文心一言 VS 讯飞星火 VS chatgpt (154)-- 算法导论12.3 1题
一、用go语言,给出 TREE-INSERT 过程的一个递归版本。
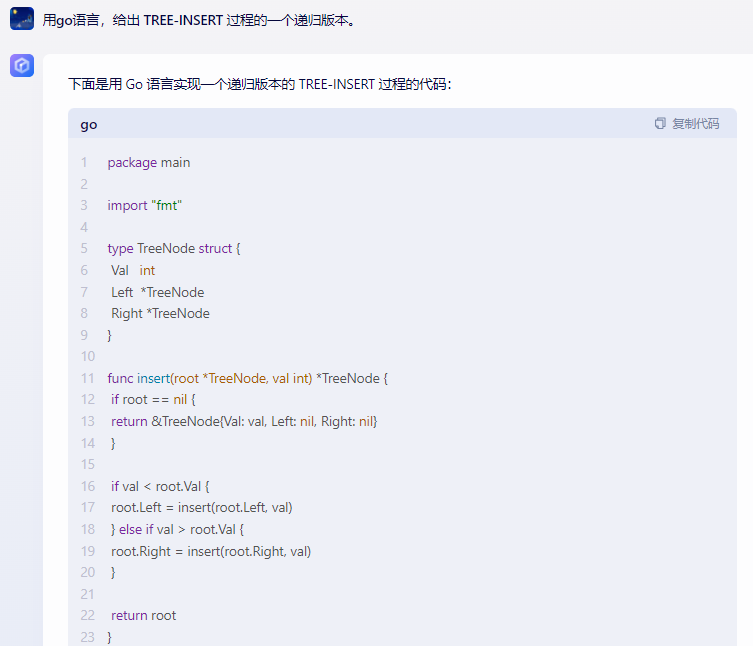
文心一言,代码不能运行:
下面是用 Go 语言实现一个递归版本的 TREE-INSERT 过程的代码:
package main
import "fmt"
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func insert(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return &TreeNode{Val: val, Left: nil, Right: nil}
}
if val < root.Val {
root.Left = insert(root.Left, val)
} else if val > root.Val {
root.Right = insert(root.Right, val)
}
return root
}
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) {
if root != nil {
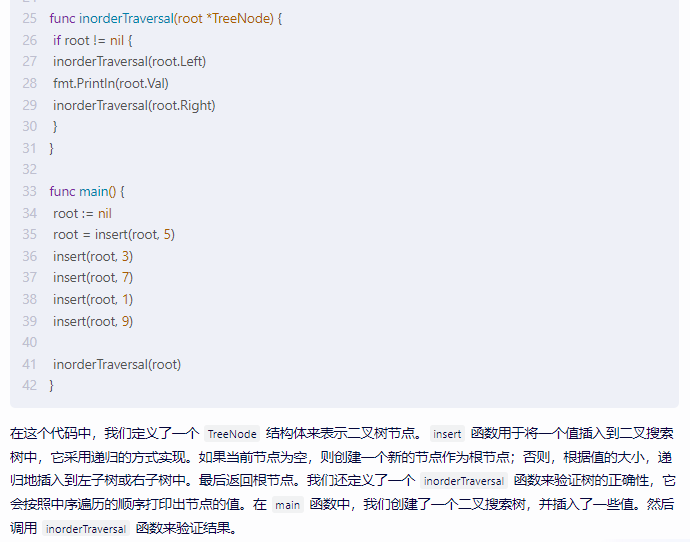
inorderTraversal(root.Left)
fmt.Println(root.Val)
inorderTraversal(root.Right)
}
}
func main() {
root := nil
root = insert(root, 5)
insert(root, 3)
insert(root, 7)
insert(root, 1)
insert(root, 9)
inorderTraversal(root)
}
在这个代码中,我们定义了一个 TreeNode 结构体来表示二叉树节点。insert 函数用于将一个值插入到二叉搜索树中,它采用递归的方式实现。如果当前节点为空,则创建一个新的节点作为根节点;否则,根据值的大小,递归地插入到左子树或右子树中。最后返回根节点。我们还定义了一个 inorderTraversal 函数来验证树的正确性,它会按照中序遍历的顺序打印出节点的值。在 main 函数中,我们创建了一个二叉搜索树,并插入了一些值。然后调用 inorderTraversal 函数来验证结果。
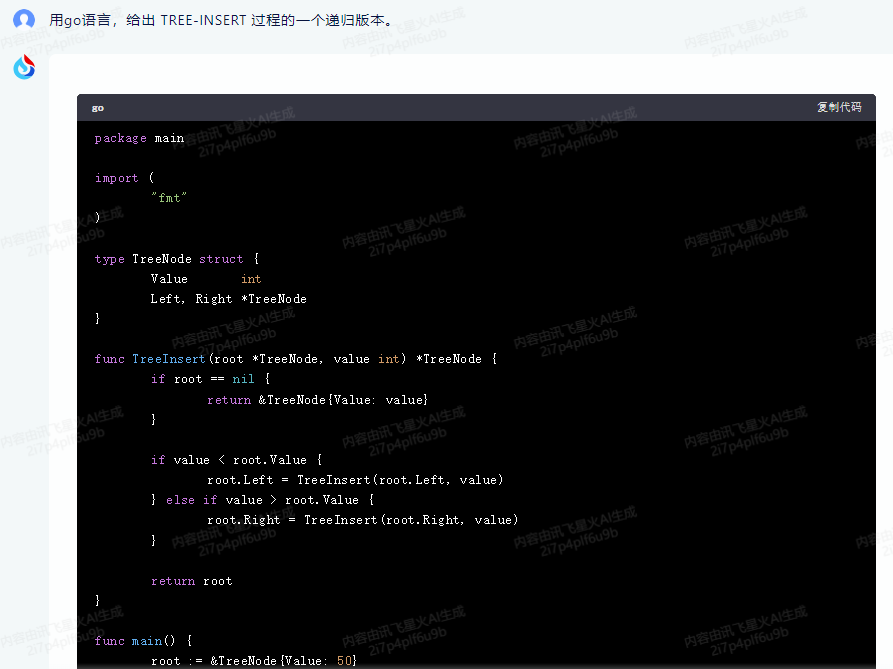
讯飞星火,代码正常运行:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type TreeNode struct {
Value int
Left, Right *TreeNode
