PTA实验4~6总结及分析
1.前言
不知不觉一个月又过去了,也再次完成了三次pta上面的作业,总的来说,这几次pta实验在题量上比之前少了很多,但相对的,难度有了很多提升,其中第六次实验我更是连及格分都没有拿到。接下来我会对这几次实验进行分析,这几次实验涵盖了正则表达式、封装性。还有菜单和日期类程序,总的来说比上次复杂了不少,也更应该好好总结。废话不多说,接下来就开始总结分析一下这几次的代码
2.设计与分析
在这一块我会重点针对题目的源码进行分析,同时也会附上power designer所做的类图用以方便理解。首先要分析的是题目集四的7-1

这个题目是后面那个菜单程序的简单版,但是对于初见的我来说仍然是一道难题,等会放在后面和最后一道题一起讲
然后是题目集5的7-5
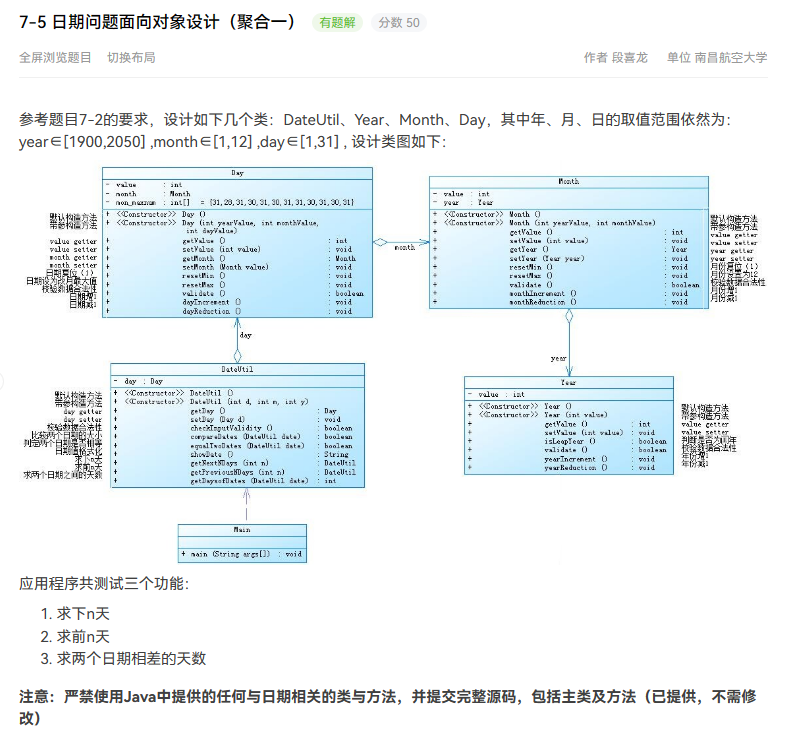
首先肯定是根据他给的设计类图给出年月日的定义,这里就只给出年的定义了,另外两个和这个相仿,就不赘述了。
class Year{ private int value; public Year(){} public Year(int value){ this.value=value; } public int getValue(){ return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value=value; } public boolean isLeapYear(){//判断是否为闰年 if((value%4==0&&value%100!=0)||value%400==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean validate(){//校验数据合法性 if(value<=2050&&value>=1900) return true; else return false; } public void yearIncrement(){ value=value+1; } public void yearReduction(){ value=value-1; } }
在把这三个主要的类都定义好之后,就要针对题目来实现功能了。
在Dateutil类里一共要完成三个功能,也就是求上下n天以及测试两日期之间相差的天数
首先是求下n天
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) day.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else day.mon_maxnum[2] = 28; day.dayIncrement(); if(day.getValue() == day.mon_maxnum[day.getMonth().getValue()]+1){// day.resetMin(); day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); } if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 13){//月份为13,月份进位 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); day.getMonth().resetMin(); } } return new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() , day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getValue()); }
求上n天和这个类似,就不给出代码了。
但是在求两日期相差的天数前,要先判断两个日期的大小,不然没办法进行比较。
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//date即为输入的年月日 if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()){//年 return true; }else if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && day.getMonth().getValue() > date.day.getMonth().getValue()){//月 return true; }else if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && this.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue()){//日 return true; } return false; }
