C#入门
2023.8.30

解答:
1.将倒数第二杯的水倒入第二杯中,再将杯子放回原位。
2.将管子首尾相连,让末端黑球滚动到前端
解题思想:首先将目标结果实现,根据结果倒推。
2023.8.31

解答:
1.将四棵树种到一个等边三角锥的四个顶点上
2.首先点燃一根香的两端和第二根香的一端,等第一根香全部烧完后点燃第二根的另一端,此时第二根烧完所需的时间就是15分钟
解题思想:第一题是空间思维;第二题是程序执行流程,如线程之类




解答:
1.Console.Write("")//打印信息不空行,Console.WriteLine("")//打印信息空行;
Console.ReadKey()//检测玩家的一键输入,Console.ReadLine()//检测玩家的一系列输入,回车键结束
2.
代码:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入用户名"); Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入年龄"); Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入班级"); Console.ReadLine(); } }
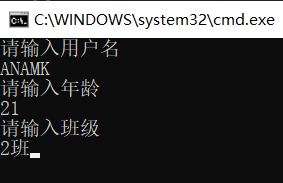
3.
代码:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("您喜欢什么运动呢?"); Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("哈哈,好巧,我也喜欢这个运动"); } }
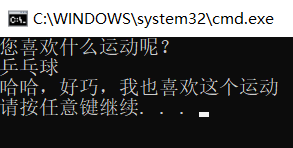
4.

代码:
using System; namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("**********"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("* *"); Console.WriteLine("**********"); } } }
9.1

笔记:
#region 知识点一 折叠代码 //主要作用 是让我们编程时 逻辑更加清晰 //它是由#region #endregion配对出现的 //它的具体作用 是可以将中间包裹的代码折叠起来 避免代码太凌乱 //本质是 编辑器提供给我们的 预处理指令 //它只会在编辑时有用 发布了代码 或执行代码 它会被自动删除 #endregion #region 知识点二 如何申明变量 //变量 可以变化的容器 变量 就是用来存储各种不同类型数值的 一个容器 //不同的 变量类型 可以存储不同类型的值 //变量申明固定写法 //变量类型 变量名 =初始值; //int i = 1; //变量类型 有14种变化 //变量名 我们自定义 要按照一定规则 //初始值 一定要和变量类型是统一 //=和; 是固定的 不变的 //变量类型 //一定要死记硬背 各种变量类型的关键字 //一定要记忆 各种不同变量类型 所能存储的范围 //一定要记忆 各种不同变量类型 所能存储的类型 //1.有符号的整形变量 是能存储 一定范围 正负数包括0的变量类型 //sbyte -128~127 sbyte sb = 1; //潜在知识点 通过+来进行拼接打印 Console.WriteLine("sbyte变量sb中存储的值是:"+sb); //int -21亿~21亿多 int i = 2; //short -32768~32767之间的数 short s = 3; //long -9百万兆~9百万兆之间的数 long l = 4; //2.无符号的整形变量 是能存储 一定范围 0和正数的变量类型 // byte 0~255 byte b = 1; // uint 0~42亿多的一个范围 uint ui = 2; // ushort 0~65535之间的一个数 ushort us = 3; // ulong 0~18百万兆之间的数 ulong ul = 4; //3.浮点数(小数) //float 存储7/8位有效数字 根据编译器不同 有效数字也可能不一样 四舍五入 //有效数字 是从左到右从非0数开始算有效数字的 //之所以要在后面加f 是因为在c#中 声明的小数 默认是double的类型 加f 是告诉系统 它是float类型 float f = 0.1234567890f; Console.WriteLine(f); //double 存储15~17位有效数字 抛弃的数字 会四舍五入 double d = 0.12345678901234567890123456789; Console.WriteLine(d); //decimal 存储27~28位的有效数字 不建议使用 decimal de = 0.123456789012345678901234567890m; Console.WriteLine(de); //4.特殊类型 //bool true false 表示真假的数据类型 真假类型 bool bo = true; bool bo2 = false; Console.WriteLine(bo+"_"+bo2); //char 是用来存储单个字符的变量类型 字符类型 char c = '马'; Console.WriteLine(c); //string 是字符串类型 用来存储多个字符的 没有上线 string str = "ajsfdlajfa手"; Console.WriteLine(str); int x = 1000; Console.WriteLine(x); //变量的使用和修改 不能无中生有 必须要先声明才能用 x = 900; Console.WriteLine(x); #endregion #region 知识点三 为什么有那么多不同的变量类型 // 不同的变量 存储的范围和类型不一样 本质是占用的内存空间不同 // 选择不同的数据(变量)类型装在不同的数据 //姓名 //char string string Name = "ANAMK"; //年龄 byte age = 21; //身高 float height = 177.5f; //体重 float weight = 68.5f; //性别 true女 false男 bool sex = false; //数字 用int 小数用float 字符串用string 真假用bool #endregion #region 知识点四 多个相同类型变量 同时声明 int i2 = 1; float f2 = 3.2f; string str2 = "123"; bool bo3 = true; //多个同类型变量申明 //固定写法 // 变量类型 变量名 =初始值,变量名 =初始值,变量名 =初始值...; int a1 = 1, b1 = 2, c1 = 3, d1 = 4; Console.WriteLine(b1); string s1 = "123", s2 = "234"; Console.WriteLine(s1+s2); #endregion #region 知识点五 变量初始化相关 //变量申明时 可以不设置初始值 但是不建议这样写 这样不安全 int a2; a2 = 1; Console.WriteLine(a2); #endregion