}
func TreeInsert(root *TreeNode, value int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return &TreeNode{Value: value}
}
if value < root.Value {
root.Left = TreeInsert(root.Left, value)
} else if value > root.Value {
root.Right = TreeInsert(root.Right, value)
}
return root
}
func main() {
root := &TreeNode{Value: 50}
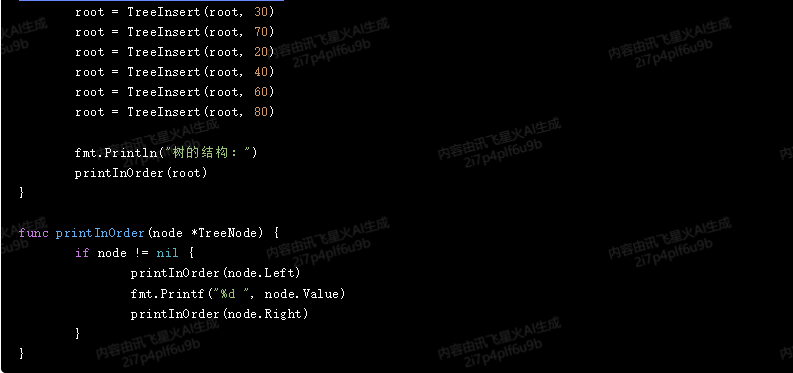
root = TreeInsert(root, 30)
root = TreeInsert(root, 70)
root = TreeInsert(root, 20)
root = TreeInsert(root, 40)
root = TreeInsert(root, 60)
root = TreeInsert(root, 80)
fmt.Println("树的结构:")
printInOrder(root)
}
func printInOrder(node *TreeNode) {
if node != nil {
printInOrder(node.Left)
fmt.Printf("%d ", node.Value)
printInOrder(node.Right)
}
}
360智脑:
以下是一个递归版本的 TREE-INSERT 过程:
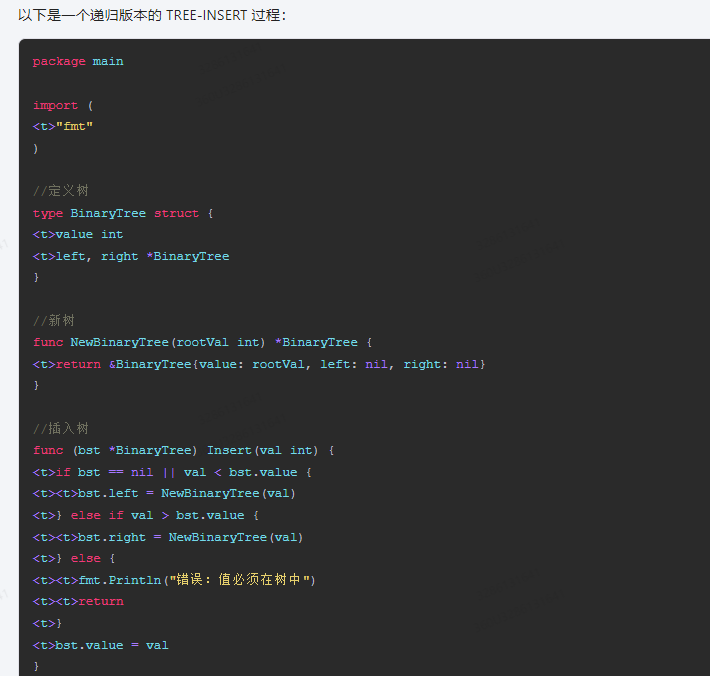
package main
import (
<t>"fmt"
)
//定义树
type BinaryTree struct {
<t>value int
<t>left, right *BinaryTree
}
//新树
func NewBinaryTree(rootVal int) *BinaryTree {
<t>return &BinaryTree{value: rootVal, left: nil, right: nil}
}
//插入树
func (bst *BinaryTree) Insert(val int) {
<t>if bst == nil || val < bst.value {
<t><t>bst.left = NewBinaryTree(val)
<t>} else if val > bst.value {
<t><t>bst.right = NewBinaryTree(val)
<t>} else {
<t><t>fmt.Println("错误:值必须在树中")