当然,两日期相同的特殊情况也是要考虑的。
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ return day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() && day.getMonth().getValue() == date.day.getMonth().getValue() && day.getValue() == date.day.getValue(); }
接下来在主函数里面用if语句来写选择就行了
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int a,b; a = input.nextInt();//输入判断类型 year = input.nextInt(); month = input.nextInt(); day = input.nextInt();//输入年月日 DateUtil c = new DateUtil(year,month,day); if(a==1){//求下n天 b = input.nextInt();//输入n if(!c.checkInputValidity()||b<0){//数据不合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getNextNDays(b).showDate()); } else if(a==2) { b = input.nextInt();//输入n if (!c.checkInputValidity() || b < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getPreviousNDays(b).showDate()); } else if(a==3){ int y1,m1,d1; y1 = input.nextInt(); m1 = input.nextInt(); d1 = input.nextInt();//输入第二个年月日 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y1,m1,d1); if(!c.checkInputValidity()||!date.checkInputValidity()){//如果数据不合法 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } else System.out.println(c.getDaysofDates(date)); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }
同时在这里给出类图方便理解。

接着是下一题,7-6,这题是上一题的升级版,正好放在一起讲。
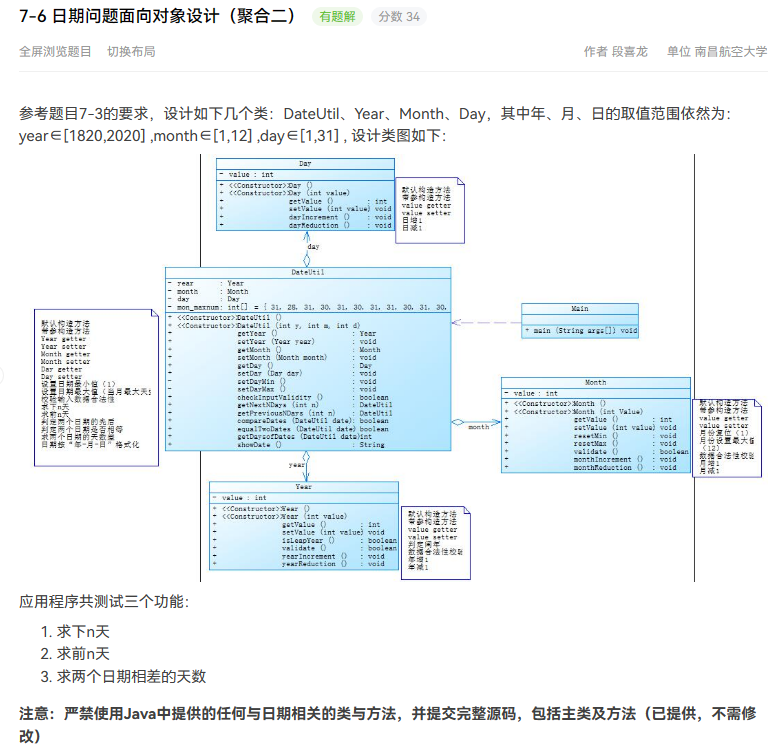
这题看似和上一题差不多(实际上确实差不多),但是其中类和类直接的关系与上一题不同了,在这一题中,Dateutil可以直接访问其他三个类的value,由于年月日的代码我上面已经给出,这里就不给了,直接上Dateutil的代码,便于对比其不同。
先是求上下n天的:
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//求下n天 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; else mon_maxnum[2]=28; day.dayIncrement(); if(day.getValue() == mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]+1){ day.setValue(1); month.monthIncrement(); } if(month.getValue() == 13){ year.yearIncrement(); month.setValue(1); } } return new DateUtil(year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue()); } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2]=29; else mon_maxnum[2]=28; day.dayReduction(); if(day.getValue() == 0){ month.monthReduction(); if(month.getValue() == 0){ year.yearReduction(); month.setValue(12); } day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()]); } } return new DateUtil(year.getValue(), month.getValue(), day.getValue()); }
然后是求两个日期之间相差天数的:
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ int res = 0; if(this.compareDates(date)){ while(true){ if(date.year.isLeapYear()) date.mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else date.mon_maxnum[2] = 28; date.day.dayIncrement(); if(date.day.getValue() == date.mon_maxnum[date.month.getValue()] + 1){ date.month.monthIncrement(); date.day.setValue(1); } if(date.month.getValue() == 13){ date.year.yearIncrement(); date.month.resetMin(); } if(date.year.getValue() == year.getValue() && date.month.getValue() == month.getValue() && date.day.getValue() == day.getValue()){ break; } res++; } }else{ while(true){ if(year.isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[2] = 29; else mon_maxnum[2] = 28; day.dayIncrement(); if(day.getValue() == mon_maxnum[month.getValue()] + 1){ month.monthIncrement(); day.setValue(1); } if(month.getValue() == 13){ year.yearIncrement(); month.resetMin(); } if(date.year.getValue() == year.getValue() && date.month.getValue() == month.getValue() && date.day.getValue() == day.getValue()){ break; } res++; } } return res + 1; } }
后面主函数啥的都大差不差了,给出类图就结束吧。
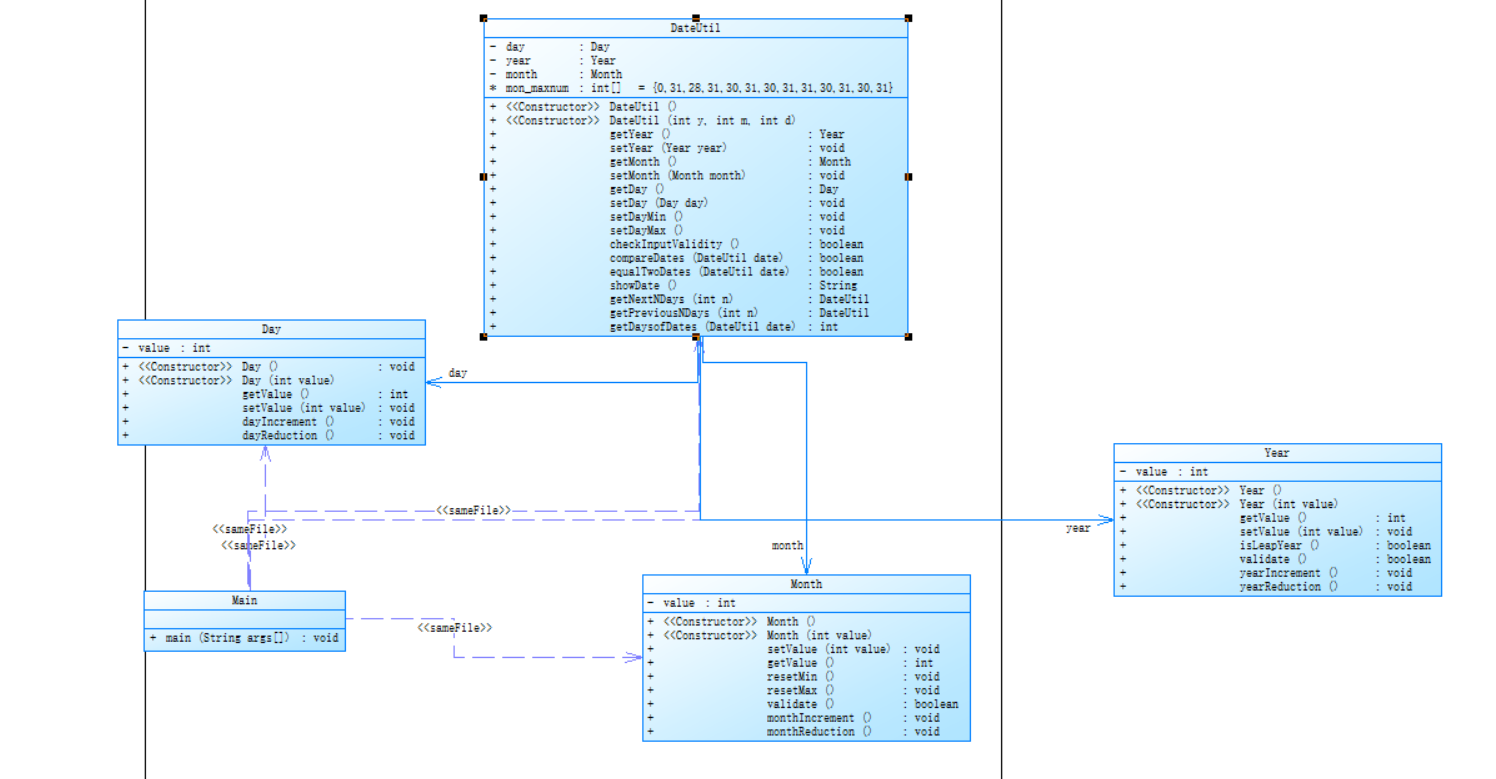
然后就是重磅的实验六了


这道题我当时并没有做出来,后来在我朋友的辅导下才得以完善代码。
首先是定义dish类
这里我还没有碰到什么问题,和之前那个7-3差不多:
class Dish{//菜品类 private String name;//菜品名称 private int unit_price;//单价 private String isSpecial = "F"; public Dish(){//无参构造 } public Dish(String name,int unit_price,String isSpecial) { this.name = name; this.unit_price = unit_price; this.isSpecial = isSpecial; } public Dish(String name,int unit_price) { this.name = name; this.unit_price = unit_price; } public void setIsSpecial(String isSpecial) { this.isSpecial = isSpecial; } public int getPrice(int portion){//计算份额 return (int)(unit_price * (1 + (float)(portion - 1) / 2) + 0.5); } public int getUnit_price() { return unit_price; } public String getIsSpecial() { return isSpecial; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getName(){ return this.name; } public int setUnit_price(int unit_price){ return this.unit_price = unit_price; } }
