少,因为,我们是先进入home页面,才能进入子路由
component: home,
// 子路由
children: [
{
path: "phone",
component: phone
},
{
path: "tablet",
component: tablet
},
{
path: "computer",
component: computer
}
]
},
{
path: "/about",
component: about
},
{
path: "/user/:id",
component: user
},
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/home'
}
]
这时当我们点击home 时,它下面出现手机等字样,但没有任何对应的组件进行显示,这通常不是我们想要的。要想点击home时,要想渲染相对应的子组件,那还需要配置一条路由。当进入到home 时,它在children中对应的路由path 是空 ‘’,完整的childrens 如下:
children: [
{
path: "phone",
component: phone
},
{
path: "tablet",
component: tablet
},
{
path: "computer",
component: computer
},
// 当进入到home时,下面的组件显示
{
path: "",
component: phone
}
]
9.命名路由
命名路由,很简单,因为根据名字就可以知道,这个路由有一个名字,那就直接给这个路由加一个name 属性,就可以了。 给user 路由加一个name 属性:
{
path: "/user/:id",
name: "user",
component: user
}
命名路由的使用, 在router-link 中to 属性就可以使用对象了,
<router-link to="/user/123">User123</router-link> // 和下面等价
<router-link :to="{ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }}">User</router-link> // 当使用对象作为路由的时候,to前面要加一个冒号,表示绑定
10.编程式导航
这主要应用到按钮点击上。当点击按钮的时候,跳转另一个组件, 这只能用代码,调用rourter.push() 方法。 当们把router 注入到根实例中后,组件中通过 this.$router 可以获取到router, 所以在组件中使用
this.$router.push("home"), 就可以跳转到home界面
看一下项目中的实际应用:
项目中的菜单结构如下:有一级菜单,二级菜单,三级菜单,看下这个三级菜单的实现
import Vue from 'vue'; import Router from 'vue-router'; /* Layout */ import Layout from '@/layout/index.vue'; Vue.use(Router); export const constantRoutes = [ { path: '/login', component: () => import('@/views/login/index'), hidden: true, }, { path: '/404', component: () => import('@/views/404'), hidden: true, }, { path: '/', redirect: '/dataOperations/productInformation/productTree', }, { path: '/dataOperations', component: Layout, alwaysShow: true, redirect: '/dataOperations/productInformation/productTree', name: 'DataOperations', meta: { title: '数据运维', icon: 'table' }, children: [ { path: 'productInformation', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/index'), meta: { title: '产品信息', icon: 'tree' }, alwaysShow: true, name: 'ProductInformation', redirect: '/dataOperations/productInformation/productTree', children: [ { path: 'productTree', name: 'ProductTree', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/productTree'), meta: { title: '产品树查询' }, }, { path: 'spu', name: 'Spu', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/spu'), meta: { title: 'SPU' }, }, { path: 'statisticsSku', name: 'StatisticsSku', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/statisticsSku'), meta: { title: 'statisticsSku' }, }, { path: 'salesSku', name: 'SalesSku', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/salesSku'), meta: { title: 'salesSku' }, }, { path: 'sku', name: 'Sku', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/sku'), meta: { title: 'SKU' }, }, { path: 'bom', name: 'Bom', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/bom'), meta: { title: 'BOM' }, }, ], }, { path: 'exception', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/exception/template'), meta: { title: '异常数据', icon: 'tree' }, alwaysShow: true, name: 'Exception', hidden: localStorage.role === '1', redirect: '/dataOperations/productInformation/exception/index', children: [ { path: 'index', name: 'ExceptionList', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/exception/index'), meta: { title: 'salesSku异常处理' }, }, { path: 'detail', name: 'exceptionDetail', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/exception/detail'), meta: { title: 'salesSku异常处理详情' }, hidden: true, }, ], }, { path: 'backup', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/backup/index'), meta: { title: '数据备份' }, name: 'ProductInformation', hidden: localStorage.role === '1', }, { path: 'backup/detail', component: () => import('@/views/productInformation/backup/detail'), meta: { title: '数据备份明细' }, name: 'ProductInformation', hidden: true, }, ], }, { path: '/permiss', component: Layout, meta: { title: '权限管理', icon: 'example', }, name: 'Permiss', redirect: '/permiss/appId', hidden: localStorage.role === '1', children: [ { path: 'appId', name: 'AppId', component: () => import('@/views/appId/index'), meta: { title: 'appId管理' }, }, { path: 'interface', name: 'Interface', component: () => import('@/views/interface/index'), meta: { title: '接口管理' }, }, { path: 'user', name: 'User', component: () => import('@/views/user/index'), meta: { title: '用户管理' }, }, ], }, // 404 page must be placed at the end !!! { path: '*', redirect: '/404', hidden: true }, ]; const createRouter = () => new Router({ // mode: 'history', // require service support scrollBehavior: () => ({ y: 0 }), routes: constantRoutes, }); const router = createRouter(); // Detail see: https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/1234#issuecomment-357941465 export function resetRouter() { setTimeout(() => { const newRouter = createRouter(); router.matcher = newRouter.matcher; // reset router }, 200); } export default router;
转自https://www.cnblogs.com/SamWeb/p/6610733.html



