【华盛顿大学-机器学习】1、A Case Study 1.3、clustering:文献数据检索
clustering
对文献进行数据分析
要求如下

用文献中的单词书面来进行展现
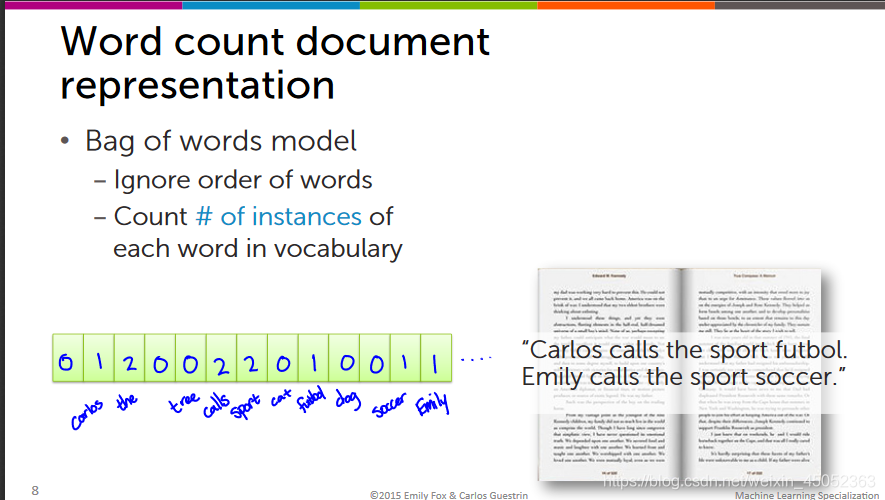

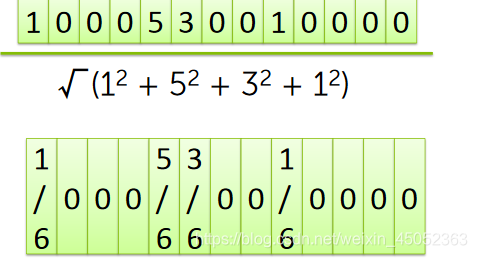
上述方法会受到倍数的影响,因此我们要将其标准化
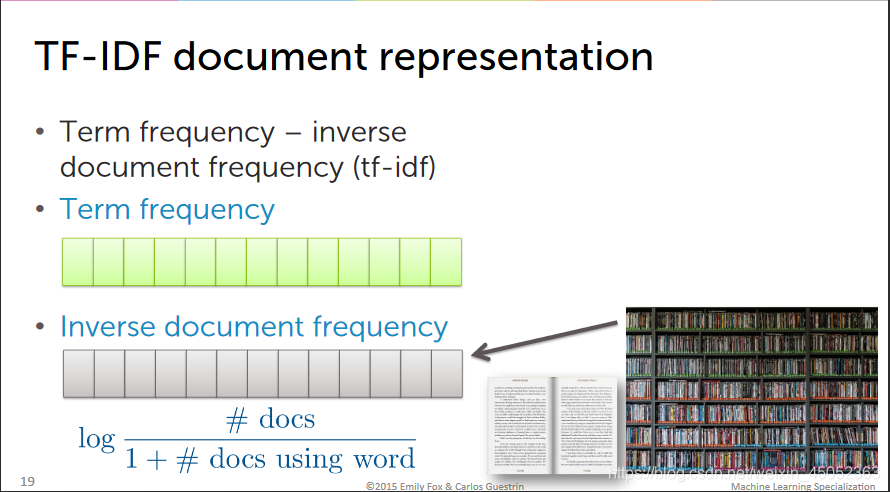
Prioritizing important words with tf-idf
- 有的单词是在所有文献中都很常见的,因此会导致这些单词的频率过高,从而影响我们的实际结果,因此我们要考虑这样常见单词(the,and,I)的影响
- TF-IDF
![在这里插入图片描述]()
聚类算法实现
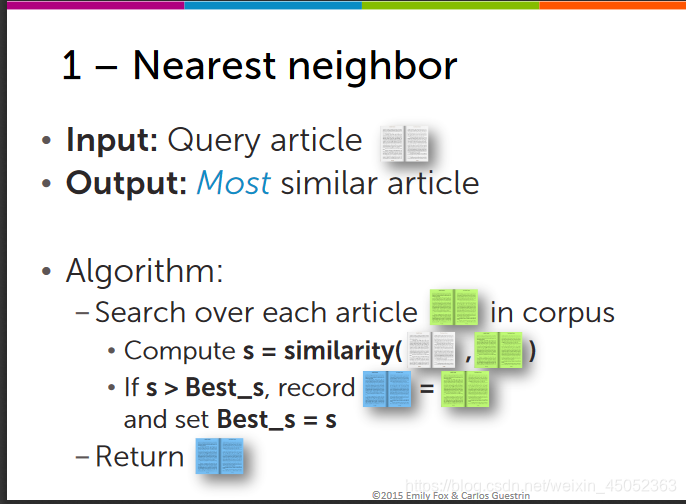
Nearest neighbor search(最近邻搜索)
- 将其他的文献与目标文献进行上面的矩阵相乘,找到最近的那个
![在这里插入图片描述]()
K-Nearest neighbor(KNN)
- 找出k个最相近的文章
![在这里插入图片描述]()
clustering
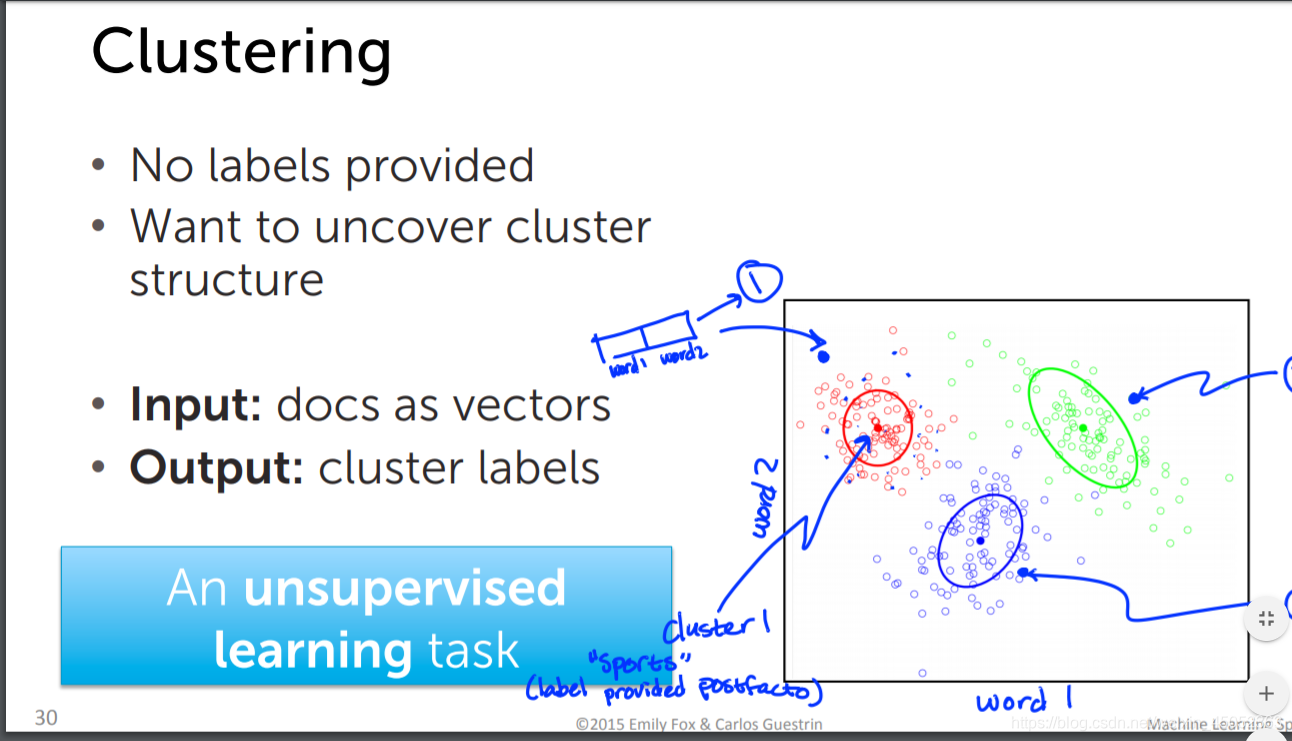
聚类属于一种无监督学习,输入的资料没有标签
k近邻算法就是将输入空间分成k个部分
