Django基于正则表达式的URL(1)
1. 此时,用户只能看到列表,如果用户想查看详细信息,应该再增加程序。

2. 把信息用a标签包起来以后,详细信息就有了可以跳转的功能。
.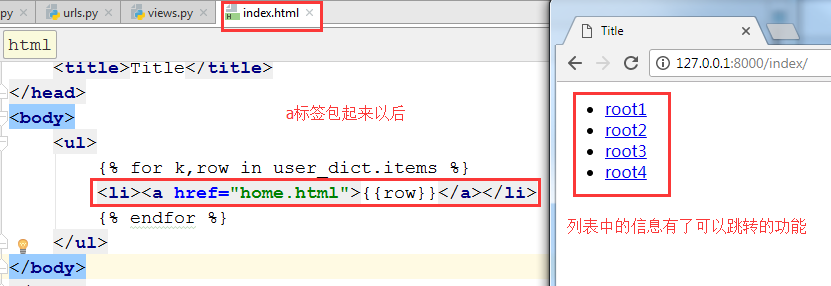
3. 点击不同的用户名时,获取到不同的信息。
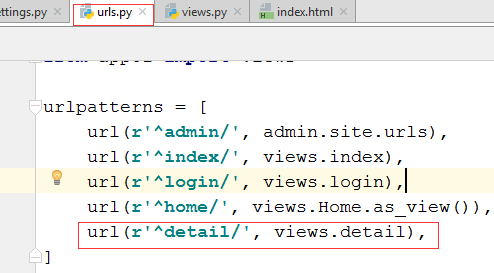
3.1 在urls.py中写对应关系
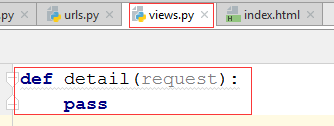
3.2 在views.py中写函数
3.3 在index.html中更新模板
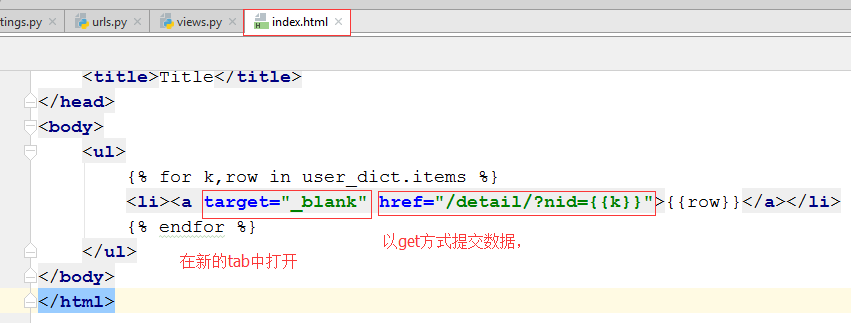
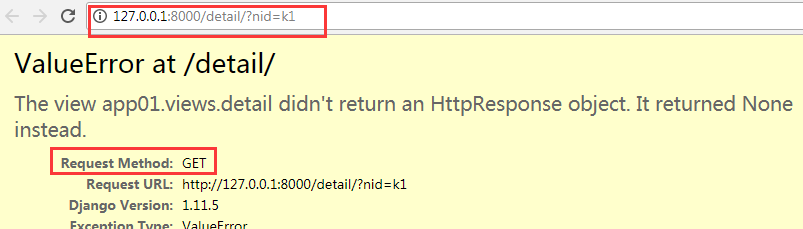
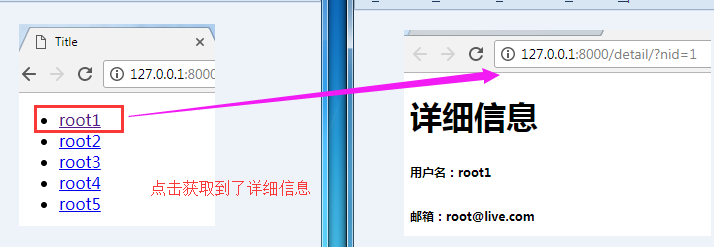
3.4 运行结果:获取到了nid
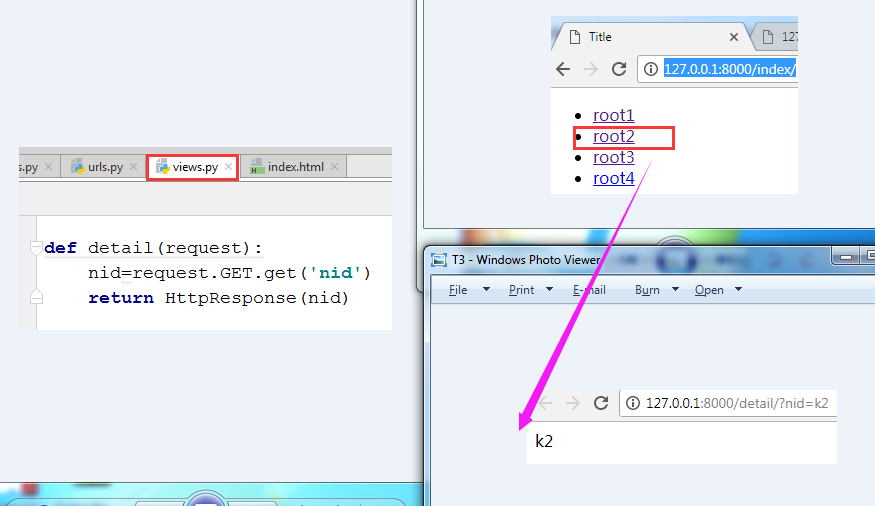
3.5 点击,获取到相应的信息。
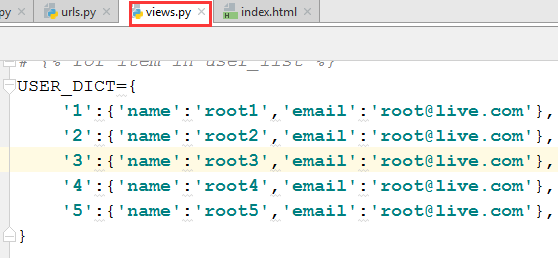
3.6 返回的信息太简单了,把views.py中的信息更新如下
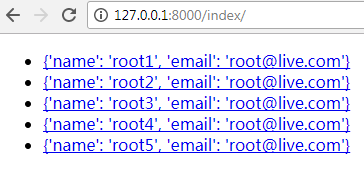
此时返回的信息如下:
3.7 更新程序
3.7.1 在urls.py中增加对应关系
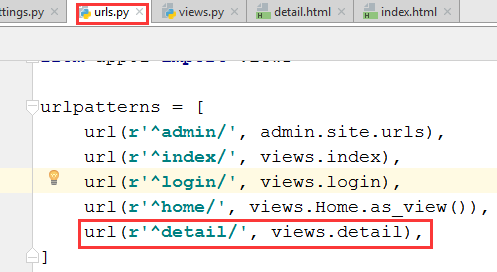
3.7.2 在views.py中更新函数

3.7.3 更新detail.html模板
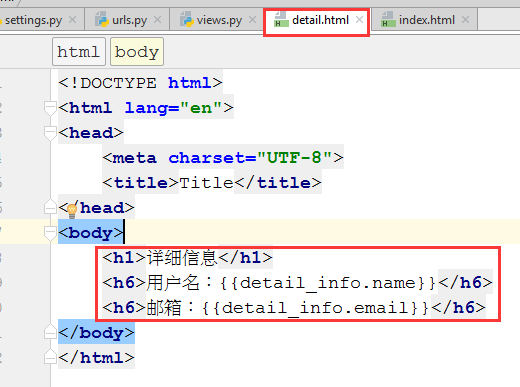
3.7.4 运行结果:
4.Django支持另外一种传参。
第1种方式:127.0.0.1:8000/detail/?nid=1,(一般用户认为这种是动态的,因为他们认为nid=XXX是可变的)
第2种方式:127.0.0.1:8000/detail-1.html,(认为这种是不变的。但其实这种的变化是在detail=XXXX处)
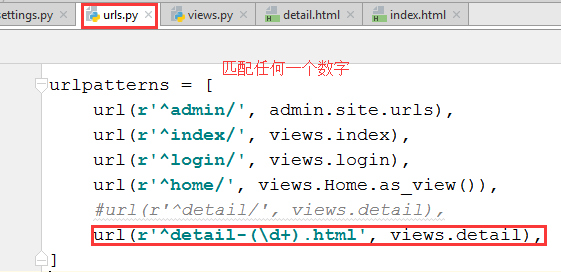
需要用到正则表达式。
4.1 在urls.py中修改对应关系
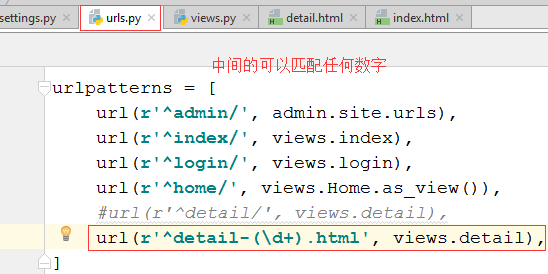
4.2 URL匹配上了,传了一个值过来。咱们的detail函数中得有个参数去获取一下。这样的话,我们就不需要通过request.get去取值了,Django已经从URL中帮我们提取出来了,
