Spring5源码分析(二) IOC 容器的初始化(二)
承接上一篇文章继续分析FileSystemXmlApplicationContextIOC容器创建的流程。
2.5 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader读取Bean定义资源,在其抽象父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 中定义了载入过程。
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法源码如下:
//重载方法,调用下面的loadBeanDefinitions(String, Set<Resource>);方法
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(location, null);
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//获取在IoC容器初始化过程中设置的资源加载器
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
//将指定位置的Bean定义资源文件解析为Spring IOC容器封装的资源
//加载多个指定位置的Bean定义资源文件
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
//委派调用其子类XmlBeanDefinitionReader的方法,实现加载功能
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
//将指定位置的Bean定义资源文件解析为Spring IOC容器封装的资源
//加载单个指定位置的Bean定义资源文件
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
//委派调用其子类XmlBeanDefinitionReader的方法,实现加载功能
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
}
//重载方法,调用loadBeanDefinitions(String);
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return counter;
}loadBeanDefinitions(Resource…resources)方法和上面分析的3个方法类似,同样也是调用XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法。从对 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法源码分析可以看出该方法做了以下两件事:
首先,调用资源加载器的获取资源方法resourceLoader.getResource(location),获取到要加载的资源。其次,真正执行加载功能是其子类XmlBeanDefinitionReader 的 loadBeanDefinitions 方法。
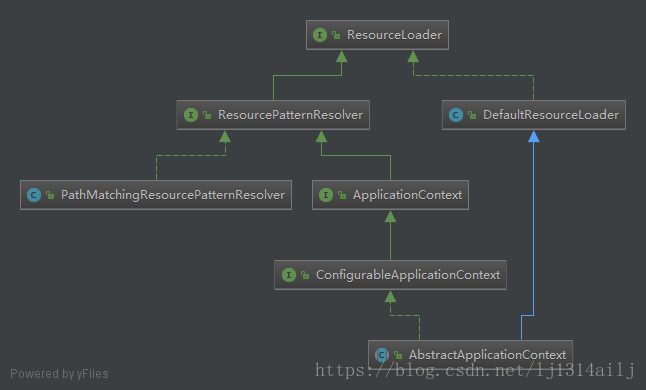
看到上面的 ResourceLoader与ApplicationContext的继承系图,可以知道其实际调用的是DefaultResourceLoader中的getSource()方法定位Resource , 因为FileSystemXmlApplicationContext本身就是DefaultResourceLoader 的实现类,所以此时又回到了 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 中来。
2.6 AbstractBeanDefinitionReader读取Bean定义资源,在其抽象父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 中定义了载入过程。
//获取Resource的具体实现方法
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) {
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
//如果是类路径的方式,那需要使用ClassPathResource 来得到bean 文件的资源对象
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
// 如果是URL 方式,使用UrlResource 作为bean 文件的资源对象
URL url = new URL(location);
return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
//如果既不是classpath标识,又不是URL标识的Resource定位,则调用
//容器本身的getResourceByPath方法获取Resource
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 容器提供了 getResourceByPath 方法的实现,就是为了处理既
不是 classpath 标识,又不是 URL 标识的 Resource 定位这种情况。
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
//这里使用文件系统资源对象来定义 bean 文件
return new FileSystemResource(path);
}这样代码就回到了FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中来,他提供了FileSystemResource 来完成从文件系统得到配置文件的资源定义。这样,就可以从文件系统路径上对IOC配置文件进行加载,当然我们可以按照这个逻辑从任何地方加载,在Spring中我们看到它提供的各种资源抽象,比如
ClassPathResource,URLResource,FileSystemResource等来供我们使用。上面我们看到的是定位Resource的一个过程,而这只是加载过程的一部分.
2.7 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 加载Bean的定义资源
继续回到 XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions(Resource …)方法看到代表bean 文件的资源定义以后的载入过程。
//XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载资源的入口方法
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//将读入的XML资源进行特殊编码处理
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
//这里是载入XML形式Bean定义资源文件方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
.......
try {
//将资源文件转为InputStream的IO流
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
//从InputStream中得到XML的解析源
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
//这里是具体的读取过程
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
//关闭从Resource中得到的IO流
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
...........
}
//从特定XML文件中实际载入Bean定义资源的方法
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//将XML文件转换为DOM对象,解析过程由documentLoader实现
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//这里是启动对Bean定义解析的详细过程,该解析过程会用到Spring的Bean配置规则
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
.....
}通过源码分析,载入Bean定义资源文件的最后一步是将Bean定义资源转换为Document对象,该过程由 documentLoader 实现.
2.8 DocumentLoader 将Bean定义资源转换为Document对象
DocumentLoader 将 Bean 定义资源转换成 Document 对象的源码如下:
//使用标准的JAXP将载入的Bean定义资源转换成document对象
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
//创建文件解析器工厂
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
//创建文档解析器
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
//解析Spring的Bean定义资源
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
protected DocumentBuilderFactory createDocumentBuilderFactory(int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware)
throws ParserConfigurationException {
//创建文档解析工厂
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setNamespaceAware(namespaceAware);
//设置解析XML的校验
if (validationMode != XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE) {
factory.setValidating(true);
if (validationMode == XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD) {
// Enforce namespace aware for XSD...
factory.setNamespaceAware(true);
try {
factory.setAttribute(SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE, XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
ParserConfigurationException pcex = new ParserConfigurationException(
"Unable to validate using XSD: Your JAXP provider [" + factory +
"] does not support XML Schema. Are you running on Java 1.4 with Apache Crimson? " +
"Upgrade to Apache Xerces (or Java 1.5) for full XSD support.");
pcex.initCause(ex);
throw pcex;
}
}
}
return factory;
}
该解析过程调用 JavaEE 标准的 JAXP 标准进行处理。
至此 Spring IOC 容器根据定位的Bean定义资源文件,将其加载读入并转换成为 Document 对象过程完成。接下来我们要继续分析 Spring IOC 容器将载入的 Bean定义资源文件转换为Document对象之后,是如何将其解析为 Spring IOC 管理的 Bean 对象并将其注册到容器中的。
2.9 XmlBeanDefinitionReader析载入的Bean定义资源文件
XmlBeanDefinitionReader 类中的 doLoadBeanDefinitions方法是从特定 XML 文件中实际载入Bean定义资源的方法,该方法在载入Bean定义资源之后将其转换为 Document 对象,接下来调用registerBeanDefinitions 启 动SpringIOC容器对Bean定义的解析过程,registerBeanDefinitions方法源码如下:
//按照Spring的Bean语义要求将Bean定义资源解析并转换为容器内部数据结构
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//得到BeanDefinitionDocumentReader来对xml格式的BeanDefinition解析
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
//获得容器中注册的Bean数量
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//解析过程入口,这里使用了委派模式,BeanDefinitionDocumentReader只是个接口,
//具体的解析实现过程有实现类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader完成
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
//统计解析的Bean数量
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}Bean 定义资源的载入解析分为以下两个过程:
首先,通过调用 XML 解析器将 Bean 定义资源文件转换得到 Document 对象,但是这些 Document对象并没有按照Spring的Bean规则进行解析。这一步是载入的过程.
其次,在完成通用的 XML 解析之后,按照 Spring 的 Bean 规则对 Document 对象进行解析。按照 Spring 的 Bean 规则对 Document 对象解析的过程是在接口BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的实现类 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 中实现的。
由于IOC 容器的初始化内容比较多一次文章无法写完,所以分了五篇进行讲解此篇为第二篇。
文档有参考其他资料,如果问题请联系我,进行删除!