<t><t>return
<t>}
<t>bst.value = val
}
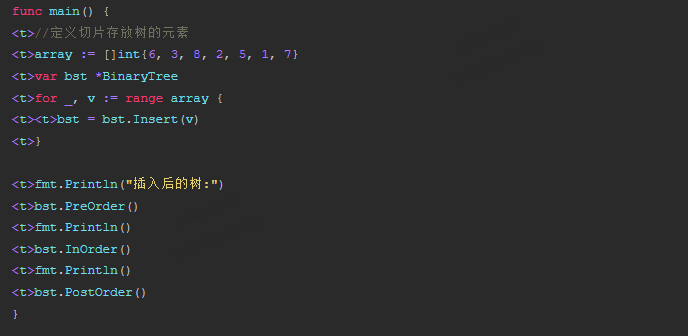
func main() {
<t>//定义切片存放树的元素
<t>array := []int{6, 3, 8, 2, 5, 1, 7}
<t>var bst *BinaryTree
<t>for _, v := range array {
<t><t>bst = bst.Insert(v)
<t>}
<t>fmt.Println("插入后的树:")
<t>bst.PreOrder()
<t>fmt.Println()
<t>bst.InOrder()
<t>fmt.Println()
<t>bst.PostOrder()
}
智谱清言,代码不能运行:
在计算机科学中,二叉搜索树(BST)是一种特殊的二叉树,它具有以下性质:
-
每个节点都有一个作为关键字的值,该值唯一存在于树中。
-
左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值。
-
右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值。
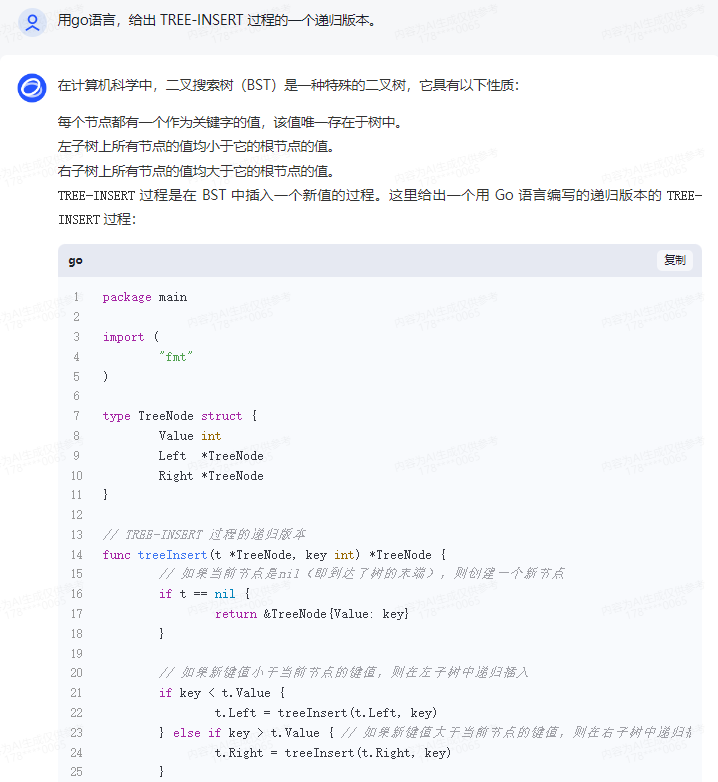
TREE-INSERT 过程是在 BST 中插入一个新值的过程。这里给出一个用 Go 语言编写的递归版本的 TREE-INSERT 过程:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type TreeNode struct {
Value int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
// TREE-INSERT 过程的递归版本
func treeInsert(t *TreeNode, key int) *TreeNode {
// 如果当前节点是nil(即到达了树的末端),则创建一个新节点
if t == nil {
return &TreeNode{Value: key}
}
// 如果新键值小于当前节点的键值,则在左子树中递归插入
if key < t.Value {
t.Left = treeInsert(t.Left, key)
} else if key > t.Value { // 如果新键值大于当前节点的键值,则在右子树中递归插入
t.Right = treeInsert(t.Right, key)
}
// 返回当前节点(可能已经更新)
return t
}
func main() {
// 创建一个空的二叉搜索树
root := nil
// 向树中插入一些键值
root = treeInsert(root, 5)