解答:
1.num(注意双引号)
2.因为这样可以让计算机识别数字后面加f的变量是float类型变量,而不是默认的double类型
3.
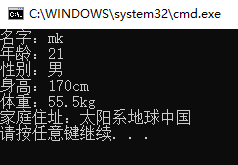
static void Main(string[] args) { string name = "mk"; Console.WriteLine("名字:"+name); int age = 21; Console.WriteLine("年龄:"+age); char sex = '男'; Console.WriteLine("性别:"+sex); int height = 170; Console.WriteLine("身高:"+height+"cm"); float weight = 55.5f; Console.WriteLine("体重:"+weight+"kg"); string location = "太阳系地球中国"; Console.WriteLine("家庭住址:"+location); }
2023-09-08
学了一点
2023-09-09
Lesson3_变量本质
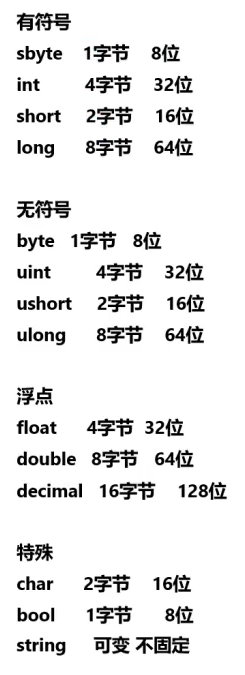
#region 知识点一 变量的存储空间(内存中) // 1byte =8bit // 1KB =1024byte // 1MB =1024KB // 1GB =1024MB // 1T =1024GB //通过sizeof方法 可以获取变量类型所占的内存空间(单位:字节) //有符号 int sbyteSize = sizeof(sbyte); Console.WriteLine("sbyte所占的字节数为"+sbyteSize); int intSize = sizeof(int); Console.WriteLine("int所占的字节数为"+intSize); int shortSize = sizeof(short); Console.WriteLine("short所占的字节数为"+shortSize); int longSize = sizeof(long); Console.WriteLine("long所占的字节数为"+longSize); Console.WriteLine("********************************************"); //无符号 int byteSize = sizeof(byte); Console.WriteLine("byte所占的字节数为" + byteSize); int uintSize = sizeof(uint); Console.WriteLine("uint所占的字节数为" + uintSize); int ushortSize = sizeof(ushort); Console.WriteLine("ushort所占的字节数为" + ushortSize); int ulongSize = sizeof(ulong); Console.WriteLine("ulong所占的字节数为" + ulongSize); Console.WriteLine("********************************************"); //浮点数 int floatSize = sizeof(float); Console.WriteLine("float所占的字节数为" + floatSize); int doubleSize = sizeof(double); Console.WriteLine("double所占的字节数为" + doubleSize); int decimalSize = sizeof(decimal); Console.WriteLine("decimal所占的字节数为" + decimalSize); //特殊类型 int boolSize = sizeof(bool); Console.WriteLine("bool所占的字节数为" + boolSize); int charSize = sizeof(char); Console.WriteLine("char所占的字节数为" + charSize); //sizeof是不能够得到string类型所占的内存大小的 //因为字符串长度是可变的,不定的 //int stringSize = sizeof(string); #endregion #region 知识点二 变量的本质 //变量的本质是2进制→计算机中所有数据的本质都是二进制 是一堆0和1 //为什么是2进制? //数据传递只能通过电信号 只有开和关两种状态。所以就用0和1来表示这两种状态 //计算机中的存储单位最小为bit(位),他只能表示0和1两个数字 //1bit就是1个数,要不是0要不是1 //为了方便数据表示 //出现了一个叫byte(字节)的单位,它是由8个bit组成的存储单位。 //所以我们一般说一个字节为8位 //2进制和10进制的对比 //2进制和10进制之间的相互转换 #endregion

2023-09-10
Lesson4_变量的命名规范
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("变量的命名规则"); #region 知识点一:必须遵守的规则 //1.不能重名 //2.不能以数字开头 //3.不能使用程序关键字命名 //4.不能有特殊符号(下划线除外) //建议的命名规则:变量名要有含义——>用英文(拼音)表示变量的作用 //非常不建议的命名规则:用汉字命名 #endregion #region 知识点二:常用命名规则 //驼峰命名法——首字母小写,之后单词首字母大写(变量) string myName = "mk"; string yourName = "wlx"; //帕斯卡命名法——所有单词首字母都大写(函数、类) string MyName = "ANAM"; //潜在知识点——C#中对大小写是敏感的 是区分的 #endregion }

1、No.1、3day、$money、discount_ 1、Shang Hai、class、int、_ 2C
2、
static void Main(string[] args) { int myAge = 21; char mySex = '男'; float myAttack = 3.141592653f; float myDefense = 2.71828f; double yourHeight = 169.9; double yourWeight = 55.5; }
Lesson5_常量
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("常量"); #region 知识点一 常量的申明 //关键字 const //固定写法: //const 变量类型 变量名 =初始值; //变量的声明 int i = 10; //常量的申明 const int i2 = 20; #endregion #region 常量的特点 //1.必须初始化 //2.不能被修改 //变量申明可以不初始化 string name; //之后可以来修改 name = "123"; name = "345"; const string myName = "ANAM"; //作用:申明一些常用不变的变量 //PI 3.1415926 const float PI = 3.141592653f; Console.WriteLine(PI); #endregion }