接着就是菜单类,这里我碰到了第一个问题,怎么查找菜品返回dish
public Dish searchDish(String dishName){//在menu中查找菜品,返回Dish int len = 0; for (int j = 0;dishes[j] != null;j ++){ len ++; } for (int j = 0;j < len;j++){ if (dishes[j].getName().equals(dishName)){ return dishes[j];
} } return null; }
除此之外,保存和添加菜品也是一大难点,
public Dish addDish(String dishName, int unit_price){//添加菜品 if (unit_price > 0 && unit_price < 300) { if (i == ) { dishes[] = new Dish(dishName, unit_price); i++; return dishes[]; } else { dishes[i] = new Dish(dishName, unit_price); i++; return dishes[i]; } } return null; } public Dish addSpecialDish(String dishName, int unit_price,String isSpecial){//添加菜品 if (unit_price > 0 && unit_price < 300) { if (i == ) { dishes[] = new Dish(dishName, unit_price, isSpecial); i++; return dishes[0]; } else { dishes[i] = new Dish(dishName, unit_price, isSpecial); i++; return dishes[i]; } } return null; }
相对的,Record类就没这么难了,但是要定义的东西比较多,这里直接给出代码:
class Record{ private int orderNum;//序号 private Dish d = new Dish();//菜品 private int portion;//份额 private int num;//份数 private int price; private boolean isValidPortion = true; private boolean isValidNum = true; public Record(){//无参构造 } public Record(int orderNum,Dish d,int portion,int num){ this.orderNum = orderNum; this.d = d; this.portion = portion; this.num = num; } public void setD(Dish d){ this.d = d; } public int getPrice(){//价格 return d.getPrice(portion)*num; } public Dish getD(){ return this.d; } public int getOrderNum(){ return this.orderNum; } public void setOrderNum(int orderNum) { this.orderNum = orderNum; } public int getPortion() { return portion; } public void setPortion(int portion) { this.portion = portion; } public int getNum() { return num; } public void setNum(int num) { this.num = num; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } public void isValidity(){ if (this.portion >= 1 && this.portion <= 3){ this.isValidPortion = true; }else{ this.isValidPortion = false; } if (this.num >= && this.num <= ){ this.isValidNum = true; }else{ this.isValidNum = false; } } }
