2023-10-14:用go语言,给定 pushed 和 popped 两个序列,每个序列中的 值都不重复, 只有当它们可能是在最初空栈上进行的推入 push 和弹出 pop 操作序列的结果时, 返回
2023-10-14:用go语言,给定 pushed 和 popped 两个序列,每个序列中的 值都不重复,
只有当它们可能是在最初空栈上进行的推入 push 和弹出 pop 操作序列的结果时,
返回 true;否则,返回 false 。
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,5,3,2,1]。
输出:true。
来自美团。
来自左程云。
答案2023-10-14:
大体过程如下:
1.初始化一个栈stack和索引指针i、j,分别指向pushed和popped的起始位置。
2.遍历pushed数组,将当前元素pushed[i]入栈,同时i自增1。
3.在入栈后,检查栈顶元素是否与popped[j]相等。若相等,则表示栈顶元素需要出栈,因此将栈顶元素出栈,同时j自增1。
4.重复步骤2和步骤3,直到遍历完pushed数组。
5.最后,判断栈是否为空。若栈为空,则返回true;否则,返回false。
时间复杂度分析:遍历pushed数组的时间复杂度为O(n),其中n为数组的长度。在每次遍历中,判断栈顶元素是否需要出栈的时间复杂度为O(1)。因此,总的时间复杂度为O(n)。
空间复杂度分析:仅使用了常数级别的额外空间,因此额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
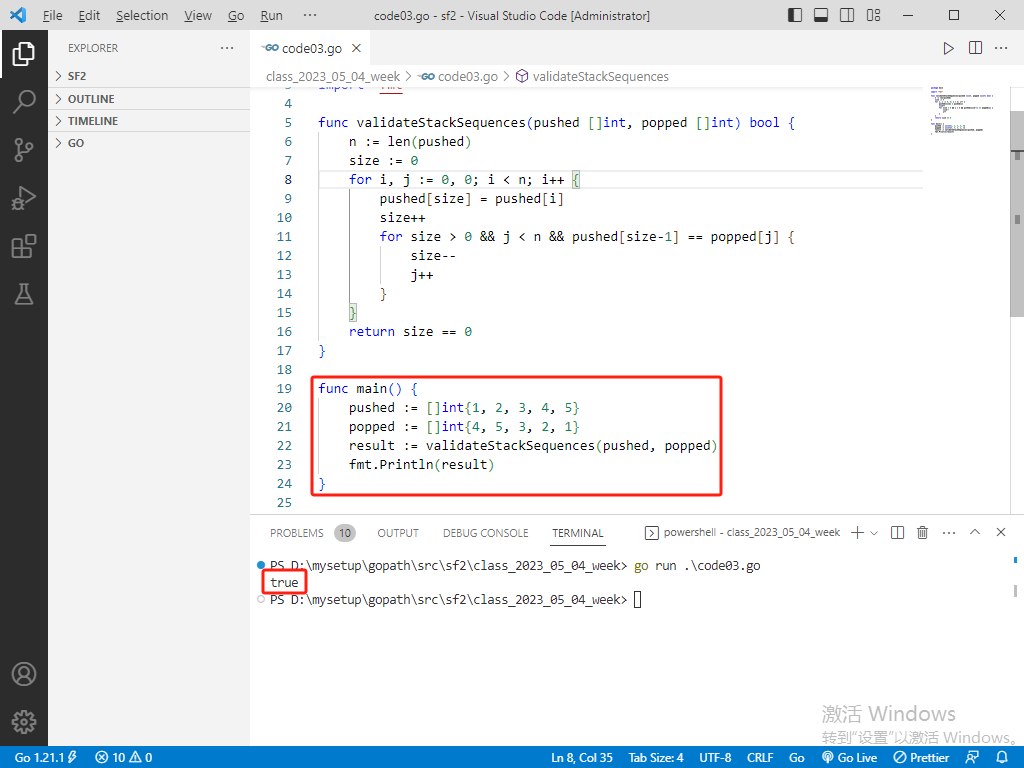
go完整代码如下:
package main
import "fmt"
func validateStackSequences(pushed []int, popped []int) bool {
n := len(pushed)
size := 0
for i, j := 0, 0; i < n; i++ {
pushed[size] = pushed[i]
size++
for size > 0 && j < n && pushed[size-1] == popped[j] {
size--
j++
}
}
return size == 0
}
func main() {
pushed := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
popped := []int{4, 5, 3, 2, 1}
result := validateStackSequences(pushed, popped)
fmt.Println(result)
}
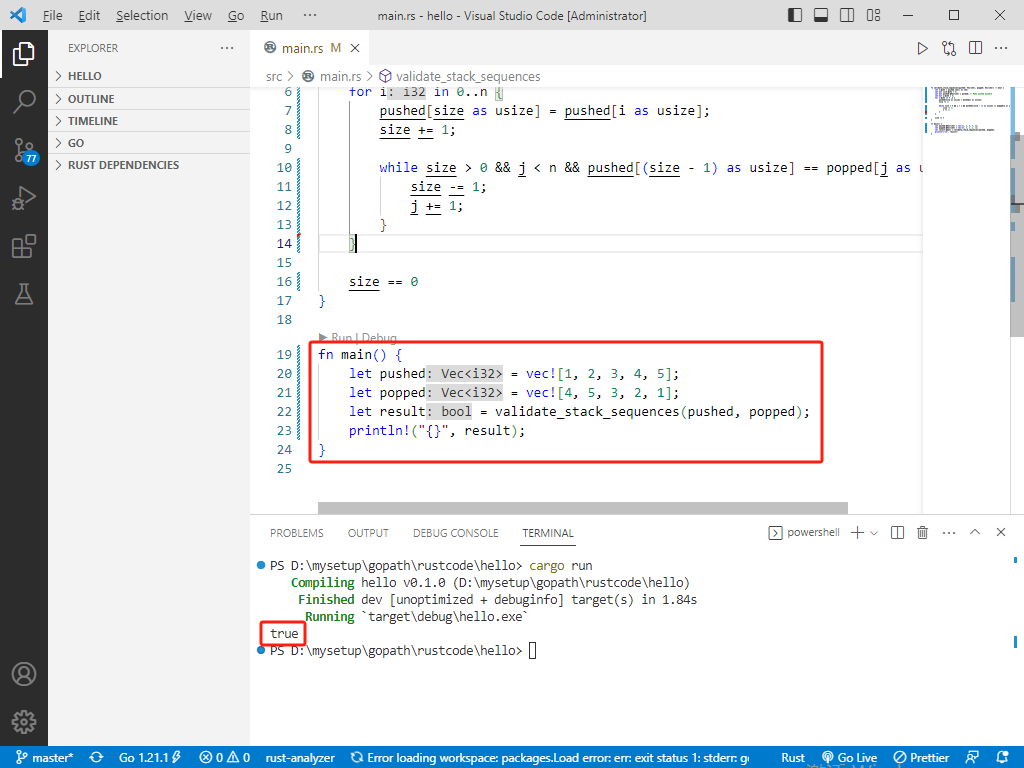
rust完整代码如下:
fn validate_stack_sequences(pushed: Vec<i32>, popped: Vec<i32>) -> bool {
let n = pushed.len() as i32;
let mut size = 0;
let mut pushed = pushed; // Make pushed mutable
let mut j = 0;
for i in 0..n {
pushed[size as usize] = pushed[i as usize];
size += 1;
while size > 0 && j < n && pushed[(size - 1) as usize] == popped[j as usize] {
size -= 1;