1、必须初始化,不能被修改
2、用来定义一些恒定的值,比如π和重力加速度之类
2023-09-11
Lesson6_转义字符
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("转义字符"); #region 知识点一 转义字符的使用 //什么是转义字符? //它是字符串的一部分 用来表示一些特殊含义的字符 //比如: 在字符串中表现 单引号 引号 空行等等 #region 固定写法 //固定写法 \字符 //不同的\和字符的组合 表示不同的含义 //常用转义字符 //单引号 \' string str = "\'哈哈哈\'"; Console.WriteLine(str); //双引号 \" str = "\"哈哈哈\""; Console.WriteLine(str); //换行 \n str = "123\n321"; Console.WriteLine(str); //斜杠 \\ 计算机文件路径要用到\符号的 str = "哈\\哈哈"; Console.WriteLine(str); //不常用转义字符(了解) //制表符(空一个tab键)\t str = "哈\t哈哈"; Console.WriteLine(str); //光标退格 \b str = "123\b123"; Console.WriteLine(str); //空字符 \0 str = "1234\0123"; Console.WriteLine(str); //警报音 \a str = "\a"; Console.WriteLine(str); Console.WriteLine("12312\n123123123\a123\t123"); #endregion #endregion #region 知识点二 取消转义字符 string str2 = @"哈哈\哈哈"; Console.WriteLine(str2); Console.WriteLine(@"\n\\"); #endregion }
Lesson7_类型转换(隐式转换)
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("类型转换——隐式转换"); //什么是类型转换 //类型转换 就是不同变量类型之间的相互转还能 //隐式转换的基本规则——>不同类型之间自动转换 //大范围装小范围 #region 知识点一 相同大类型之间的转换 //有符号 long——>int——>short——>sbyte long l = 1; int i = 1; short s = 1; sbyte sb = 1; //隐式转换 int隐式转换成了long //可以用大范围 装小范围的 类型 (隐式转换) l = i; //不能够用小范围的类型去装在大范围的类型 //i =l; //无符号 ulong——>uint——>ushort——>byte //浮点数 decimal double——>float decimal de = 1.1m; double d = 1.1; float f = 1.1f; //decimal这个类型 没有办法用隐式转换的形式 去存储 double和float //de = d; //de = f; //float 是可以隐式转换成double d = f; //特殊类型 bool char string //他们之间 不存在隐式转换 bool b = true; char c = 'A'; string str = "12123"; #endregion #region 知识点二 不同大类型之间的转换 #region 无符号和有符号之间 //无符号 不能装负数 byte b2 = 1; //0~255 ushort us2 = 1; uint ui2 = 1; ulong ul2 = 1; //有符号 sbyte sb2 = 1; short s2 = 1; int i2 = 1; long l2 = 1; //无符号装有符号 //有符号的变量 是不能够 隐式转换成 无符号的 //b2 = sb2; //us2 = sb2; //ul2 = sb2; //有符号装无符号 //有符号变量 是可以 装 无符号变量的 前提是 范围一定是涵盖的 存在隐式转换 //i2 = ui2;//因为 有符号的变量 可能会超过 这个无符号变量的范围 i2 = b2;//因为 有符号的变量 不管是多少 都在 无符号变量的范围内 #endregion #region 浮点数和整数(有、无符号)之间 //浮点数装整数 整形转为浮点数 是存在隐式转换的 float f2 = 1.1f; double d2 = 1.1; decimal de2 = 1.1m; //浮点数 是可以装载任何类型的 整数的 f2 = l2; f2 = i2; f2 = s2; f2 = sb2; f2 = ul2; f2 = ui2; f2 = us2; f2 = b2; f2 = 10000000000000000000; Console.WriteLine(f2); //decimal 不能隐式存储 float和double //但是它可以隐式的存储整形 de = l2; de = ul2; //double——>float——>所有整形(无符号、有符号) //decimal——>所有整形(无符号、有符号) //整数装浮点数 整数是不能隐式存储 浮点数 因为 整数 不能存小数 #endregion #region 特殊类型和其他类型之间 //bool bool没有办法和其它类型 相互隐式转换 //char char 没有办法隐式的存储 其它类型的变量 //char类型 可以隐式的转换成 整形和浮点型 //char隐式转换成 数值类型是 //对应的数字 其实是一个 ASCII码 //计算机里面存储 2进制 // 字符 中文 英文 标点符号 在计算机中都是一个数字 //一个字符 对应一个数字 ASCII码就是一种对应关系 char c2 ='a'; i2 = c2; Console.WriteLine(i2); //string 类型 无法和其它类型进行隐式转换 #endregion #endregion //总结 //高精度(大范围)装低精度(小范围) //double——>float——>整数(无符号、有符号)——>char //decimal——>整数(无符号、有符号)——>char //string和bool 不参与隐式转换规则的 }

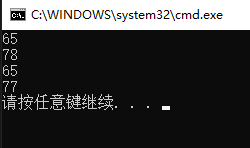
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int i1, i2, i3, i4; char n1 = 'A'; char n2 = 'N'; char n3 = 'A'; char n4 = 'M'; i1 = n1; i2 = n2; i3 = n3; i4 = n4; Console.WriteLine(i1); Console.WriteLine(i2); Console.WriteLine(i3); Console.WriteLine(i4); } }

2023-10-08
Lesson8_显示转换
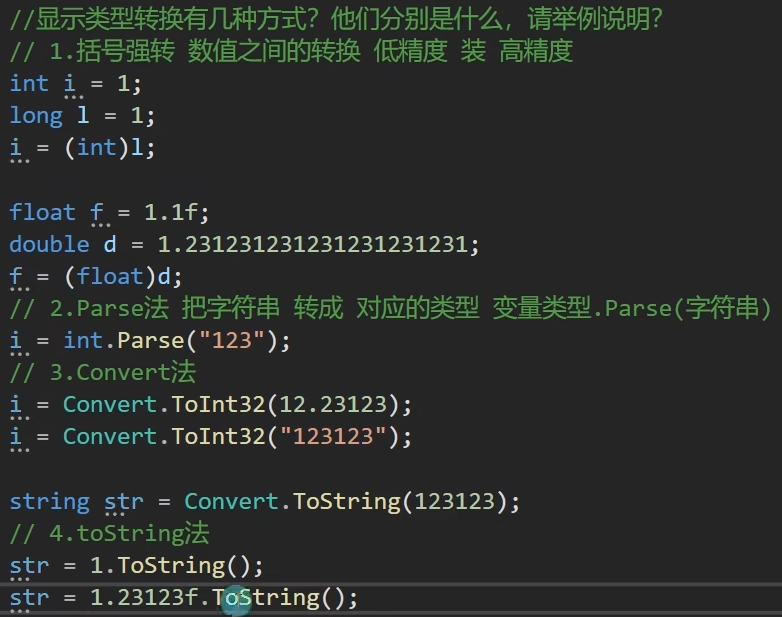
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("类型转换——显示转换"); //显示转换——>手动处理 强制转换 #region 知识点一 括号强转 //作用 一般情况下 将高精度的类型强制转换为低精度 //语法: 变量类型 变量名 =(变量类型)变量; //注意: 精度问题 范围问题 //相同大类的整形 //有符号整形 sbyte sb = 1; short s = 1; int i = 40000; long l = 1; //括号强转 可能会出现范围问题 造成的异常 s = (short)i; Console.WriteLine(s); i = (int)l; sb = (sbyte)s; sb = (sbyte)i; sb = (sbyte)l; //无符号整形 byte b = 1; uint ui = 1; b = (byte)ui; //浮点之间 float f = 1.1f; double d = 1.1234567890123456789f; f = (float)d; Console.WriteLine(f); //无符号和有符号 uint ui2 = 1; int i2 = -1; //在强转时 一定要注意范围 不然得到的结果 可能有异常 ui2 = (uint)i2; Console.WriteLine(ui2); i2 = (int)ui2; //浮点和整形 浮点数强转成整数时 会直接抛弃掉小数点后面的小数 i2 = (int)1.64f; Console.WriteLine(i2); //char和数值类型 i2 = 'A'; char c = (char)i2; Console.WriteLine(c); //bool和string是不能够通过 括号强转的 //bool bo = true; //int i3 = (bool)bo; //string str ="123"; //i3 =(int)str; #endregion #region 知识点二 Parse法 //作用 把字符串类型转换为对应的类型 //语法: 变量类型.Parse("字符串") //注意: 字符串必须能够转换成对应类型 否则报错 //有符号 //string str2 = "123"; int i4 = int.Parse("123"); Console.WriteLine(i4); //我们填写字符串 必须是要能够转成对应类型的字符 如果不符合规则 会报错 //i4 = int.Parse("123.45"); //Console.WriteLine(i4); // 值的范围 必须是能够被变量存储的值 否则报错 //short s3 = short.Parse("40000"); //Console.WriteLine(s3); sbyte sb3 = sbyte.Parse("1"); Console.WriteLine(sb3); //他们的意思是相同的 Console.WriteLine(sbyte.Parse("1")); Console.WriteLine(long.Parse("123123")); //无符号 Console.WriteLine(byte.Parse("1")); Console.WriteLine(ushort.Parse("1")); Console.WriteLine(ulong.Parse("1")); Console.WriteLine(uint.Parse("1")); //浮点数 float f3 = float.Parse("1.2323"); double d3 = double.Parse("1.2323"); //特殊类型 bool b5 = bool.Parse("true"); Console.WriteLine(b5); char c2 = char.Parse("A"); Console.WriteLine(c2); #endregion #region 知识点三 Convert法 //作用 更准确的将 各个类型之间进行相互转换 //语法: Convert.To目标类型(变量或常量) //注意: 填写的变量或常量必须正确 否则出错 //转字符串 如果是把字符串转对应类型 那字符串一定要合法合规 int a = Convert.ToInt32("12"); Console.WriteLine(a); //精度更准确 // 精度比括号强转好一点 会四舍五入 a = Convert.ToInt32(1.45845f); Console.WriteLine(a); //特殊类型转换 //把bool类型也可以转成 数值类型 true对应1 false对应0 a = Convert.ToInt32(true); Console.WriteLine(a); a = Convert.ToInt32(false); Console.WriteLine(a); a = Convert.ToInt32('A'); Console.WriteLine(a); //每一个类型都存在对应的 Convert中的方法 sbyte sb5 = Convert.ToSByte("1"); short s5 = Convert.ToInt16("1"); int i5 = Convert.ToInt32("1"); long l5 = Convert.ToInt64("1"); byte b6 = Convert.ToByte("1"); ushort us5 = Convert.ToUInt16("1"); uint ui5 = Convert.ToUInt32("1"); ulong ul5 = Convert.ToUInt64("1"); float f5 = Convert.ToSingle("13.2"); double d5 = Convert.ToDouble("13.2"); decimal de5 = Convert.ToDecimal("13.2"); bool bo5 = Convert.ToBoolean("true"); char c5 = Convert.ToChar("A"); string str5 = Convert.ToString(123123); #endregion #region 知识点四 其它类型转string //作用:拼接打印 //语法:变量.toString(); string str6 = 1.ToString(); str6 = true.ToString(); str6 = 'A'.ToString(); str6 = 1.2f.ToString(); int aa = 1; str6 = aa.ToString(); bool bo6 = true; str6 = bo6.ToString(); //当我们进行字符串拼接时 就自动会调用 tostring转成string Console.WriteLine("123123" + 1 + true); str6 = "123123" + 1 + true + 1.23; #endregion }

