Android数据存储之JSON数据解析(读取部分)
读取部分在输出部分项目中新建一个Activity即可。
本部分比输出部分要麻烦一些,主要流程为:以字符串形式读入json数据 ---> 解析字符串形式的json数据 ---> 在组件中显示数据
Activity组件等准备:
 View Code
View Code
public class ReadJSONActivity extends Activity { private TextView dataText = null; private Button readJSONBtn = null; private File file = null; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_readjson); dataText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.dataText); readJSONBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.readJSONBtn); readJSONBtn.setOnClickListener(new ReadJSONBtnListener()); }
按钮事件绑定:
 View Code
View Code
private class ReadJSONBtnListener implements OnClickListener { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 首先调用检测储存环境的方法 if(!ReadJSONActivity.this.checkEnvironment()) { return; } else { // 调用读取JSON方法 readJSON(); Toast.makeText(ReadJSONActivity.this, "成功读取JSON", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } } }
检测储存环境与输出部分一致,此处省略。
读入json数据方法:readJSON()
 View Code
View Code
private void readJSON() { String temp = null; // 取得输入流 FileInputStream fis = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream(file); br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); temp = br.readLine(); // 调用显示数据方法,传入参数为parseJSON()方法传回的Map对象 showJSONFile(parseJSON(temp)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (JSONException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (br != null || fis != null) { br.close(); br = null; fis.close(); fis = null; } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
解析字符串形式的json数据方法:parseJSON()
 View Code
View Code
private Map<String, Object> parseJSON(String temp) throws JSONException { Map<String, Object> resultMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); JSONObject myJSONData = new JSONObject(temp); // 先读取单个数据 resultMap.put("feature", myJSONData.getString("feature")); resultMap.put("favorite", myJSONData.getString("favorite")); // 再读取数组数据,先将JSONArray对象提取出来 JSONArray myJSONArray = myJSONData.getJSONArray("info"); List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>(); for (int i = 0; i < myJSONArray.length(); i++) { // 遍历JSONArray中的JSONObject,把每个JSONObject的键值对填入一个临时Map对象中 Map<String, Object> tempMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); JSONObject tempObject = myJSONArray.getJSONObject(i); tempMap.put("id", tempObject.getInt("id")); tempMap.put("name", tempObject.getString("name")); // 最终JSONArray中的所有JSONObject转化为list中的所有Map list.add(tempMap); } // 将整个list装入最终结果Map resultMap.put("info", list); return resultMap; }
显示数据方法:showJSONFile()
 View Code
View Code
private void showJSONFile(Map<String, Object> resultMap) { StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(); // 先处理单个数据 buffer.append("feature: " + resultMap.get("feature") + "\n"); buffer.append("favorite: " + resultMap.get("favorite") + "\n"); // 再处理数组数据 List<Map<String, Object>> list = (List<Map<String, Object>>) resultMap.get("info"); Iterator<Map<String, Object>> it = list.iterator(); buffer.append("info: " + "\n"); while (it.hasNext()) { Map<String, Object> tempMap = it.next(); buffer.append(" id: " + tempMap.get("id") + "\n"); buffer.append(" name: " + tempMap.get("name") + "\n"); } // 显示数据 ReadJSONActivity.this.dataText.setText(buffer.toString()); }
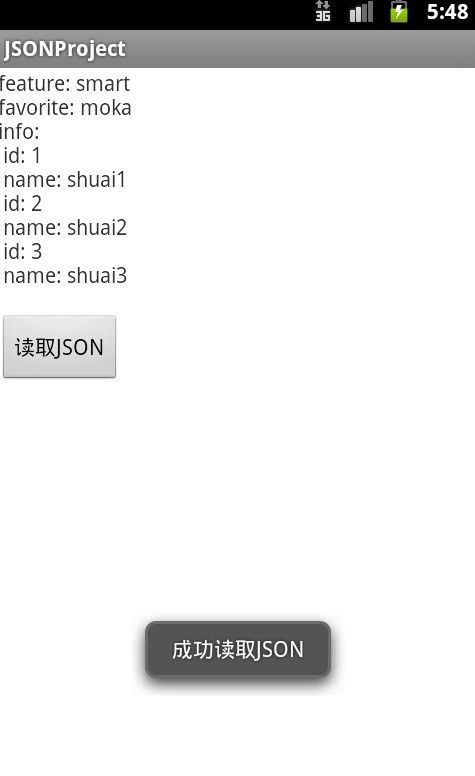
显示效果: