2020-07-28:已知sqrt (2)约等于 1.414,要求不用数学库,求sqrt (2)精确到小数点后 10 位。
福哥答案2020-07-28:
1.二分法。
2.手算法。
3.牛顿迭代法。基础是泰勒级数展开法。
4.泰勒级数法。
5.平方根倒数速算法,卡马克反转。基础是牛顿迭代法。
golang代码如下:
package test28_sqrt
import (
"fmt"
"math"
"strconv"
"testing"
)
const (
EPSINON = 0.0000000001
)
//go test -v -test.run TestSqrt
func TestSqrt(t *testing.T) {
f := 2.0
fmt.Printf("%v 系统自带\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(math.Sqrt(f), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Println("--------------------------------------------")
fmt.Printf("%v 二分法结果\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(sqrtDichotomy(f), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Printf("%v 手算法\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(sqrtHand(f), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Printf("%v 牛顿迭代法结果\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(sqrtNewton(f), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Printf("%v 泰勒级数法结果\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(sqrtTaylor(f), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Printf("%v 64位平方根倒数速算法结果1,精度上不符合\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(sqrtRootFloat64(f), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Printf("%v 64位平方根倒数速算法结果2,精度上不符合\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(float64(InvSqrt64(f)), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Println("--------------------------------------------")
f2 := float32(f)
fmt.Printf("%v 32位平方根倒数速算法结果1,精度上不符合\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(float64(sqrtRootFloat32(f2)), 'f', -1, 64))
fmt.Printf("%v 32位平方根倒数速算法结果2,精度上不符合\r\n", strconv.FormatFloat(float64(InvSqrt32(f2)), 'f', -1, 64))
}
//二分法
func sqrtDichotomy(f float64) float64 {
left := 0.0
right := f
if f < 1 {
right = 1
}
mid := f / 2 //不写0.0的原因是for循环可能进不了,0值明显不对
mid_mid := 0.0 //mid*mid的值
for right-left > EPSINON {
mid = (left + right) / 2.0
mid_mid = mid * mid
if mid_mid > f {
right = mid
} else if mid_mid < f {
left = mid
} else {
return mid
}
}
return mid
}
//牛顿迭代法.基础是泰勒级数展开法
func sqrtNewton(f float64) float64 {
z := 1.0
for math.Abs(z*z-f) > EPSINON {
z = (z + f/z) / 2
}
return z
}
//手算法
func sqrtHand(f float64) float64 {
i := int64(f)
ret := 0.0 //返回值
rettemp := 0.0 //大的返回值
retsinge := 0.5 //单个值
//获取左边第一个1,retsingle就是左边的第一个1的值
for i > 0 {
i >>= 2
retsinge *= 2
}
rettemp_rettemp := 0.0
for {
rettemp = ret + retsinge
rettemp_rettemp = rettemp * rettemp
if math.Abs(rettemp_rettemp-f) > EPSINON {
if rettemp_rettemp > f {
} else {
ret = rettemp
}
retsinge /= 2
} else {
return rettemp
}
}
}
//泰勒级数展开法
func sqrtTaylor(f float64) float64 {
correction := 1.0
for f >= 2.0 {
f /= 4
correction *= 2
}
return taylortemp(f) * correction
}
func taylortemp(x float64) float64 { //计算[0,2)范围内数的平方根
var sum, coffe, factorial, xpower, term float64
var i int
sum = 0
coffe = 1
factorial = 1
xpower = 1
term = 1
i = 0
for math.Abs(term) > EPSINON {
sum += term
coffe *= 0.5 - float64(i)
factorial *= float64(i) + 1
xpower *= x - 1
term = coffe * xpower / factorial
i++
}
return sum
}
//32位平方根倒数速算法1.卡马克反转。基础是牛顿迭代法。
func sqrtRootFloat32(number float32) float32 {
var i uint32
var x, y float32
f := float32(1.5)
x = float32(number * 0.5)
y = number
i = math.Float32bits(y) //内存不变,浮点型转换成整型
i = 0x5f3759df - (i >> 1) //0x5f3759df,注意这一行,另一个数字是0x5f375a86
y = math.Float32frombits(i) //内存不变,浮点型转换成整型
y = y * (f - (x * y * y))
y = y * (f - (x * y * y))
return number * y
}
//32位平方根倒数速算法2
func InvSqrt32(x1 float32) float32 {
x := x1
xhalf := float32(0.5) * x
i := math.Float32bits(xhalf) // get bits for floating VALUE
i = 0x5f375a86 - (i >> 1) // gives initial guess y0
x = math.Float32frombits(i) // convert bits BACK to float
x = x * (float32(1.5) - xhalf*x*x) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
x = x * (float32(1.5) - xhalf*x*x) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
x = x * (float32(1.5) - xhalf*x*x) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
return 1 / x
}
//64位平方根倒数速算法1.卡马克反转。基础是牛顿迭代法。
func sqrtRootFloat64(number float64) float64 {
var i uint64
var x, y float64
f := 1.5
x = number * 0.5
y = number
i = math.Float64bits(y) //内存不变,浮点型转换成整型
i = 0x5fe6ec85e7de30da - (i >> 1) //0x5f3759df,注意这一行,另一个数字是0x5f375a86
y = math.Float64frombits(i) //内存不变,浮点型转换成整型
y = y * (f - (x * y * y))
y = y * (f - (x * y * y))
return number * y
}
//64位平方根倒数速算法2
func InvSqrt64(x1 float64) float64 {
x := x1
xhalf := 0.5 * x
i := math.Float64bits(xhalf) // get bits for floating VALUE
i = 0x5fe6ec85e7de30da - (i >> 1) // gives initial guess y0
x = math.Float64frombits(i) // convert bits BACK to float
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
x = x * (1.5 - xhalf*x*x) // Newton step, repeating increases accuracy
return 1 / x
}
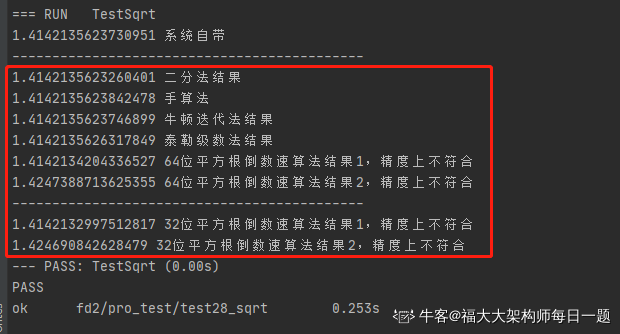
敲命令 go test -v -test.run TestSqrt后,结果如下:
公众号:福大大架构师每日一题



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号