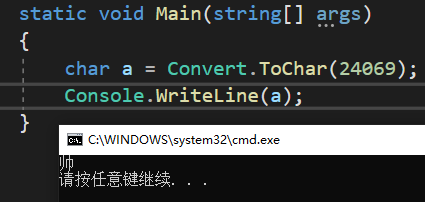
2023-10-10
Lesson9_异常捕获
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("异常捕获"); #region 作用 //将玩家输入的内容 存储 string类型的变量(容器)中 //string str = Console.ReadLine(); //Parse转字符串为 数值类型时 必须 要合法合规 //int i = int.Parse(str); //通过对异常捕获的学习 可以避免当代码报错时 造成程序卡死的情况 #endregion #region 基本语法 //必备部分 try { //希望进行异常捕获的代码块 //放到try中 //如果try中的代码 报错了 不会让程序卡死 } catch { //如果出错了 会执行 catch中的代码 来捕获异常 //catch(Exception e)具体报错跟踪 通过e得到 具体的错误信息 } //可选部分 finally { //最后执行的代码 不管有没有出错 都会执行其中的代码 //目前 大家可以不用写 } //注意:异常捕获代码基本结构中 不需要加; 在里面去写代码逻辑时 每一句代码才加; #endregion #region 实践 try { string str = Console.ReadLine(); int i = int.Parse(str); Console.WriteLine(i); } catch { Console.WriteLine("请输入合法数字"); } //finally //{ // Console.WriteLine("执行完毕"); //} #endregion } }