url(r'^detail-(\d+).html', views.detail),
detail(request,nid): 随便一个参数名字都可以,用于接收(\d+)
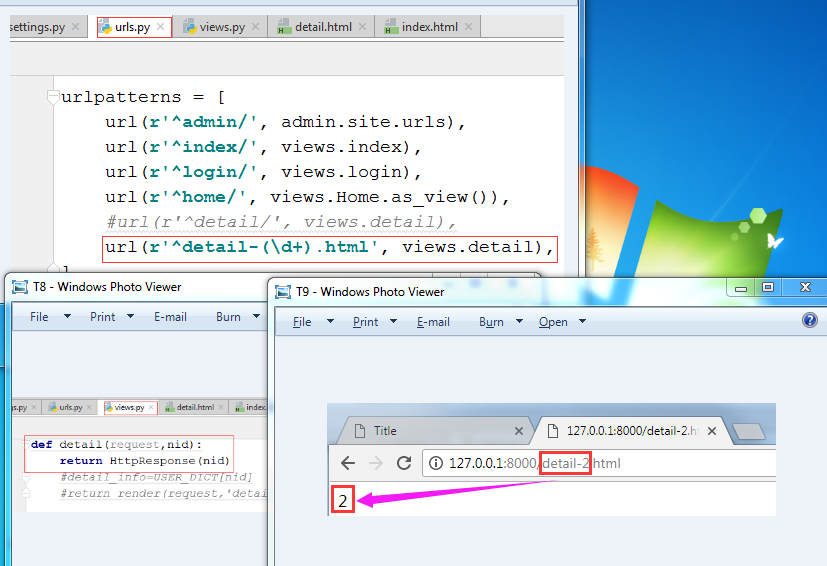
相当于写了一个动态路由关系。过程如下:
4.3 在urls.py中修改对应关系
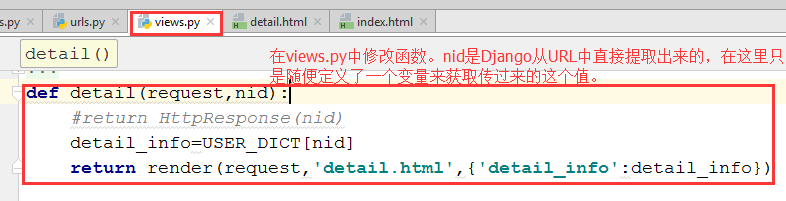
4.4 在views.py中修改函数
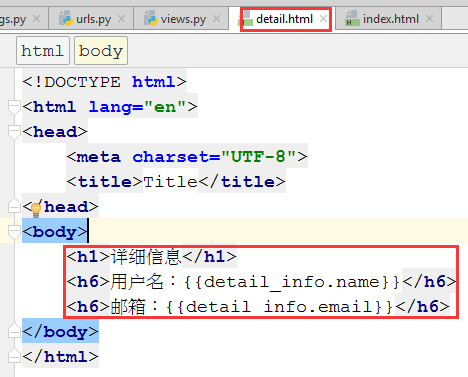
4.5 detail.html中程序如下
4.6修改index.html中的程序
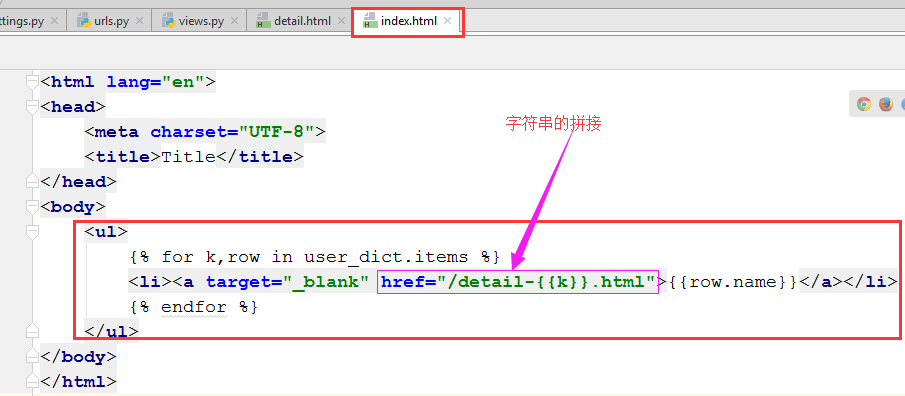
整个流程是:index里面有个a标签,里面的href指向了detail.html标签。detail的这个对应关系也应该写到urls.py中。
urls.py程序
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^index/', views.index),
url(r'^login/', views.login),
url(r'^home/', views.Home.as_view()),
#url(r'^detail/', views.detail),
url(r'^detail-(\d+).html', views.detail),
]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect
# Create your views here.
# USER_DICT={
# 'k1':'root1',
# 'k2':'root2',
# 'k3':'root3',
# 'k4':'root4',
# }
# USER_LIST=[
# {'name':'root'},
# {'name':'root'},
# {'name':'root'}
# ]
#
# {% for item in user_list %}
USER_DICT={
'1':{'name':'root1','email':'root@live.com'},
'2':{'name':'root2','email':'root@live.com'},
'3':{'name':'root3','email':'root@live.com'},
'4':{'name':'root4','email':'root@live.com'},