接着是table类,也就是看在哪一桌,这里要判断输入的订单桌号信息是否有效,有效则将桌号记录下来,无效则纪录无效,以及要判断日期是否合法
class Table{ private OrderTime orderTime = new OrderTime();//点菜时间 private int tableNum; private boolean isValidTable = true; private boolean isValidNum = true;//桌号范围 private boolean isValidNumFormat = true;//桌号是否为数字 private boolean dateData = true;//日期的数据是否合法 private boolean isValidDateData = true;//日期是否在范围内 private boolean isValidDateFormat = true;//日期格式是否合法 public boolean isValidNumFormat() { return isValidNumFormat; } public boolean isValidDateData() { return isValidDateData; } public boolean isValidDateFormat() { return isValidDateFormat; } public boolean isDateData() { return dateData; } public OrderTime getOrderTime() { return orderTime; } public void setOrderTime(OrderTime orderTime) { this.orderTime = orderTime; } public Table(OrderTime orderTime) { this.orderTime = orderTime; } public Table() { } public boolean isValidTable() { return isValidTable; } public boolean isValidNum() { return isValidNum; } public void isValidity(String str){ String[] splitedStr = str.split(" "); String[] splitedDate = splitedStr[splitedStr.length - 2].split("/"); String[] splitedDay = splitedStr[splitedStr.length - 1].split("/"); if (Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[0]) >= 2022 && Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[0]) <= 2023){ isValidDateData = true; }else{ isValidDateData = false; } if (splitedStr[0].equals("table")){ isValidTable = true; }else{ isValidTable = false; } if (splitedDate[0].matches("\\d{4}") && splitedDate[1].matches("\\d{1,2}") && splitedDate[2].matches("\\d{1,2}") && splitedDay[0].matches("\\d{1,2}") && splitedDay[1].matches("\\d{1,2}") && splitedDay[2].matches("\\d{1,2}")){ isValidDateFormat = true; }else{ isValidDateFormat = false; } if (splitedStr[splitedStr.length - 3].matches("[1-9]\\d+")){ isValidNumFormat = true; if (splitedStr[splitedStr.length - 3].matches("[1-9]|[1-4]\\d|5[0-5]")){ isValidNum = true; }else{ isValidNum = false; } tableNum = Integer.parseInt(splitedStr[splitedStr.length-3]); if (Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[1]) > 0 && Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[1]) <= 12) {//判断输入的年月是否合法 Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar.set(Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[0]), Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[1]), Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[2])); if (Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[2]) > 0 && Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[2]) <= calendar.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)) { if (Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[0]) >= 0 && Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[0]) <= 23 && Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[1]) >= 0 && Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[1]) <= 59 &&Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[2]) >= 0 && Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[2]) <= 59) { orderTime.setOrderTime(Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[0]), Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[1]), Integer.parseInt(splitedDate[2]) , Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[0]), Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[1]), Integer.parseInt(splitedDay[2])); } }else{ dateData = false; } }else{ dateData = false; } }else{ isValidNumFormat = false; } } public int getTableNum() { return tableNum; } public void setTableNum(int tableNum) { this.tableNum = tableNum; } }
最后就是时间日期这一块难点了,我将下面的代码批注了一下,这样更便于理解。
class WhichDay{//日期 private Order order = new Order(); private boolean isValidDate = true; private int week = order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); Calendar[] compareTime = new Calendar[]; public WhichDay() { } public Order getOrder() { return order; } public void setOrder(Order order) { this.order = order; } public void