root = treeInsert(root, 3)
root = treeInsert(root, 8)
root = treeInsert(root, 1)
root = treeInsert(root, 4)
root = treeInsert(root, 6)
root = treeInsert(root, 9)
root = treeInsert(root, 2)
root = treeInsert(root, 7)
// 以 inorder 遍历的方式打印树,验证是否正确插入
var inorder func(t *TreeNode)
inorder = func(t *TreeNode) {
if t == nil {
return
}
inorder(t.Left)
fmt.Println(t.Value)
inorder(t.Right)
}
// 开始 inorder 遍历
inorder(root)
}
在这个代码中,treeInsert 函数以递归方式向 BST 中插入一个新值。如果当前节点是 nil,它将返回一个新节点。如果新值小于当前节点的值,它将在左子树中递归插入,如果新值大于当前节点的值,它将在右子树中递归插入。main 函数中展示了如何使用 treeInsert 函数,并通过 inorder 遍历打印出树的键值,以验证插入是否正确。

通义千问,代码正常运行:
在 Go 语言中,你可以使用递归来实现 TREE-INSERT 过程。这里是一个简单的示例,假设你有一个名为 Tree 的结构体表示二叉搜索树(BST)的节点,并且该结构体包含一个指向左子节点和右子节点的指针以及一个值。
package main
import "fmt"
type Tree struct {
value int
left *Tree
right *Tree
}
// Recursive TREE_INSERT function
func treeInsert(root **Tree, z *Tree) {
if *root == nil {
*root = z
return
}
// Compare the new node's value with the current root's value
if (*root).value > z.value {
// If the new node's value is smaller, insert into the left subtree
treeInsert(&(*root).left, z)
} else {
// If the new node's value is larger or equal, insert into the right subtree
treeInsert(&(*root).right, z)
}
}
func main() {