'5':{'name':'root5','email':'root@live.com'},
}
def index(request):
return render(request,'index.html',{'user_dict':USER_DICT})
def login(request):
if request.method=='GET':
return render(request,'login.html')
elif request.method=='POST':
#radio
#v1=request.POST.get('gender')
#print(v1)
#checkbox
#v2=request.POST.getlist('favor')
#print(v2)
#v3=request.POST.get('fafafa')
#print(v3)
obj=request.FILES.get('fafafa')
print(obj,type(obj),obj.name)
import os
file_path=os.path.join('upload',obj.name)
f=open(file_path, mode="wb")
for i in obj.chunks():
f.write(i)
f.close()
return render(request,'login.html')
else:
# put,delete,head,option.....
return redirect('/index/')
# def detail(request,nid):
# nid=request.GET.get('nid')
# detail_info=USER_DICT[nid]
# return render(request,'detail.html',{'detail_info':detail_info})
def detail(request,nid):
#return HttpResponse(nid)
detail_info=USER_DICT[nid]
return render(request,'detail.html',{'detail_info':detail_info})
from django.views import View
class Home(View):
def dispatch(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
#调用父类中的dispatch
print('before')
result=super(Home,self).dispatch(request,*args,**kwargs)
print('after')
return result
def get(self,request):
print(request.method)
return render(request,'home.html')
def post(self,request):
print(request.method)
return render(request,'home.html')
"""def login(request):
if request.method=='GET':
return render(request,'login.html')
elif request.method=='POST':
u = request.POST.get('user')
p = request.POST.get('pwd')
if u=='root' and p=='123':
return redirect('/index/')
else:
return render(request,'login.html')
else:
# put,delete,head,option.....
return redirect('/index/')
"""
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
{% for k,row in user_dict.items %}
<li><a target="_blank" href="/detail-{{k}}.html">{{row.name}}</a></li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</body>
</html>
detail.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>详细信息</h1>
<h6>用户名:{{detail_info.name}}</h6>
<h6>邮箱:{{detail_info.email}}</h6>
</body>
</html>
整个流程图整理一下:
本节笔记:
一,路由系统,URL 1.一个URL对应一个函数或者对应一个类 url(r'^index/',views.index),url(r'^home/',views.Home.as_view()), 2.一类URL对应一个函数或类 url(r'^detail-(\d+).html',views.index),



