编译原理 算法3.8 LR分析 c++11实现
LR分析简介
LR分析是应用最广泛的一类分析方法,它是实用的编译器功能中最强的分析器,其特点是:
1,采用最一般的无回溯移进-规约方法。
2,可分析的文法是LL文法的真超集。
3,能够及时发现错误,及时从左扫描输入序列的最大可能。
4,分析表较为复杂,难以手工构造。
实验内容
根据LR分析表action和goto实现LR分析。
实验步骤
输入 序列$\omega$和文法$G$的LR分析表action与goto。
输出 若$\omega \in L(G)$,得到$\omega$的规范规约,否则指出一个错误。
具体实现
见代码。

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <fstream> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <map> 5 #include <set> 6 #include <stack> 7 #include <vector> 8 using namespace std; 9 10 using Production = pair<string, vector<string>>; 11 12 const int max_state = 110; 13 const int delay_num = 5e8; 14 15 struct ParserLR 16 { 17 18 map<string, int> mp_n; //非终结符映射 19 map<string, int> mp_t; //终结符映射 20 vector<Production> P; //产生式 21 vector<string> N, T; //非终结符,终结符 22 int state_num, operator_num, nonterminal_num, terminal_num, production_num; 23 vector<string> action[max_state]; 24 vector<int> _goto[max_state]; 25 int init(string filename) 26 { 27 N.clear(); 28 T.clear(); 29 P.clear(); 30 mp_n.clear(); 31 mp_t.clear(); 32 for (int i = 0; i < max_state; i++) 33 { 34 action[i].clear(); 35 _goto[i].clear(); 36 } 37 state_num = operator_num = nonterminal_num = terminal_num = production_num = 0; 38 ifstream in(filename, ios::in); 39 if (!in.is_open()) 40 return 0; 41 in >> terminal_num; 42 for (int i = 0; i < terminal_num; i++) 43 { 44 string tmp; 45 in >> tmp; 46 T.emplace_back(tmp); 47 mp_t[tmp] = i; 48 } 49 in >> nonterminal_num; 50 for (int i = 0; i < nonterminal_num; i++) 51 { 52 string tmp; 53 in >> tmp; 54 N.emplace_back(tmp); 55 mp_n[tmp] = i; 56 } 57 in >> production_num; 58 for (int i = 0; i < production_num; i++) 59 { 60 Production cur; 61 in >> cur.first; 62 int sz; 63 in >> sz; 64 for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++) 65 { 66 string t; 67 in >> t; 68 cur.second.emplace_back(t); 69 } 70 P.emplace_back(cur); 71 } 72 in >> state_num; 73 for (int i = 0; i <= state_num; i++) 74 for (int j = 0; j < terminal_num; j++) 75 { 76 string tmp; 77 in >> tmp; 78 action[i].emplace_back(tmp); 79 } 80 for (int i = 0; i <= state_num; i++) 81 for (int j = 0; j < nonterminal_num; j++) 82 { 83 int tmp; 84 in >> tmp; 85 _goto[i].emplace_back(tmp); 86 } 87 return 1; 88 } 89 Production getProduction(int idx) 90 { 91 return P[idx - 1]; 92 } 93 pair<int, vector<Production>> analyze(vector<string> input) //first->出错位置,-1代表无错 94 { 95 vector<Production> error; 96 vector<Production> success; 97 stack<string> ch; //符号栈 98 stack<int> st; //状态栈 99 ch.emplace("#"); 100 st.emplace(0); 101 input.emplace_back("#"); 102 int sz = input.size(); 103 for (int i = 0; i < sz;) 104 { 105 string now = input[i]; 106 if (!mp_t.count(now)) 107 return make_pair(i, success); 