j += 1;
}
}
size == 0
}
fn main() {
let pushed = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let popped = vec![4, 5, 3, 2, 1];
let result = validate_stack_sequences(pushed, popped);
println!("{}", result);
}
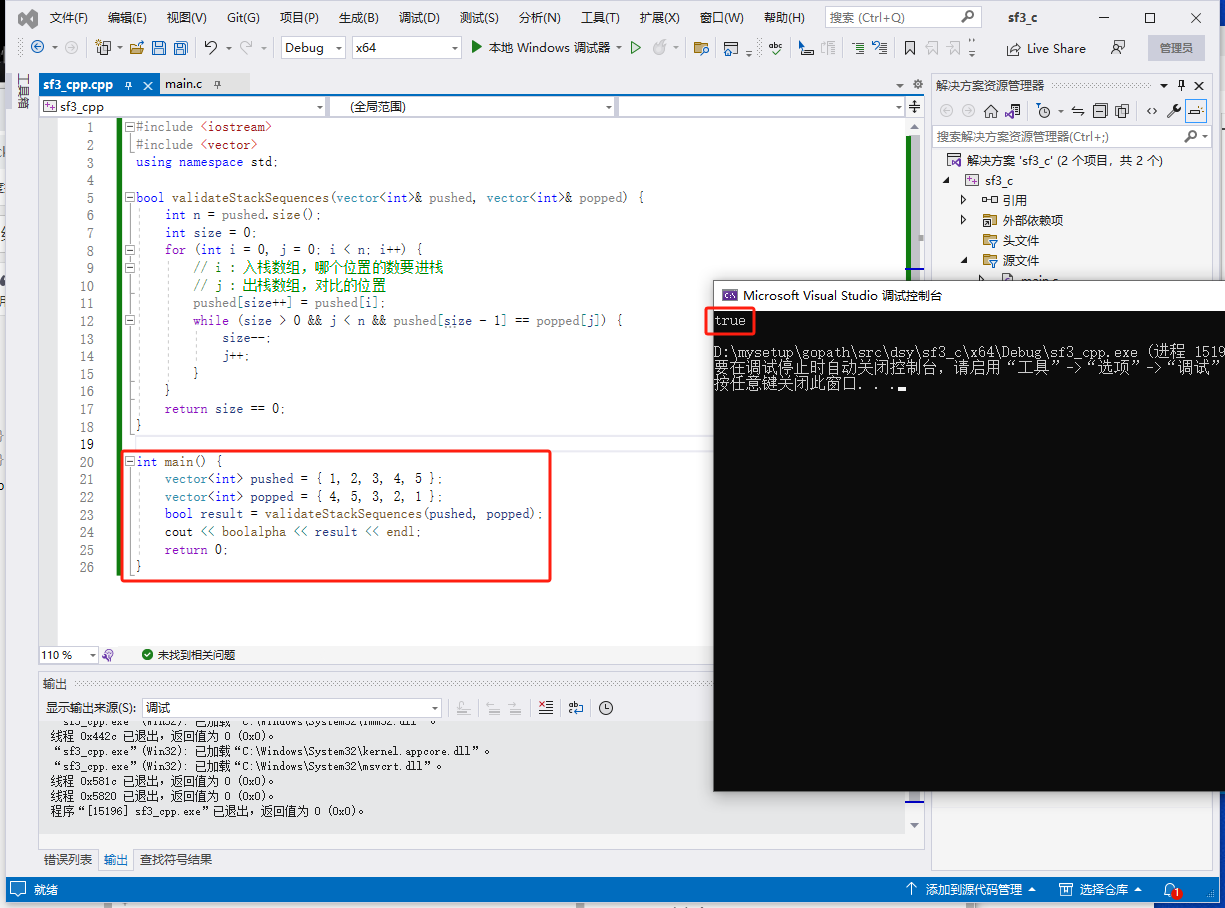
c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
int n = pushed.size();
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {
// i : 入栈数组,哪个位置的数要进栈
// j : 出栈数组,对比的位置
pushed[size++] = pushed[i];
while (size > 0 && j < n && pushed[size - 1] == popped[j]) {
size--;
j++;
}
}
return size == 0;
}
int main() {
vector<int> pushed = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int> popped = { 4, 5, 3, 2, 1 };
bool result = validateStackSequences(pushed, popped);
cout << boolalpha << result << endl;
return 0;
}
