5、输入输出重定向
我们知道,Linux 中标准的输入设备默认指的是键盘,标准的输出设备默认指的是显示器。而本节所要介绍的输入、输出重定向,完全可以从字面意思去理解,也就是:
- 输入重定向:指的是重新指定设备来代替键盘作为新的输入设备;
- 输出重定向:指的是重新指定设备来代替显示器作为新的输出设备。
通常是用文件或命令的执行结果来代替键盘作为新的输入设备,而新的输出设备通常指的就是文件。
Linux输入重定向
对于输入重定向来说,其需要用到的符号以及作用如表 1 所示。
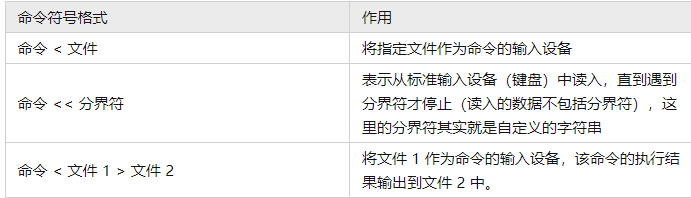
【例 1】 默认情况下,cat 命令会接受标准输入设备(键盘)的输入,并显示到控制台,但如果用文件代替键盘作为输入设备,那么该命令会以指定的文件作为输入设备,并将文件中的内容读取并显示到控制台。
以 /etc/passwd 文件(存储了系统中所有用户的基本信息)为例,执行如下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd
\#这里省略输出信息,读者可自行查看
[root@localhost ~]# cat < /etc/passwd
\#输出结果同上面命令相同
注意,虽然执行结果相同,但第一行代表是以键盘作为输入设备,而第二行代码是以 /etc/passwd 文件作为输入设备。
例 2】
[root@localhost ~]# cat << 0
\>linuxyz.cn
\>Linux
\>0
linuxyz.cn
Linux
可以看到,当指定了 0 作为分界符之后,只要不输入 0,就可以一直输入数据。
【例 3】 首先,新建文本文件 a.tx,然后执行如下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# cat a.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat < /etc/passwd > a.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat a.txt
\#输出了和 /etc/passwd 文件内容相同的数据
可以看到,通过重定向 /etc/passwd 作为输入设备,并输出重定向到 a.txt,最终实现了将 /etc/passwd 文件中内容复制到 a.txt 中。
Linux输出重定向
相较于输入重定向,我们使用输出重定向的频率更高。并且,和输入重定向不同的是,输出重定向还可以细分为标准输出重定向和错误输出重定向两种技术。
例如,使用 ls 命令分别查看两个文件的属性信息,但其中一个文件是不存在的,如下所示:
[root@localhost ~]# touch demo1.txt
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l demo1.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 root root 0 Oct 12 15:02 demo1.txt
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l demo2.txt <-- 不存在的文件
ls: cannot access demo2.txt: No such file or directory
上述命令中,demo1.txt 是存在的,因此正确输出了该文件的一些属性信息,这也是该命令执行的标准输出信息;而 demo2.txt 是不存在的,因此执行 ls 命令之后显示的报错信息,是该命令的错误输出信息。
再次强调,要想把原本输出到屏幕上的数据转而写入到文件中,这两种输出信息就要区别对待。
在此基础上,标准输出重定向和错误输出重定向又分别包含清空写入和追加写入两种模式。因此,对于输出重定向来说,其需要用到的符号以及作用如表 2 所示。
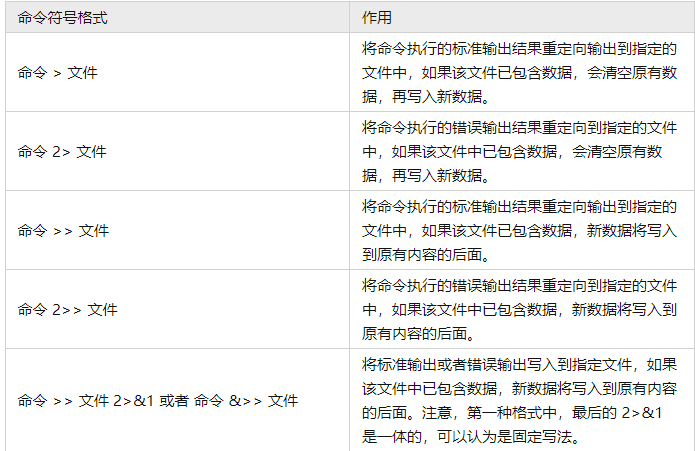
例 4】新建一个包含有 "Linux" 字符串的文本文件 Linux.txt,以及空文本文件 demo.txt,然后执行如下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# cat Linux.txt > demo.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat demo.txt
Linux
[root@localhost ~]# cat Linux.txt > demo.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat demo.txt
Linux <--这里的 Linux 是清空原有的 Linux 之后,写入的新的 Linux
[root@localhost ~]# cat Linux.txt >> demo.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat demo.txt
Linux
Linux <--以追加的方式,新数据写入到原有数据之后
[root@localhost ~]# cat b.txt > demo.txt
cat: b.txt: No such file or directory <-- 错误输出信息依然输出到了显示器中
[root@localhost ~]# cat b.txt 2> demo.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat demo.txt
cat: b.txt: No such file or directory <--清空文件,再将错误输出信息写入到该文件中
[root@localhost ~]# cat b.txt 2>> demo.txt
[root@localhost ~]# cat demo.txt
cat: b.txt: No such file or directory
cat: b.txt: No such file or directory <--追加写入错误输出信息
实验-输出重定向
echo qin > test
cat test
echo bing > test
cat test
echo qinbing >> test
cat test
实验-错误重定向
wadwadwad 2> test
cat test
实验-双重输出重定向
find / -user qin > test
cat test
find / -name passwd 2> test
cat test
find / -name passwd &> test
cat test
find / -name passwd > test 2>&1
cat test
实验-输入重定向
mail qin < test
su - qin
mail
cat > ok << EOF
123
456
EOF
cat ok
实验-管道
cat /etc/passwd | grep root
cat /etc/passwd | grep ^root
cat /boot/grub2/grub.cfg | grep -v ^# | grep -v ^$ > newgrub
cat /boot/grub2/grub.cfg | tee file1 | grep -v ^# | tee file2 | grep -v ^$ | tee file3 > newgrub