第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) { try { Console.WriteLine("请输入一个数字:"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int i = int.Parse(str); } catch { Console.WriteLine("用户输入错误"); } }
第二题:
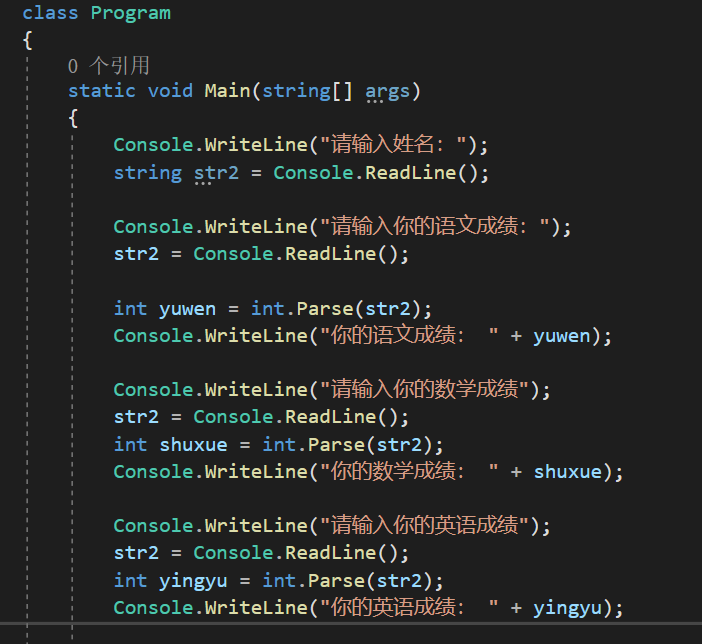
static void Main(string[] args) { try { Console.WriteLine("请输入用户名"); string yourName = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入语文成绩:"); string yuWenStr = Console.ReadLine(); int yuwen = int.Parse(yuWenStr); Console.WriteLine("请输入数学成绩"); //一步到位的写法 int shuXue = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); Console.WriteLine("请输入英语成绩"); int yingYu = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); } catch { Console.WriteLine("你的输入不合法,成绩请输入数字"); } }
2023-10-14
Lesson10_算数运算符
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("算数运算符"); //算数运算符 是用于 数值类型变量计算的运算符 //它的返回结果是数值 #region 知识点一:赋值符号 // = // 关键知识点 : // 先看右侧 再看左侧 把右侧的值赋值给左侧的变量 string myName = "mk"; int myAge = 18; float myHeight = 177.5f; #endregion #region 知识点二:算数运算符 #region 加 + // 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int i = 1; //3 i = i + 2; Console.WriteLine(i); // 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 // 99 i = 1 + 3 + 89 + i + i; Console.WriteLine(i); //4 i = 1 + 2 + 1; Console.WriteLine(i); // 初始化时就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int i2 = 1 + 2 + 4 + i; Console.WriteLine(i2); #endregion #region 减 - // 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int j = 1; j = j - 1; Console.WriteLine(j); // 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 j = 1 - 2 - 3; Console.WriteLine(j); j = 1 - j; Console.WriteLine(j); // 初始化就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int j2 = 1 - j - 0; Console.WriteLine(j2); #endregion #region 乘 * // 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int c = 1; c = c * 10; Console.WriteLine(c); // 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 c = 1 * 2 * 3; Console.WriteLine(c); c = 2 * c * 2; Console.WriteLine(c); // 初始化就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int c2 = c * 2; Console.WriteLine(c2); #endregion #region 除 / // 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int chu = 1; chu = 10 / chu; Console.WriteLine(chu); // 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 // 初始化就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 chu = 1; chu = 1 / 2; Console.WriteLine(chu); //默认的整数 是int 如果用来做除法运算 要注意 会丢失小数点后的小数 //如果你想用浮点数来存储 一定是 在运算时要有浮点数的特征 float f = 1 / 2f; Console.WriteLine(f); #endregion #region 取余 % // 用自己计算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 int y = 4; // 4 / 2 得到余数0 y = y % 3; Console.WriteLine(y); // 连续运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 y = 4 % 3 % 2; Console.WriteLine(y); // 初始化就运算 先算右侧结果 再赋值给左侧变量 #endregion #endregion #region 知识点三:算术运算符的 优先级 //优先级 是指 在混合运算时的运算顺序 //乘除取余 优先级高于 加减 先算乘除取余 后算加减 // 1 + 3 + 1 +6 int a = 1 + 2 * 3 / 2 + 1 + 2 * 3; Console.WriteLine(a); a = 1 + 4 % 2 * 3 / 2 + 1; Console.WriteLine(a); //括号可以改变优先级 优先计算括号内内容 a = 1 + 4 % (2 * 3 / 2) + 1; //多组括号 先算最里层括号 依次往外算 a = 1 + (4 % (2 * (3 / 2))) + 1; Console.WriteLine(a); #endregion #region 知识点四:算术运算符的 复合运算符 // 固定写法 运算符= // += -= *= /= %= //复合运算符 是用于 自己=自己进行运算 int i3 = 1; i3 = i3 + 2; Console.WriteLine(i3); i3 = 1; i3 += 2;//i3 = i3 + 2; Console.WriteLine(i3); i3 = 2; i3 += 2;//4 i3 -= 2;//2 i3 /= 2;//1 i3 *= 2;//2 i3 %= 2;//0 Console.WriteLine(i3); int i4 = 10; // i4+=20*2/10; Console.WriteLine(i4); //注意:复合运算符 只能进行一种运算 不能混合运算 //i4 */-= 2; #endregion #region 知识点五:算术运算符的 自增减 int a2 = 1; a2 = a2 + 1; a2 = 1; a2 += 1; //自增运算符 让自己+1 a2 = 1; a2++;//先用再加 Console.WriteLine(a2); ++a2;//先加再用 Console.WriteLine(a2); a2 = 1; Console.WriteLine(a2++);//1 //2 Console.WriteLine(++a2);//3 //自减运算符 让自己-1 a2 = 1; a2--;//先用再减 --a2;//先减再用 a2 = 1; Console.WriteLine(a2--);//1 //0 Console.WriteLine(--a2);//-1 #endregion }

第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入你的年龄"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int age = int.Parse(str); Console.WriteLine("十年后你的年龄是" + (age + 10)); }

第二题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int r = 5; Console.WriteLine("半径为5的圆的面积为" + (Math.PI*r*r)); Console.WriteLine("半径为5的周长为" + 2 * Math.PI * r); }
第三题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入你的c#成绩:"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int score1 = int.Parse(str); Console.WriteLine("请输入你的Unity成绩:"); string str2 = Console.ReadLine(); int score2 = int.Parse(str2); Console.WriteLine("请输入你的Math成绩:"); string str3 = Console.ReadLine(); int score3 = int.Parse(str3); Console.WriteLine("三门成绩的总分是:" + (score1 + score2 + score3)); Console.WriteLine("三门成绩的平均分是:" + (score1 + score2 + score3) /3); }
第四题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int tprice = 285; int kuprice = 720; Console.WriteLine("2件T恤和3条裤子的价格是:" + (2 * tprice + 3 * kuprice)); Console.WriteLine("2件T恤和3条裤子的价格打完3.8折是:" + (2 * tprice + 3 * kuprice)*0.38); }
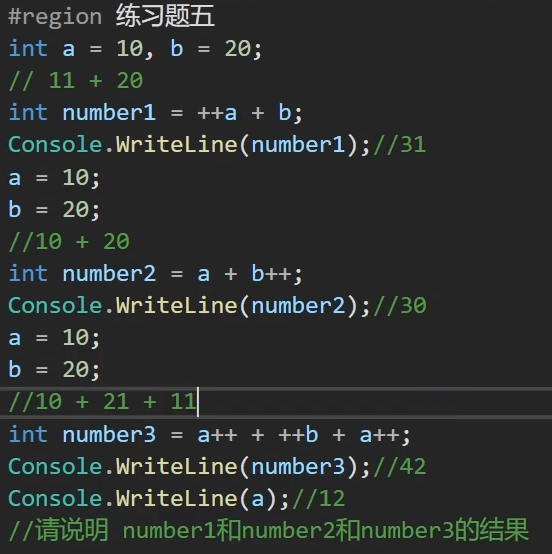
第五题:
31,30,42
第六题:
static void Main(string[] args) { //法一 int a = 99, b = 87; Console.WriteLine("交换前a为" + a); Console.WriteLine("交换前b为" + b); int c; c = b; b = a; a = c; Console.WriteLine("交换后a为" + a); Console.WriteLine("交换后b为" + b); //法二 }