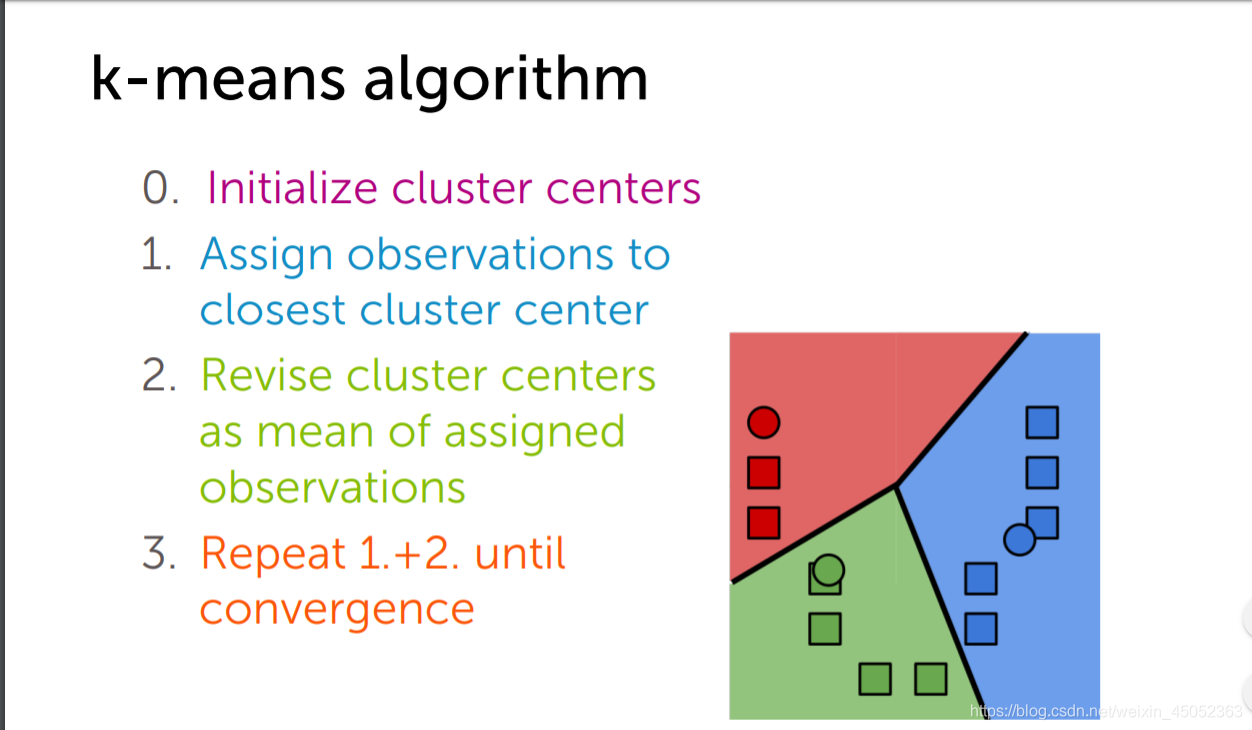
- 1 选取集群中心
- 2 将离集群中心最近的点聚类
- 3 重新选取集群中心直到其它点到集群中心的距离最小
代码及作业部分
课堂笔记
- Load text data
import graphlab
people = graphlab.SFrame('people_wiki.sframe')
- Get the word counts for Obama article
obama['word_count'] = graphlab.text_analytics.count_words(obama['text']
- Sort the word counts for the obama article
obama_word_count_table = obama[['word_count']].stack('word_count', new_column_name=['word','count'])
- Compute TF-IDF for the corpus
people['word_count'] = graphlab.text_analytics.count_words(people['text'])#先将文进行分析
tfidf = graphlab.text_analytics.tf_idf(people['word_count'])#使用tf_idf直接求得我们的目标
- Examine the TF-IDF for the Obama article
obama = people[people['name']=='Barack Obama']#先选出obama的数据
obama[['tfidf']].stack('tfidf',new_column_name=['word','tfidf']).sort('tfidf',ascending=False)#再进行tfidf计算及排序
- Is Obama closer to clinton or beckham
graphlab.distances.cosine(obama['tfidf'][0],clinton['tfidf'][0])# 计算余弦距离
graphlab.distances.cosine(obama['tfidf'][0],beckham['tfidf'][0])
- Build a nearest neighbor model for ducument retrival
knn_model = graphlab.nearest_neighbors.create(people,features=['tfidf'],label='name')#knn模型创建
- 直接用query方法直接调用knn_model
knn_model.query(beckham)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号