var root *Tree
z := &Tree{value: 10}
treeInsert(&root, z)
y := &Tree{value: 5}
treeInsert(&root, y)
x := &Tree{value: 15}
treeInsert(&root, x)
fmt.Println("In-order traversal:")
inorderTraversal(root)
}
// Helper function to print in-order traversal of a binary search tree
func inorderTraversal(t *Tree) {
if t != nil {
inorderTraversal(t.left)
fmt.Printf("%d ", t.value)
inorderTraversal(t.right)
}
}
在这个例子中,我们首先定义了一个 Tree 结构体来表示二叉搜索树的节点。接下来,我们实现了 treeInsert 函数,它接受一个指向树根的指针和一个新的节点 z。函数通过比较新节点的值与当前根节点的值来决定将新节点插入到左子树还是右子树。如果当前根为空,那么新节点就成为新的根节点。
在 main 函数中,我们创建了一个空的根节点,并使用 treeInsert 函数插入了几个新节点。最后,我们调用了一个辅助函数 inorderTraversal 来打印出二叉搜索树的中序遍历结果。
请注意,这个示例仅用于演示如何使用递归实现 TREE-INSERT 过程。在实际应用中,你需要根据你的具体需求对代码进行调整。


天工:
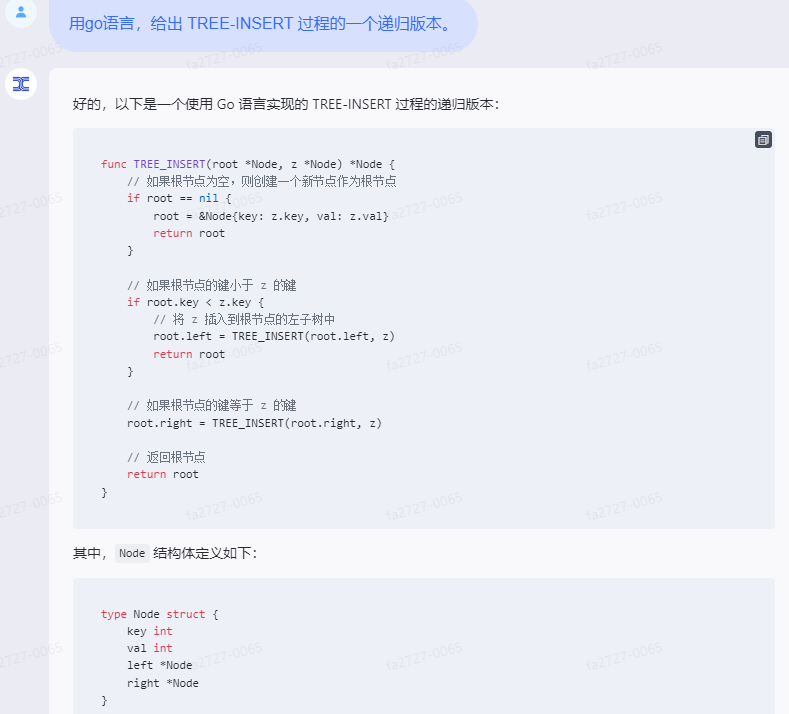
好的,以下是一个使用 Go 语言实现的 TREE-INSERT 过程的递归版本:
func TREE_INSERT(root *Node, z *Node) *Node {
// 如果根节点为空,则创建一个新节点作为根节点
if root == nil {
root = &Node{key: z.key, val: z.val}
return root
}
// 如果根节点的键小于 z 的键
if root.key < z.key {
// 将 z 插入到根节点的左子树中
root.left = TREE_INSERT(root.left, z)
return root
}
// 如果根节点的键等于 z 的键
root.right = TREE_INSERT(root.right, z)
// 返回根节点
return root
}
其中,Node 结构体定义如下:
type Node struct {
key int
val int
left *Node
right *Node
}
该递归版本的实现思路与参考信息中的伪代码基本一致。当递归到叶子节点时,返回的根节点即为最后一个插入的元素。