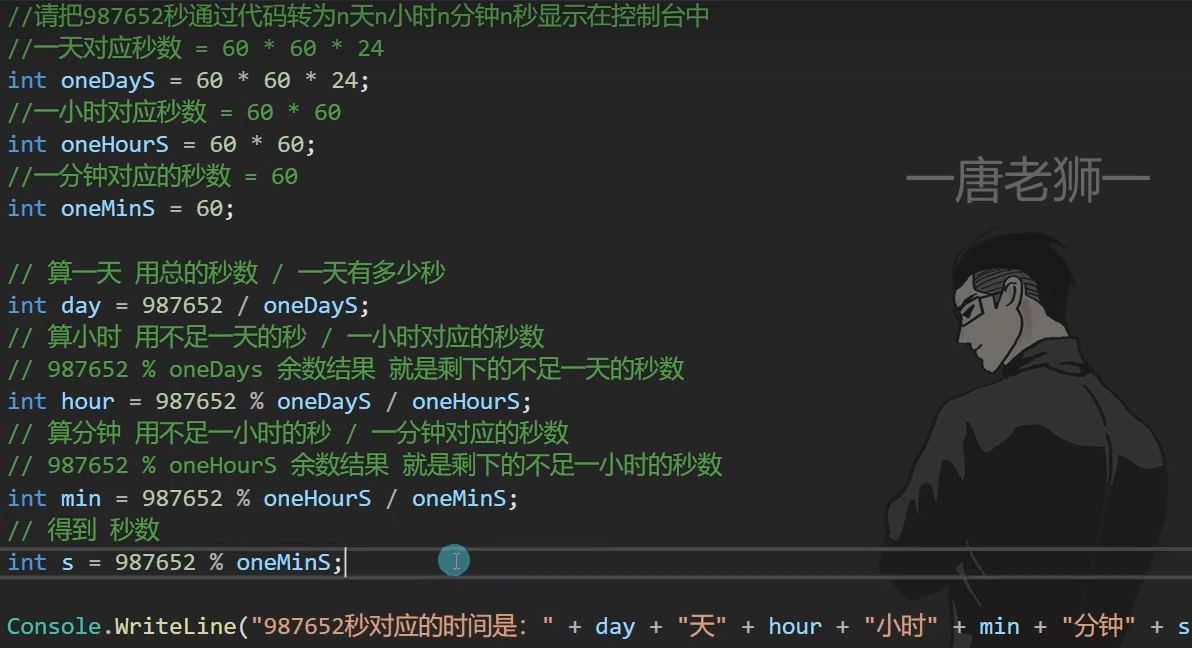
第七题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int second = 987652; int day = (second/ (24 * 60 * 60)); int hour = ((second - (day * 24* 60 * 60)) /(60*60)); int minute = (second- (day * 24 * 60 * 60) - (hour * 60 * 60)) / 60; int seconds = second - (day * 24 * 60 * 60) - (hour * 60 * 60) - minute * 60; Console.WriteLine("现在是:"+day+"天"+hour+"小时"+minute+"分钟"+seconds+"秒"); }
2023-10-17
Lesson11_字符串拼接
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 知识点一 字符串拼接方式1 //之前的算数运算符 只是用来数值类型变量进行数学运算的 //而string不存在算数运算符不能计算 但是可以通过+号来进行字符串拼接 string str = "123"; //用+号进行字符串拼接 str = str + "456"; Console.WriteLine(str); str = str + 1; Console.WriteLine(str); // 复合运算符 += str = "123"; str += "1" + 4 + true; Console.WriteLine(str); str += 1 + 2 + 3 + 4; Console.WriteLine(str); str += "" + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4; Console.WriteLine(str); str = ""; str += 1 + 2 + "" + (3 + 4); Console.WriteLine(str); str = str + (1 + 2 + 3); Console.WriteLine(str); //注意: 用+号拼接 是用符号唯一方法 不能用-*/%.... #endregion #region 知识点二 字符串拼接方式2 //固定语法 //string.Format("待拼接的内容",内容1,内容2,......); //拼接内容中的固定规则 //想要被拼接的内容用占位符替代 {数字} 数字:0~n 依次往后 string str2 = string.Format("我是{0},我今年{1}岁,我想要{2}", "mk", "23", "学好unity,找个好工作"); Console.WriteLine(str2); str2 = string.Format("x{0}y{1}z{2}", 1, 2, 3); Console.WriteLine(str2); #endregion #region 控制台打印拼接 //后面的 内容 比占位符多 不会报错 //后面的 内容 比占位符少 会报错 Console.WriteLine("A{0}B{1}C{2}", 1, true,false,1,2); Console.Write("A{0}B{1}C{2}", 1, true); #endregion } }

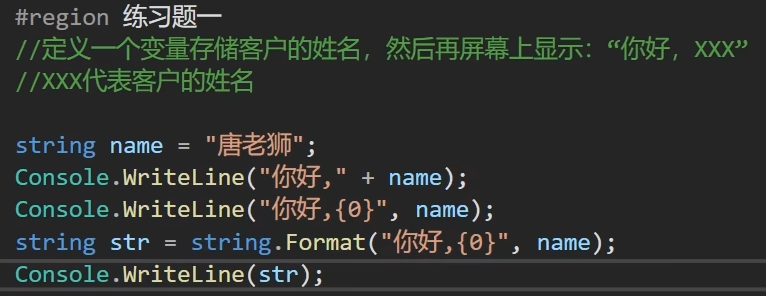
第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("请输入存储客户的姓名"); string name = Console.ReadLine(); string str = "你好," + name; Console.WriteLine(str); }
第二题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入客户姓名"); string name = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入客户年龄"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int age = int.Parse(str); Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}岁了", name, age); }
第三题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入姓名:"); string name = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入年龄:"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int age = int.Parse(str); Console.WriteLine("请输入邮箱:"); string email = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入家庭住址:"); string address = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入期望工资:"); string str2 = Console.ReadLine(); int money = int.Parse(str2); Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0},年龄:{1},邮箱:{2},地址:{3},期望工资:{4}",name,age,email,address,money); }
第四题:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入用户名:");
string name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("请输入年龄:");
string str = Console.ReadLine();
int age = int.Parse(str);
Console.WriteLine("请输入班级:");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
int banji = int.Parse(str2);
Console.WriteLine("用户名:{0},年龄:{1},班级:{2}",name,age,banji);
}
这里直接使用string就可以,不需要转成int类型
2023-10-18
lesson12_条件运算符
static void Main(string[] args) { #region 知识点一 条件运算符 // 用于比较两个变量或常量 // 是否大于 > // 是否小于 < // 是否等于 == // 是否不等于 != // 是否大于等于 >= // 是否小于等于 <= // 条件运算符 一定存在左右两边的内容 // 左边内容 条件运算符 右边内容 int a = 5; int b = 10; //条件运算符 不能直接这样使用 //纯比较不用结果 那么对于我们来说 没有任何的意义 //a>b; // 比较的结果 返回的是 一个 bool 类型的值 // true和false 如果比较的条件满足 那就返回true 不满足 就返回false // 先算右边 再赋值给左边 bool result = a > b; Console.WriteLine(result); result = a < b; Console.WriteLine(result); result = a >= b; Console.WriteLine(result); result = a <= b; Console.WriteLine(result); result = a == b; Console.WriteLine(result); result = a != b; Console.WriteLine(result); #endregion #region 知识点二 各种应用写法 //变量和变量比较 a = 5; b = 10; result = a < 10;// true //变量和数值(常量)比较 result = a < 10;// true result = b > 5;// true //数值和数值比较 result = 5 > 3;//true result = 5 == 3;//false result = 5 != 3;//true //计算结果比较 //条件运算符的 优先级 低于算数运算符 // 8>6 // 先计算 再比较 result = a + 3 > a - 2 + 3;// true result = 3 + 3 < 5 - 1;//false //左边 条件运算符 右边 #endregion #region 知识点三 不能进行范围比较 a = 5; //判断是否在两个值之间 // 1 < a < 6; //在c#中都不能这样写 //result = 1 < a < 6; //要判断 一个变量是否在两个数之间 要结合 逻辑运算符的知识点 #endregion #region 知识点四 不同类型之间的比较 //不同数值类型之间 可以随意进行条件运算符比较 int i = 5; float f= 1.2f; double d= 12.4f; short s= 2; byte by = 20; uint ui = 222; //只要是数值 就能够进行条件运算符比较 比较大于小于等于等等 result = i > f; result = f < d; result = i > by; result = f > ui; result = ui > d; //特殊类型 char string bool 只能同类型进行 == 和 != 比较 string str = "123"; char c = 'A'; bool bo = true; result = str == "234";//false result = str == "123";//true result = str != "123";//false result = c == 'B';//false //不仅可以和自己类型进行 == !=还可以和数值类型进行比较 //还可以和 字符类型进行大小比较 result = c > 123; result = bo == true;//true #endregion }

