ASP.NET Core EventStream (SSE) 使用以及 WebSocket 比较
在开发环境中,对于实时数据流的需求非常常见,最常用的技术包括 Server-Sent Events (SSE) 和 WebSocket。
什么是 Server-Sent Events (SSE)?
SSE (服务器发送事件)是一种基于 HTTP/1.1 协议的传达模型,允许服务器向浏览器不断发送数据更新。它直接使用 HTTP GET 请求,服务器送选用的字符串及内容。
举例: 让我们将一个服务器的实时状态传达给前端浏览器:
1. 添加服务器端 API
在 ASP.NET Core 中实现 SSE,示例是一个简单的项目实时监控。
项目结构如下:
Starup.cs文件新增如下代码:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.HttpsPolicy; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using Microsoft.OpenApi.Models; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace WebApplication { public class Startup { public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddControllers(); // 允许跨域请求 services.AddCors(options => { options.AddPolicy("AllowLocalhost", builder => builder.WithOrigins("https://localhost:5001") // 允许来自 https://localhost:5001 的请求 .AllowAnyHeader() // 允许任何头部 .AllowAnyMethod()); // 允许任何方法 }); services.AddSwaggerGen(c => { c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "WebApplication", Version = "v1" }); }); } // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); app.UseSwagger(); app.UseSwaggerUI(c => c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "WebApplication v1")); } // 启用 CORS 中间件 app.UseCors("AllowLocalhost"); app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); // 启用静态文件中间件 app.UseStaticFiles(); // 默认提供 wwwroot 下的静态文件 app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllers(); }); } } }
控制器代码:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.IO; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; namespace WebApplication.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class ServerStatusController : ControllerBase { // 定义性能计数器来获取 CPU 使用率 private readonly PerformanceCounter _cpuCounter = new PerformanceCounter("Processor", "% Processor Time", "_Total"); [HttpGet("status")] public async Task GetServerStatus() { // 设置响应头,声明是 SSE 流 Response.ContentType = "text/event-stream"; Response.Headers.Add("Cache-Control", "no-cache"); Response.Headers.Add("Connection", "keep-alive"); // 获取当前进程的基本信息 var process = Process.GetCurrentProcess(); await using var writer = new StreamWriter(Response.Body, Encoding.UTF8, leaveOpen: true); while (!HttpContext.RequestAborted.IsCancellationRequested) { // 获取 CPU 使用率 var cpuUsage = _cpuCounter.NextValue(); // CPU 使用率百分比 var memoryUsage = process.WorkingSet64 / (1024 * 1024); // 内存使用(MB) var uptime = (DateTime.Now - process.StartTime).ToString(@"hh\:mm\:ss"); // 服务器运行时间 // 获取系统的磁盘使用情况 var diskUsage = GetDiskUsage(); // 获取系统的网络使用情况(假设 Windows 上可用) var networkUsage = new NetworkUsage().GetNetworkUsage(); // 构建状态信息 var status = new { CPU = $"{cpuUsage:F2}%", Memory = $"{memoryUsage} MB", Uptime = uptime, DiskUsage = diskUsage, NetworkUsage = networkUsage, Timestamp = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") }; // 将状态信息转化为 JSON 格式并发送 await writer.WriteLineAsync($"data: {System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Serialize(status)}\n"); await writer.FlushAsync(); // 确保立即推送数据 await Task.Delay(1000*2); // 每秒更新一次 } } // 获取磁盘使用情况(Windows) private string GetDiskUsage() { if (RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows)) { var drive = DriveInfo.GetDrives().FirstOrDefault(d => d.IsReady); if (drive != null) { return $"{drive.TotalFreeSpace / (1024 * 1024 * 1024)} GB free of {drive.TotalSize / (1024 * 1024 * 1024)} GB"; } } return "N/A"; } } }
网路获取类:
using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Net.NetworkInformation; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; using System.Text; public class NetworkUsage { public string GetNetworkUsage() { if (RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows)) { return GetWindowsNetworkUsage(); } else if (RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Linux)) { return GetLinuxNetworkUsage(); } else { return "Unsupported operating system."; } } private string GetWindowsNetworkUsage() { try { // 获取 PerformanceCounter 支持的所有网络接口实例 var category = new PerformanceCounterCategory("Network Interface"); var validInstances = category.GetInstanceNames(); // 返回支持的实例名称 // 获取系统中活动的网络接口 var interfaces = NetworkInterface.GetAllNetworkInterfaces() .Where(ni => ni.OperationalStatus == OperationalStatus.Up && validInstances.Contains(ni.Description)) // 匹配实例名称 .ToList(); if (!interfaces.Any()) { return "No valid network interfaces found."; } var result = new StringBuilder(); foreach (var iface in interfaces) { try { var networkIn = new PerformanceCounter("Network Interface", "Bytes Received/sec", iface.Description); var networkOut = new PerformanceCounter("Network Interface", "Bytes Sent/sec", iface.Description); var receivedBytes = networkIn.NextValue() / (1024 * 1024); // 转换为 MB var sentBytes = networkOut.NextValue() / (1024 * 1024); // 转换为 MB result.AppendLine($"{iface.Name} ({iface.Description}): {receivedBytes:F2} MB received, {sentBytes:F2} MB sent per second"); } catch (Exception ex) { result.AppendLine($"Error retrieving data for {iface.Name} ({iface.Description}): {ex.Message}"); } } return result.ToString(); } catch (Exception ex) { return $"Error retrieving network usage on Windows: {ex.Message}"; } } private string GetLinuxNetworkUsage() { try { if (!File.Exists("/proc/net/dev")) return "Unable to access network statistics (Linux only)"; string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines("/proc/net/dev"); var networkInterfaces = lines .Skip(2) // 跳过前两行标题 .Select(line => line.Trim()) .Where(line => line.Contains(":")) .Select(ParseNetworkLine) .ToList(); return string.Join("\n", networkInterfaces.Select(ni => $"{ni.Interface}: {ni.ReceivedMB:F2} MB received, {ni.TransmittedMB:F2} MB sent")); } catch (Exception ex) { return $"Error retrieving network usage on Linux: {ex.Message}"; } } private (string Interface, double ReceivedMB, double TransmittedMB) ParseNetworkLine(string line) { var parts = line.Split(new[] { ' ', ':' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); string interfaceName = parts[0]; long receivedBytes = long.Parse(parts[1]); // 接收字节 long transmittedBytes = long.Parse(parts[9]); // 发送字节 return ( Interface: interfaceName, ReceivedMB: receivedBytes / (1024.0 * 1024.0), // 转换为 MB TransmittedMB: transmittedBytes / (1024.0 * 1024.0) // 转换为 MB ); } }
2. 前端展示 SSE
在浏览器中使用 JavaScript 接收服务器数据:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Server Status</title> </head> <body> <h1>Server Status</h1> <div id="status"> <p>Loading...</p> </div> <script> const eventSource = new EventSource('/api/serverstatus/status'); eventSource.onmessage = function (event) { const status = JSON.parse(event.data); document.getElementById('status').innerHTML = ` <p><strong>CPU Usage:</strong> ${status.CPU}</p> <p><strong>Memory Usage:</strong> ${status.Memory}</p> <p><strong>Uptime:</strong> ${status.Uptime}</p> <p><strong>Disk Usage:</strong> ${status.DiskUsage}</p> <p><strong>Network Usage:</strong> ${status.NetworkUsage}</p> <p><strong>Timestamp:</strong> ${status.Timestamp}</p> `; }; eventSource.onerror = function (error) { console.error("Error occurred: ", error); }; </script> </body> </html>
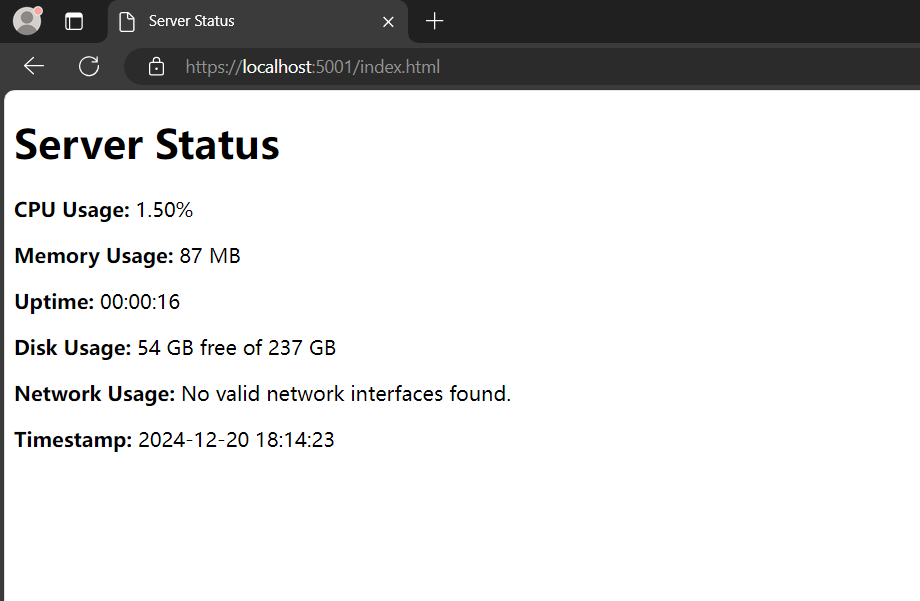
运行网站后效果如下,2s刷新一次:
比较 SSE 和 WebSocket
| 特性 | SSE | WebSocket |
|---|---|---|
| 通讯方式 | 服务器 -> 客户端 | 双向通信 |
| 使用协议 | HTTP/1.1 | TCP/HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2 |
| 解析方式 | 浏览器内置,无需额外应用 | 需要设计应用协议 |
| 应用场景 | 更新速度不高,如实时通知 | 高频发送,如游戏体验和客制游戏 |
| 应用端支持 | 原生支持,不需额外学习 | 需要客户端实现 |
| 考虑问题 | 支持 HTTP 跨域,比 WebSocket 更简单 | 需要第三方应用支持,解决处理诡机 |
总结
-
-
SSE 适合于不高频、安全性优先的场景,如通知信息。它具有以下优点:
-
单向通信的效率:服务器可以在需要时直接推送更新,无需客户端不断轮询,减少资源消耗。
-
基于 HTTP/1.1 的简单性:由于 SSE 使用标准 HTTP 请求和响应机制,无需额外的协议支持。
-
与现有 HTTP 基础设施的兼容性:例如,代理服务器、负载均衡器等无需特殊配置即可支持 SSE。
-
WebSocket 是一种全双工通信协议,基于 TCP 连接。它允许客户端和服务器之间实时双向通信,特别适用于高频、低延迟的应用场景,如在线游戏、实时协作编辑、股票交易和聊天应用。
WebSocket 的特点包括:
-
支持子协议:例如用于消息格式的 STOMP 和用于加密传输的 WAMP。
-
自定义消息格式的能力:可以选择 JSON、Protobuf 或二进制数据来优化通信效率。
-
实时交互场景的处理:WebSocket 的低延迟特性使其能够快速响应用户的实时交互需求。
-
高效的资源利用:相比于轮询或长轮询,WebSocket 使用单一持久连接,减少了频繁的 HTTP 开销。
此外,WebSocket 在需要多客户端实时同步状态的场景中表现优异,如协作工具(文档编辑、白板)和物联网设备管理。
-




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号