c语言-----劫持自己02
在上一节 c语言-----劫持原理01 已经叙述了劫持原理,下边正式进入劫持实战
1. 需要实现的功能
在c语言中
system("notepad") 可以打开一个记事本
system("mspaint") 可以打开画图工具
所以这次我们需要把 可以打开一个记事本 这个功能更改为 在控制台打印 "notepad"
可以打开画图工具 这个功能更改为 在控制台打印 "mspaint" ,即实现监控的日志功能
2. 需要的工具
vs2017
Detours
3. 劫持原理实现
(1) 查看system()函数定义
_DCRTIMP int __cdecl system( _In_opt_z_ char const* _Command );
去掉一些不需要的符号
int system( char const* _Command );
(2) 获取原system()的地址
int (*plodsystem)(char const* _Command) = system;
(3) 劫持后system()函数
int newsystem(char const* _Command){ printf("你执行的是:%s", _Command); }
(4) 劫持函数
void hook(){ DetourRestoreAfterWith(); //恢复之前的状态 DetourTransactionBegin(); //开始劫持 DetourUpdateThread(GetCurrentThread());//更新当前线程 DetourAttach((void **)&plodsystem, newsystem);//劫持 DetourTransactionCommit(); //提交 }
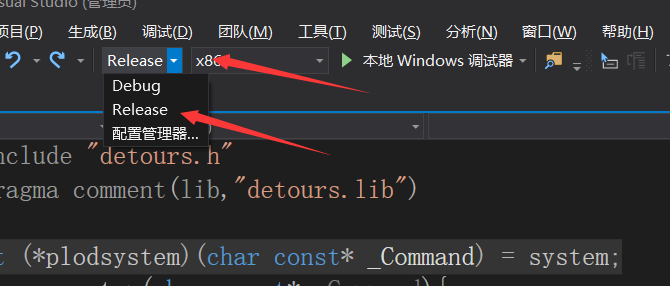
(5) 修改vs配置 Debug -> Release
(6) 完整源代码
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<Windows.h> #include "detours.h" #pragma comment(lib,"detours.lib") int (*plodsystem)(char const* _Command) = system; int newsystem(char const* _Command){ printf("你执行的是:%s", _Command); } void hook(){ DetourRestoreAfterWith(); DetourTransactionBegin(); DetourUpdateThread(GetCurrentThread()); DetourAttach((void **)&plodsystem, newsystem); DetourTransactionCommit(); } int main(){ system("notepad"); hook(); system("notepad"); return 0; }
3. 解释说明
system()函数是一个int类型的函数 int system( char const* _Command );
所以需要一个一级函数指针plodsystem
获取plodsystem的地址 &plodsystem,需要一个二级指针