108 int ip = mp_t[now]; 109 int top = st.top(); //栈顶状态 110 string at = action[top][ip]; 111 if (at[0] == 'r') //规约 112 { 113 string res = at.substr(1, at.size()); 114 int num = stoi(res); 115 Production trans = getProduction(num); 116 for (int i = 0; i < trans.second.size(); i++) 117 { 118 st.pop(); 119 ch.pop(); 120 } 121 top = st.top(); 122 string cur = trans.first; 123 ch.emplace(cur); 124 st.emplace(_goto[top][mp_n[cur]]); 125 success.emplace_back(trans); 126 } 127 else if (at[0] == 's') //移进 128 { 129 string res = at.substr(1, at.size()); 130 int to_state = stoi(res); 131 st.emplace(to_state); 132 ch.emplace(now); 133 i++; 134 } 135 else if (at == "acc") //接受 136 return make_pair(-1, success); 137 else //error 138 { 139 if (now == "#") 140 return make_pair(i - 1, success); 141 return make_pair(i, success); 142 } 143 } 144 return make_pair(1, error); 145 } 146 }; 147 inline void delay() 148 { 149 for (int i = 0; i < delay_num; i++) 150 ; 151 } 152 inline void display(const pair<int, vector<Production>> &out) 153 { 154 if (out.first == -1) 155 { 156 for (int i = 0; i < out.second.size(); i++) 157 { 158 cout << out.second[i].first << "->"; 159 for (int j = 0; j < out.second[i].second.size(); j++) 160 cout << out.second[i].second[j]; 161 cout << "\n"; 162 } 163 } 164 else 165 cout << "在第" << out.first + 1 << "个终结符出错.\n"; 166 } 167 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 168 { 169 ParserLR app; 170 string filename = "prj3_8_in.txt"; 171 if (app.init(filename)) 172 { 173 174 cout << "构建分析器中"; 175 delay(); 176 cout << "."; 177 delay(); 178 cout << "."; 179 delay(); 180 cout << ".\n"; 181 delay(); 182 cout << "构建成功.\n"; 183 cout << "请输入终结符个数:"; 184 int sz; 185 cin >> sz; 186 cout << "请输入包含" << sz << "个终结符的待分析序列, 终结符间需用空格分离:"; 187 vector<string> al; 188 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) 189 { 190 string tmp; 191 cin >> tmp; 192 al.emplace_back(tmp); 193 } 194 cout << "开始分析"; 195 delay(); 196 cout << "."; 197 delay(); 198 cout << "."; 199 delay(); 200 cout << ".\n"; 201 delay(); 202 cout << "分析结束.\n"; 203 pair<int, vector<Production>> out = app.analyze(al); 204 cout << "分析成功,结果如下:\n"; 205 display(out); 206 } 207 return 0; 208 }

4 id - * # 3 E T F 6 E 3 E - T E 1 T T 3 T * F T 1 F F 2 - F F 1 id 10 s4 s5 null null null s6 null acc null r2 s7 r2 null r4 r4 r4 null r6 r6 r6 s4 s5 null null s4 s5 null null s4 s5 null null null r5 r5 r5 null r1 s7 r1 null r3 r3 r3 1 2 3 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 8 -1 9 3 -1 -1 10 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
效果展示
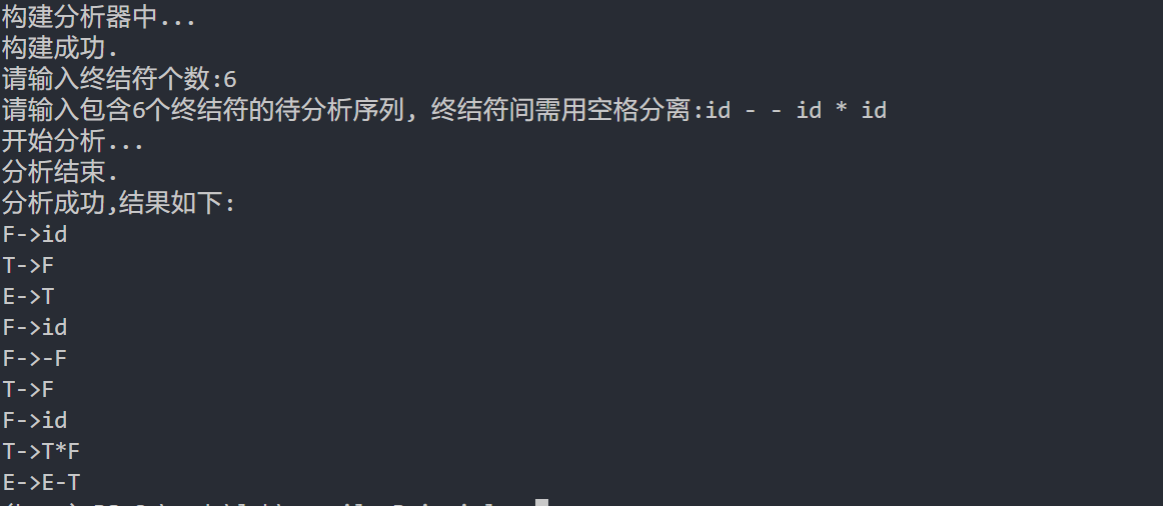
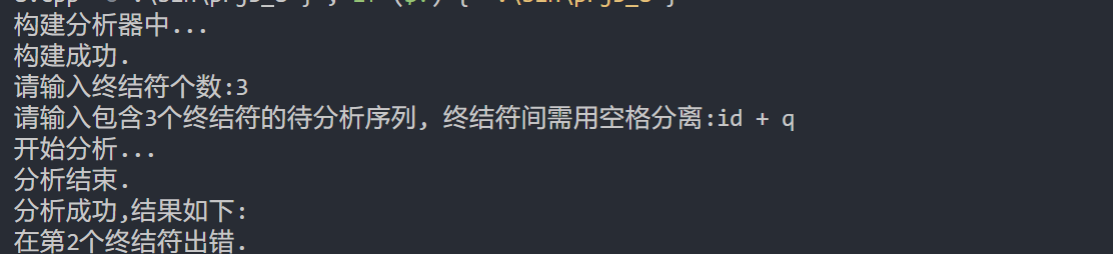
代码使用部分c++11特性,如有本地编译需要,请确认环境。
欢迎下方留言。