第一题:
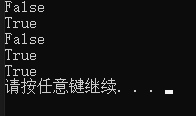
false,false,fasle,true
第二题:
第三题:
最终打印结果为true
lesson13_逻辑运算符
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("逻辑运算符"); //对bool类型 进行逻辑运算 #region 知识点一 逻辑与 //符号 && 并且 //规则 对两个bool值进行逻辑运算 有假则假 同真为真 bool result = true && false; Console.WriteLine(result); result = true && true; Console.WriteLine(result); result = false && true; Console.WriteLine(result); //bool相关的类型 bool变量 条件运算符 //逻辑运算符优先级 低于 条件运算符 算术运算 //true && true result = 3 > 1 && 1 < 2; Console.WriteLine(result); int i = 3; //1<i<5; //true&&true result = i > 1 && i < 5; Console.WriteLine(result); //多个逻辑与 组合运用 int i2 = 5; // true && false && true && true //在没有括号的情况下 从左到右 依次看即可 //有括号 先看括号内 result = i2 > 1 && i2 < 5 && i2 > 1 && i < 5; Console.WriteLine(result); #endregion #region 知识点二 逻辑或 //符号 || 或者 //规则 对两个bool值进行逻辑运算 有真则真 同假为假 result = true || false; Console.WriteLine(result); result = true || true; Console.WriteLine(result); result = false || true; Console.WriteLine(result); result = false || false; Console.WriteLine(result); //false||true result = 3 > 10 || 3 < 5; Console.WriteLine(result);//true int a = 5; int b = 11; // true || true || false result = a > 1 || b < 20 || a > 5; Console.WriteLine(result); //?&&? //?||? //?可以是写死的bool变量 或者 bool值 //还可以是 条件运算符相关 #endregion #region 知识点三 逻辑非 //符号 ! //规则 对一个bool值进行取反 真变假 假变真 result = !true; Console.WriteLine(result); result = !false; Console.WriteLine(result); result = !!true; Console.WriteLine(result); //逻辑非的 优先级 较高 result = !(3 > 2); Console.WriteLine(result); a = 5; result = !(a > 5); Console.WriteLine(result); #endregion #region 知识点四 混合使用优先级问题 //规则 !(逻辑非)优先级最高 &&(逻辑与)优先级高于||(逻辑或) // 逻辑运算符优先级 优于 算术运算符 条件运算符(逻辑非除外) bool gameOver = false; int hp = 100; bool isDead = false; bool isMustOver = true; //false || false && true || true; //false || false || true; result = gameOver || hp < 0 && !isDead || isMustOver; Console.WriteLine(result); #endregion #region 知识点五 逻辑运算符短路规则 int i3 = 1; // || 有真则真 // 只要 逻辑与或者逻辑或 左边满足了条件 // i3 > 0 true // 只要 满足条件 右边的内容 对于我们来说 已经不重要 //逻辑或 有真则真 那左边只要为真了 右边就不重要 result = i3 > 0 || ++i3 >= 1; Console.WriteLine(i3); Console.WriteLine(result); // false && i3 ++ > 1;抛弃后面不去计算 //逻辑与 有假则假 那左边只要为假了 右边就不重要 result = i3 < 0 && i3++ > 1; Console.WriteLine(i3); Console.WriteLine(result); #endregion }

