IO重定向
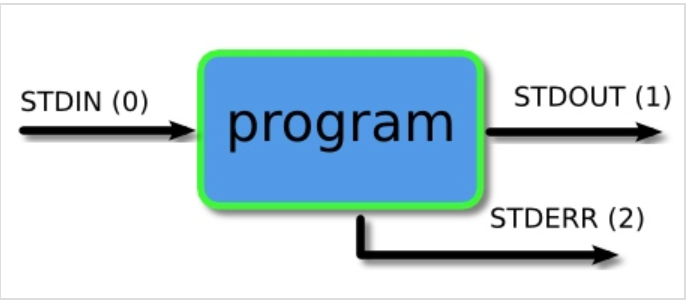
标准IO(Standard Input/Output)
可用于做输入的设备:
键盘设备、文件系统上的常规文件、网卡等。
可用于做输出的设备:
显示器、文件系统上的常规文件、网卡等。
程序的数据流有三种:
- 输入的数据流:<– 标准输入(
stdin(standard input)),默认接受来自键盘的输入。 - 输出的数据流:–> 标准输出(
stdout(standard output)),默认输出到终端窗口。 - 错误输出流:–> 标准错误(
stderr(standard error)),默认输出到终端窗口。
fd:file descriptor,文件描述符
标准输入:0
标准输出:1
标准错误:2
echo $?(bash脚本编程中,很多判断基于$?这个来决定)
IO重定向(Input/Output Redirection)
输入本来默认是键盘,我们改成其他输入,就是输入重定向 :例如从文本文件里输入。
本来输出的位置是显示器,我们改成其他输出,就是输出重定向:例如输出到文件。
set -C:
禁止覆盖输出重定向到已存在的文件(在这种模式下,如果你非要覆盖,可以使用
>|)
set +C:
关闭上述特性
/dev/null
特殊设备,空设备,也叫黑洞,数据进去都没了。
输出重定向(Output Redirection)的几种方法
1. 正常输出重定向:
>(覆盖输出)、>>(追加输出)例子:
2. 错误输出重定向:
2>(覆盖输出)、2>>(追加输出)
正确和错误的都进行输出重定向:
- 新写法:
COMMAND &> /path/to/somefile、COMMAND &>> /path/to/somefile- 老写法:
COMMAND > /path/to/somefile 2>&1、COMMAND >> /path/to/somefile 2>&1
输入重定向(Input Redirection)的方法
tr命令
tr [OPTION]... SET1 [SET2]
把输入的数据当中的字符,凡是在SET1定义范围内出现的,通通对位转换为SET2出现的字符
tr SET1 SET2 < /path/from/somefile对位转化SET1中的字符为SET2中的字符tr -d SET1 < /path/from/somefile删除指定集合里出现的字符tr -s "\n" /path/from/somefile把指定的连续的字符以一个字符表示,压缩。tr -cComplement ,取字符集的补集,通常与其他参数结合使用,例如-dc
tips:如果是输入后再输出到同一个文件,就会清空这个文件,所以最好不要这么用,下面是一个错误示范:
追加是可以的,在原有文件基础上再追加一段:
dc结合使用
Here documents
输出到屏幕,或创建多行文档):
<<终止词例子:
-代表输出流搭配
cat
cat -:如果指定cat的文件为-,表示从标准输入读取(和直接使用cat,好像没什么区别)搭配
|
echo 123 | cat -:表示把管道符前面的输出流,在交给cat执行一遍(这就很牛逼了)例子:
如果操作系统没有scp命令,只有ssh,那么是不是就不能远程拷贝了(前提:没有openssh-clients软件包)
利用
-,就可以实现:
cat jdk.tar.gz产生输出流, 在管道后面的-,则可以接受输出流,并重定向到/tmp/jdk.tar.gz



