paper 114:Mahalanobis Distance(马氏距离)
(from:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mahalanobis_distance)
Mahalanobis distance
In statistics, Mahalanobis distance is a distance measure introduced by P. C. Mahalanobis in 1936.It is based on correlations between variables by which different patterns can be identified and analyzed. It gauges similarity of an unknown sample set to a known one. It differs fromEuclidean distance in that it takes into account the correlations of the data set and is scale-invariant. In other words, it is a multivariateeffect size.
Definition
Formally, the Mahalanobis distance of a multivariate vector 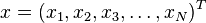 from a group of values with mean
from a group of values with mean 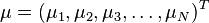 and covariance matrix
and covariance matrix 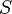 is defined as:
is defined as:
(注:1.这个是X和总体均值的马氏距离。2.这里的S是可逆的,那么协方差矩阵不可逆的话怎么办?)
Mahalanobis distance (or "generalized squared interpoint distance" for its squared value) can also be defined as a dissimilarity measure between two random vectors  and
and  of the same distribution with the covariance matrix
of the same distribution with the covariance matrix 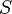 :
:
If the covariance matrix is the identity matrix, the Mahalanobis distance reduces to the Euclidean distance. If the covariance matrix is diagonal, then the resulting distance measure is called the normalized Euclidean distance:
where 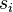 is the standard deviation of the
is the standard deviation of the 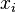 (
(  ) over the sample set.
) over the sample set.
(源自:百度百科)
马氏优缺点:
欧式距离和马氏距离都可以计算两个变量的相似度。
马氏距离能够描述不同维之间的关联性,其关键在于它用到了协方差矩阵,下面是wiki上的介绍:
--------------------------
在统计学与概率论中,协方差矩阵(或称共变异矩阵)是一个矩阵,其每个元素是各个向量元素之间的方差。这是从标量随机变量到高维度随机向量的自然推广。
假设X是以n个标量随机变量组成的列向量(一个列向量代表一个变量,而不是一个记录),
并且μi 是其第i个元素的期望值, 即, μi = E(Xi)。协方差矩阵被定义的第i,j项是如下协方差:
即:
矩阵中的第(i,j)个元素是Xi与Xj的协方差。这个概念是对于标量随机变量方差的一般化推广。
尽管协方差矩阵很简单,可它却是很多领域里的非常有力的工具。它能导出一个变换矩阵,这个矩阵能使数据完全去相关(decorrelation)。从不同的角度看,也就是说能够找出一组最佳的基以紧凑的方式来表达数据。(完整的证明请参考瑞利商)。 这个方法在统计学中被称为主成分分析(principal components analysis),在图像处理中称为Karhunen-Loève 变换(KL-变换)。
-----------------------------------
马氏距离是由印度统计学家马哈拉诺比斯(P. C. Mahalanobis)提出的,表示数据的协方差距离。它是一种有效的计算两个未知样本集的相似度的方法。与欧氏距离不同的是它考虑到各种特性之间的联系(例如:一条关于身高的信息会带来一条关于体重的信息,因为两者是有关联的)并且是尺度无关的(scale-invariant),即独立于测量尺度。 对于一个均值为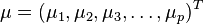 协方差矩阵为Σ的多变量向量
协方差矩阵为Σ的多变量向量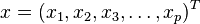 ,其马氏距离为
,其马氏距离为
马氏距离也可以定义为两个服从同一分布并且其协方差矩阵为Σ的随机变量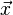 与
与 的差异程度:
的差异程度:
如果协方差矩阵为单位矩阵,那么马氏距离就简化为欧式距离,如果协方差矩阵为对角阵,则其也可称为正规化的欧氏距离'.
其中σi 是 xi 的标准差.
http://www.360doc.com/content/10/0804/20/1202138_43697183.shtml
http://people.revoledu.com/kardi/tutorial/Similarity/MahalanobisDistance.html

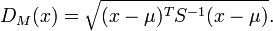
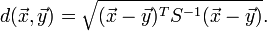

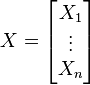

![马氏距离与协方差矩阵 \Sigma=\mathrm{E} \left[ \left( \textbf{X} - \mathrm{E}[\textbf{X}] \right) \left( \textbf{X} - \mathrm{E}[\textbf{X}] \right)^\top \right]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/1/8/1/1811f942680a72974597be42c28d31d2.png)
![马氏距离与协方差矩阵 = \begin{bmatrix} \mathrm{E}[(X_1 - \mu_1)(X_1 - \mu_1)] & \mathrm{E}[(X_1 - \mu_1)(X_2 - \mu_2)] & \cdots & \mathrm{E}[(X_1 - \mu_1)(X_n - \mu_n)] \\ \ \mathrm{E}[(X_2 - \mu_2)(X_1 - \mu_1)] & \mathrm{E}[(X_2 - \mu_2)(X_2 - \mu_2)] & \cdots & \mathrm{E}[(X_2 - \mu_2)(X_n - \mu_n)] \\ \ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ \ \mathrm{E}[(X_n - \mu_n)(X_1 - \mu_1)] & \mathrm{E}[(X_n - \mu_n)(X_2 - \mu_2)] & \cdots & \mathrm{E}[(X_n - \mu_n)(X_n - \mu_n)] \end{bmatrix}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/a/1/2/a12a573ecd1d853abd8c01fab9fccfbe.png)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号