setCompareTime() {//记录营业时间 for (int i = ;i < ;i++){ compareTime[i] = Calendar.getInstance(); } compareTime[].set(order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.YEAR),order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.MONTH) ,order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.DATE),,,); compareTime[].set(order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.YEAR),order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.MONTH) ,order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.DATE),,,); compareTime[].set(order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.YEAR),order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.MONTH) ,order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.DATE),,,); compareTime[].set(order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.YEAR),order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.MONTH) ,order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.DATE),,,); compareTime[].set(order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.YEAR),order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.MONTH) ,order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.DATE),,,); compareTime[].set(order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.YEAR),order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.MONTH) ,order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime().get(Calendar.DATE),,,); } public WhichDay(Order order) { this.order = order; } public int getWeek() { return week; } public void isValidDate(){//看是否为有效时间 if (week >= && week <= ){ if (((((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() >= compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())) && (order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() <= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())) || (((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() >= (compareTime[]).getTimeInMillis()) && ((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() <= (compareTime[]).getTimeInMillis()))){ isValidDate = true; }else if((((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() >= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())) && (order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() <= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())) || (((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() >= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())) && ((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() <= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())))){ isValidDate = true; }else{ isValidDate = false; } }else{ if ((((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() >= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())) && ((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() <= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())))){ isValidDate = true; }else if ((((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() >= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())) && ((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).getTimeInMillis() <= (compareTime[].getTimeInMillis())))){ isValidDate = true; }else{ isValidDate = false; } } } public double setDiscount(){ double discount; if (((order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).compareTo(compareTime[]) == 1) && (order.getTable().getOrderTime().getOrderTime()).compareTo(compareTime[]) == -1){ discount = .; }else{ discount = .; } return discount; } public void setValidDate(boolean validDate) { isValidDate = validDate; } public boolean getValidDate(){ return isValidDate; } }
最后再给出类图总结一下

3.踩坑心得
要说踩了的坑的话,那肯定还是不少的,比如7-1的时候曾经因为matches方法错过(没加^和&)
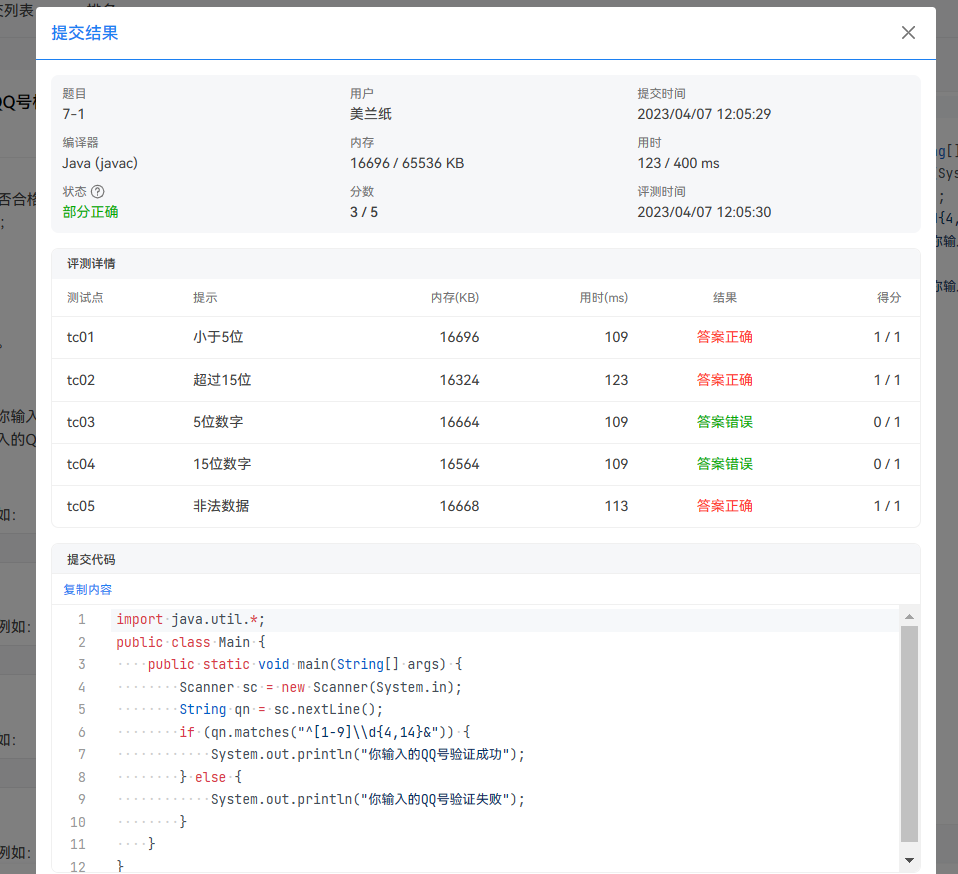
还有因为输出时用了printf导致输出超时
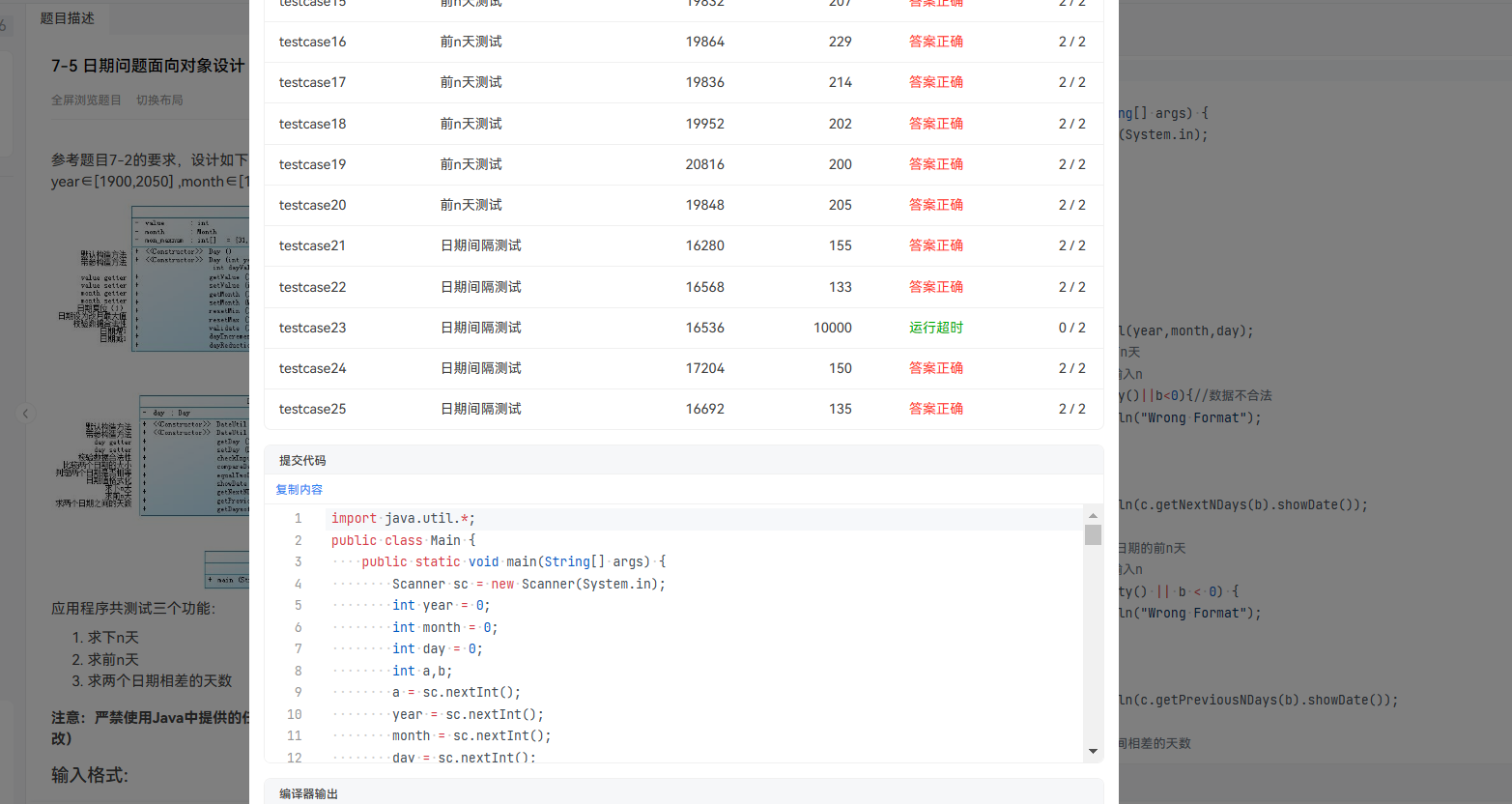
包括日期输出的时候没注意格式
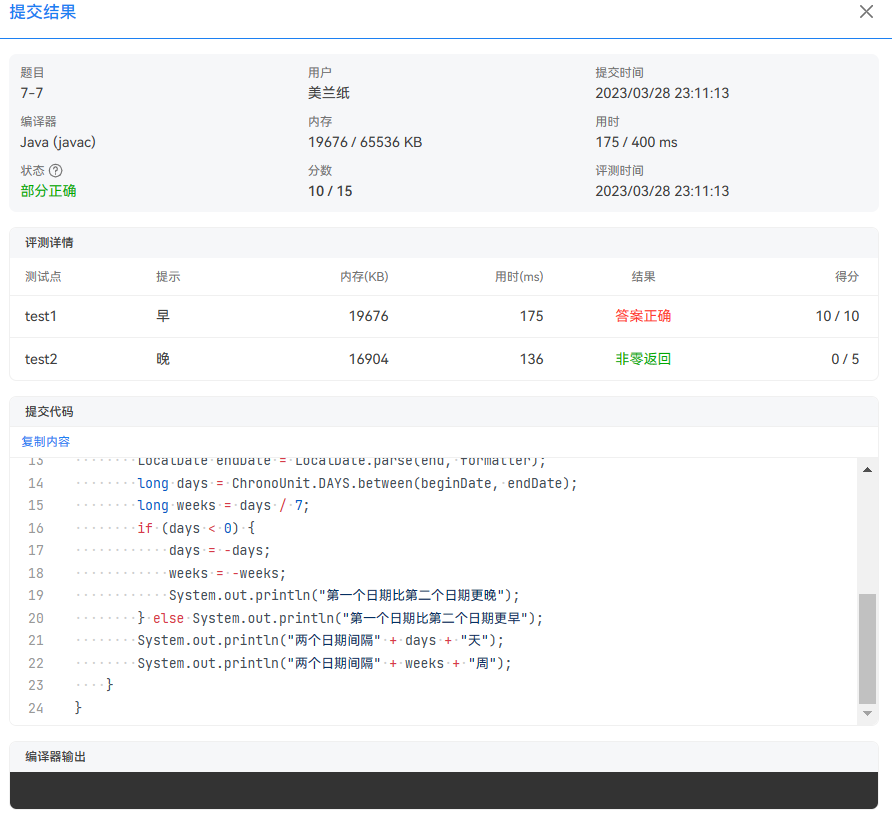
这些都是现在踩的坑,也是吸取的经验。
4.改进建议
和之前一样,我有的时候还是改不掉printf的习惯,同时测试点较多的情况下,也会对自己错误的几个测试点怎么错的感到迷茫。另外,我发现有些题目如果改成正则表达式的形式会让代码不那么冗长,同时我的类与类之间的关系还是没有太清楚,也是要改进的点。
5.总结
最后,和之前一样做个总结,这几次作业可谓是让我初步体验到了Java的困难之处,甚至有一次pta作业没有做到及格,接下来不能怠惰了,要好好练习自己的代码水平,写出更好的代码。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号