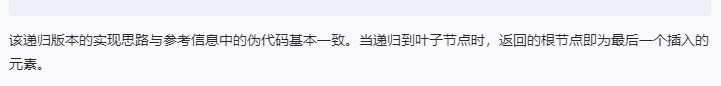
灵小智,代码正常运行:
以下是一个用Go语言编写的递归版本的TREE-INSERT过程示例:
package main
import "fmt"
type Node struct {
key int
left *Node
right *Node
}
func insert(root *Node, key int) *Node {
if root == nil {
root = &Node{key: key, left: nil, right: nil}
return root
}
if key < root.key {
root.left = insert(root.left, key)
} else if key > root.key {
root.right = insert(root.right, key)
}
return root
}
func inorder(root *Node) {
if root != nil {
inorder(root.left)
fmt.Printf("%d ", root.key)
inorder(root.right)
}
}
func main() {
var root *Node
keys := []int{15, 10, 20, 8, 12, 18, 25}
for _, key := range keys {
root = insert(root, key)
}
fmt.Println("Inorder traversal of the binary search tree:")
inorder(root)
}
以上代码定义了一个名为Node的结构体,表示二叉搜索树中的节点。insert函数是一个递归函数,用于插入一个新的键值到二叉搜索树中。inorder函数用于按照中序遍历的顺序输出二叉搜索树中的节点。
在main函数中,我们创建一个空的二叉搜索树,并依次插入一些键值。最后,调用inorder函数打印二叉搜索树的中序遍历结果。
请注意,这只是一个示例,并没有涉及错误处理和其他边界情况的处理。实际使用时,您可能需要进行适当的错误处理和鲁棒性改进。
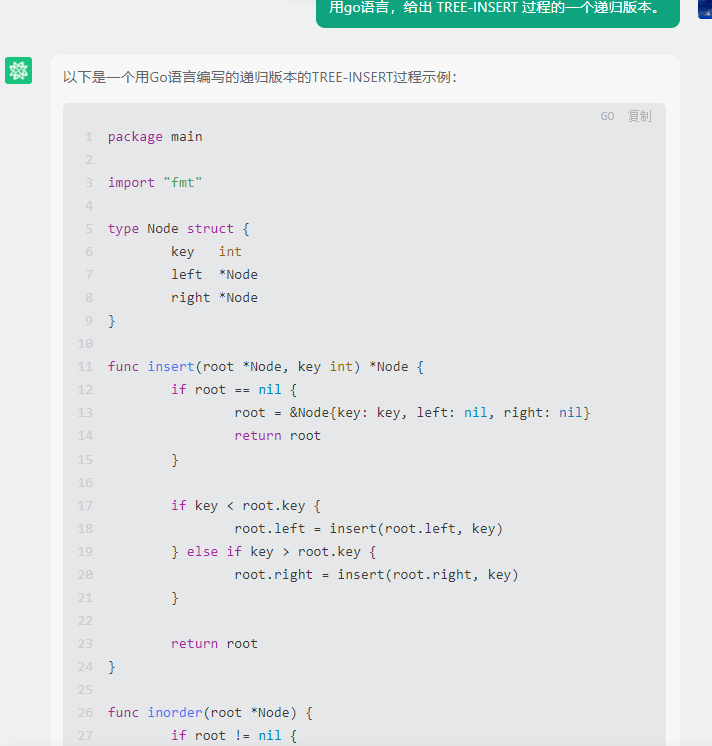

chatgpt:
以下是一个使用递归实现的TREE-INSERT过程的示例代码(假设节点数据类型为整数):
type Node struct {
key int
left *Node
right *Node
}
func insert(root *Node, key int) *Node {
if root == nil {
return &Node{key: key}
}
if key < root.key {