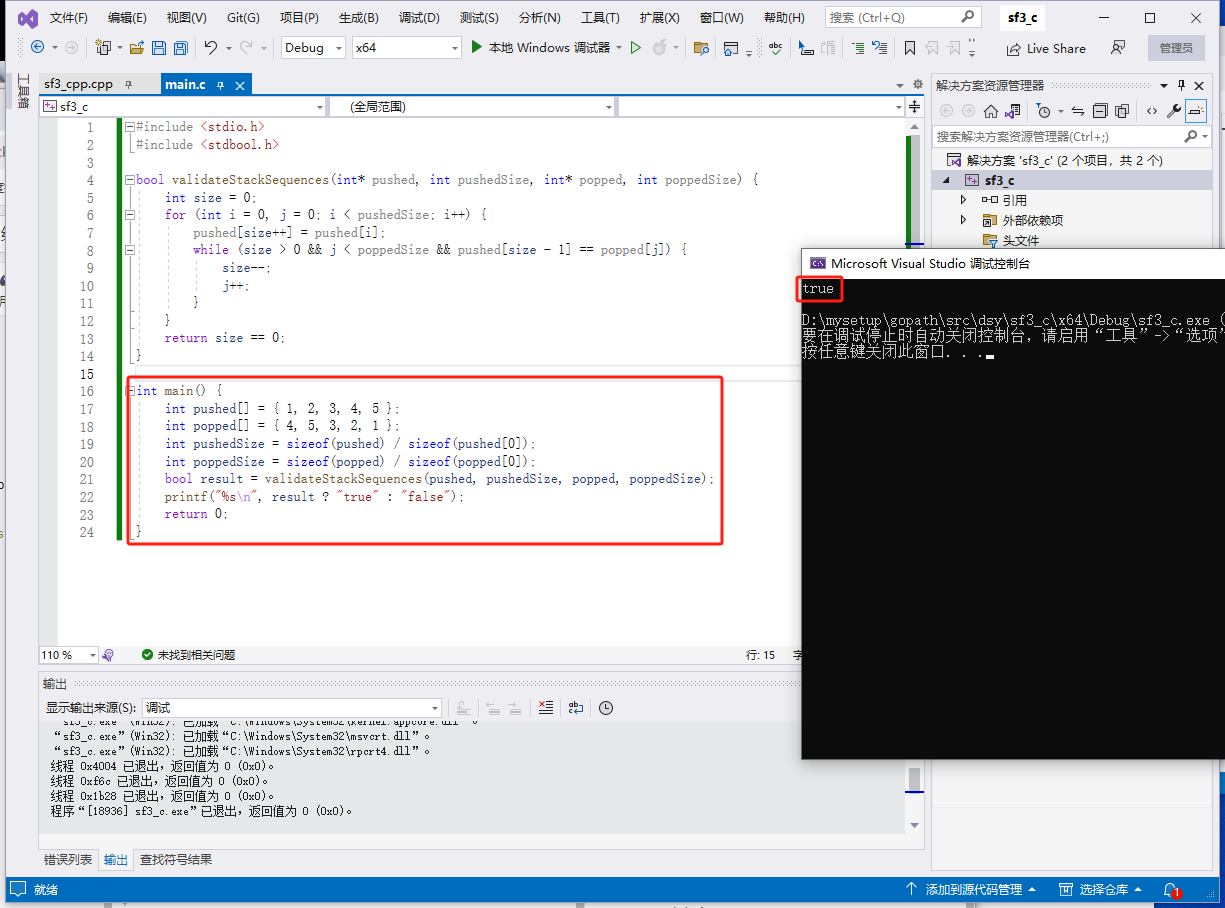
c完整代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
bool validateStackSequences(int* pushed, int pushedSize, int* popped, int poppedSize) {
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < pushedSize; i++) {
pushed[size++] = pushed[i];
while (size > 0 && j < poppedSize && pushed[size - 1] == popped[j]) {
size--;
j++;
}
}
return size == 0;
}
int main() {
int pushed[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int popped[] = { 4, 5, 3, 2, 1 };
int pushedSize = sizeof(pushed) / sizeof(pushed[0]);
int poppedSize = sizeof(popped) / sizeof(popped[0]);
bool result = validateStackSequences(pushed, pushedSize, popped, poppedSize);
printf("%s\n", result ? "true" : "false");
return 0;
}
公众号:福大大架构师每日一题



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号