root.left = insert(root.left, key)
} else if key > root.key {
root.right = insert(root.right, key)
}
return root
}
你可以将上述代码中的insert函数作为TREE-INSERT过程的递归版本。它会接收一个二叉搜索树的根节点和要插入的关键字作为参数,然后在树中递归地插入新节点,最终返回更新后的根节点。
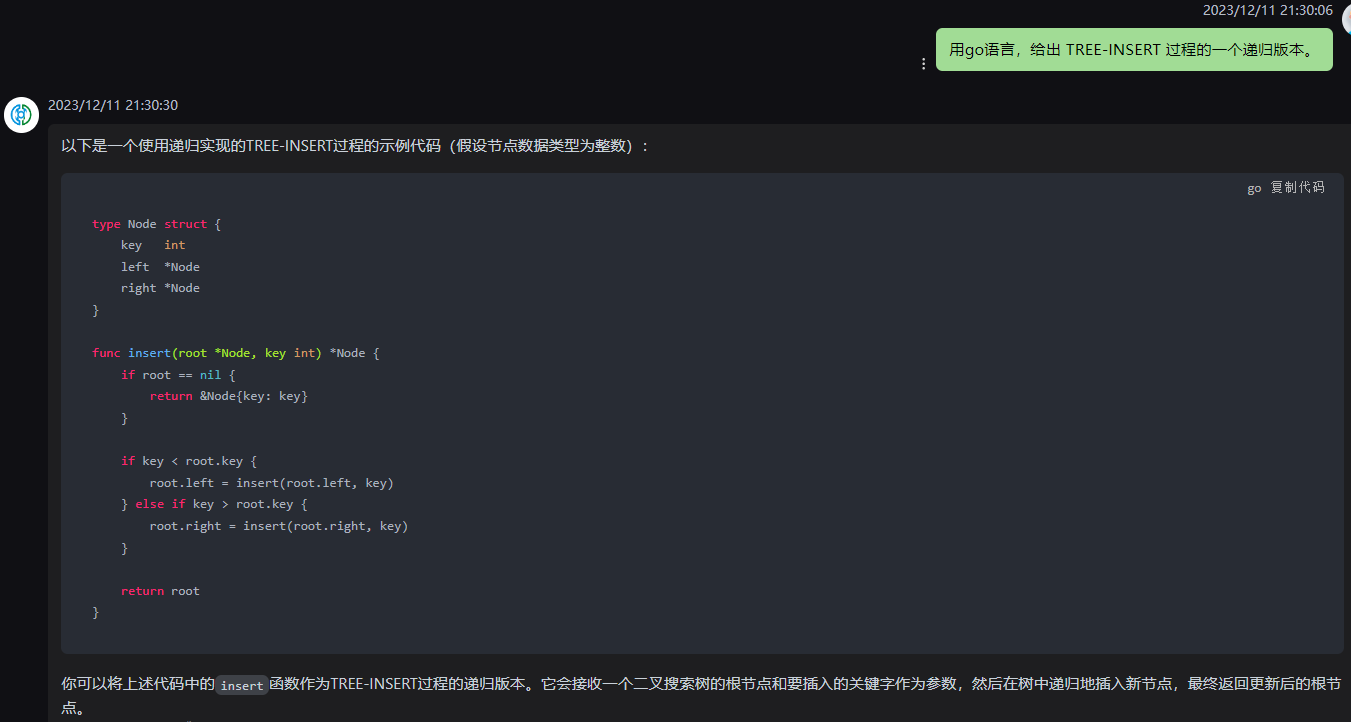
kimi,抛panic:
在 Go 语言中,我们可以实现一个递归版本的 TREE-INSERT 过程。以下是一个简单的实现:
package main
type Node struct {
key interface{} // 可以是任何可比较的数据类型,如 int、string 等
left *Node
right *Node
}
func (n *Node) TreeInsert(key interface{}) *Node {
if n == nil {
return &Node{key: key}
}
if key.(int) < n.key.(int) {
n.left = n.left.TreeInsert(key)
} else {
n.right = n.right.TreeInsert(key)
}
return n
}
func main() {
root := &Node{}
keys := []int{8, 3, 10, 1, 6, 14, 4, 7, 13}
for _, key := range keys {
root = root.TreeInsert(key)
}
// 中序遍历(左子树 -> 当前节点 -> 右子树),输出二叉搜索树的元素
inOrderTraversal(root)
}
func inOrderTraversal(n *Node) {
if n != nil {
inOrderTraversal(n.left)
fmt.Println(n.key)
inOrderTraversal(n.right)
}
}
在这个实现中,我们首先定义了一个 Node 结构体,表示二叉搜索树的节点。TreeInsert 方法是一个递归方法,它接受一个关键字作为参数。当树为空时,我们创建一个新的节点。然后,我们根据给定的关键字与当前节点的关键字的大小关系,将其插入到左子树或右子树中。
在 main 函数中,我们创建了一个空的根节点,并插入了一些整数。然后,我们使用 inOrderTraversal 函数按顺序遍历二叉搜索树并输出其元素。这个函数也是一个递归函数,它按照左子树 -> 当前节点 -> 右子树的顺序遍历树的节点。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号