第一题:
true,true,true,false,false
第二题:
true
lesson14_位运算符
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("位运算符"); //位运算符 主要用数值类型进行计算的 //将数值转换为2进制 再进行位运算 #region 知识点一 位与 & // 规则 连接两个数值进行位计算 将数值转为2进制 // 对位运算 有0则0 int a = 1;// 001 int b = 5;// 101 // 001 //& 101 // 001 = 1 int c = a & b; Console.WriteLine(c); a = 3;// 011 b = 19;// 10011 // 00011 //& 10011 // 00011 c = a & b;//3 Console.WriteLine(c); //多个数值进行位运算 没有括号时 从左到右 依次计算 a = 1;// 001 b = 5;// 101 c = 19;// 10011 // 00001 //& 00101 // 00001 //& 10011 // 00001 int d = a & b & c; Console.WriteLine(d); a = 1;//001 b = 2;//010 Console.WriteLine(a & b); #endregion #region 知识点二 位或 | // 规则 连接两个数值进行位计算 将数值转为2进制 // 对位运算 有1则1 a = 1;//001 b = 3;//011 c = a | b; // 001 //| 011 // 011 Console.WriteLine(c); a = 5; // 101 b = 10; // 1010 c = 20; // 10100 // 00101 // 01010 // 01111 // 10100 // 11111 => 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16 = 31 Console.WriteLine(a | b | c); #endregion #region 知识点三 异或 ^ // 规则 连接两个数值进行位计算 将数值转为2进制 // 对位运算 相同为0 不同为1 a = 1; //001 b = 5; //101 // 001 //^ 101 // 100 c = a ^ b; Console.WriteLine(c); a = 10; // 1010 b = 11; // 1011 c = 4; // 100 // 1010 //^ 1011 // 0001 //^ 0100 // 0101 = 5 Console.WriteLine(a ^ b ^ c); #endregion #region 知识点四 位取反 ~ // 规则 写在数值前面 将数值转为2进制 // 对位运算 0变1 1变0 a = 5; // 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101 // 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1010 // 反码补码知识 c = ~a; Console.WriteLine(c); #endregion #region 知识点五 左移<< 和 右移 >> // 规则 让一个数的2进制数进行左移和右移 // 左移几位 右侧加几个0 a = 5; // 101 c = a << 5; // 1位 1010 // 2位 10100 // 3位 101000 // 4位 1010000 // 5位 10100000 = 32 + 128 = 160 Console.WriteLine(c); // 右侧几位 右侧去掉几个数 a = 5; // 101 c = a >> 2; // 1位 10 // 2位 1 Console.WriteLine(c); #endregion }

第一题:
560(1000110000)
33(100001)
第二题:
66
93
lesson15_三目运算符
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("三目运算符"); #region 知识点一 基本语法 //套路: 3个空位 2个符号!!! //固定语法:空位 ?空位 :空位 //关键信息:bool类型 ?bool类型为真返回内容 :bool类型为假返回内容; //三目运算符 会有返回值,这个返回值类型必须一致,并且必须使用! #endregion #region 知识点二 具体使用 string str = false ? "条件为真" : "条件为假"; Console.WriteLine(str); int a = 5; str = a < 1 ? "a大于1" : "a不满足条件"; Console.WriteLine(str); int i = a > 1 ? 123 : 234; //第一个空位 始终是结果为bool类型的表达式 bool变量 条件表达式 逻辑运算符表达式 //第二三个空位 什么表达式都可以 只要保证他们的结果类型是一致的 bool b = a > 1 ? a > 6 : !false; #endregion }

第一题:
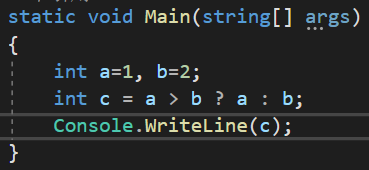
答案:

第二题:
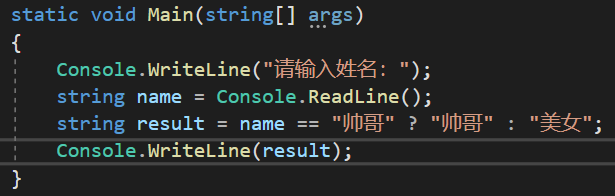
第三题:
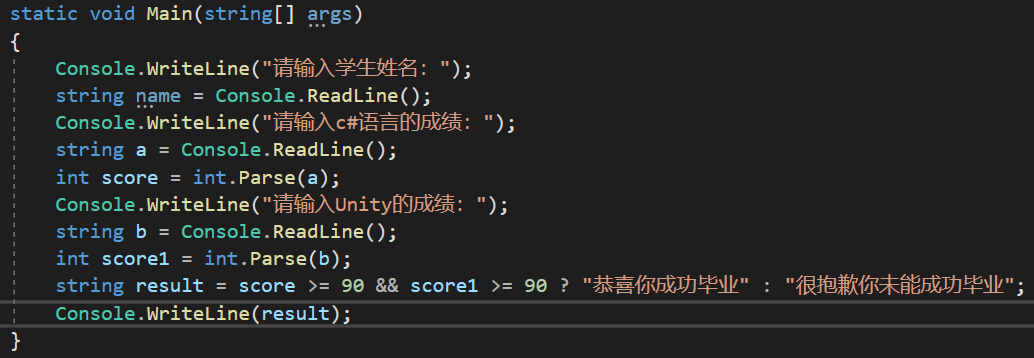
第四题:
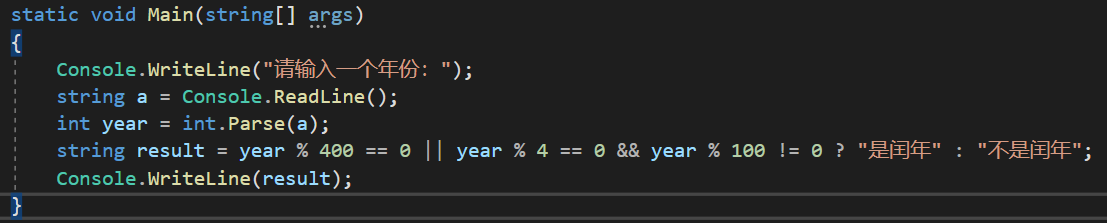
Lesson16_条件分支语句_if
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Lesson16_条件分支语句_if { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("条件分支语句"); #region 知识点一 作用 //让顺序执行的代码 产生分支 //if语句是第一个 可以让我们的程序 产生逻辑变化的 语句 #endregion #region 知识点二 if语句 //作用: 满足条件时 多执行一些代码 //语法: // if(bool类型值) // bool类型相关:bool变量 条件运算符表达式 逻辑运算符表达式 //{ // 满足条件要执行的代码 写在if代码块中; //} // 注意: // 1.if语句的语法部分, 不需要写分号 // 2.if语句可以嵌套使用 if (false) { Console.WriteLine("进入了if语句代码块,执行其中的代码逻辑"); Console.WriteLine("进入了if语句代码块,执行其中的代码逻辑"); Console.WriteLine("进入了if语句代码块,执行其中的代码逻辑"); } Console.WriteLine("if语句外的代码"); int a = 1; if (a > 0 && a < 5) { Console.WriteLine("a在0到5之间"); } string name = "唐老师"; string password = "666"; if(name =="唐老师"&&password =="666") { Console.WriteLine("登陆成功"); } //嵌套使用 if(name == "唐老狮") { Console.WriteLine("用户名验证成功"); if (password == "666") { Console.WriteLine("密码验证成功"); //可以无限嵌套 } //可以无限嵌套 } #endregion #region 知识点三 if...else语句 // 作用: 产生两条分支 十字路 满足条件做什么 不满足条件做什么 //语法: // if( bool类型值) // { // 满足条件执行的代码; // } // else // { // 不满足条件执行的代码: // } // 注意: // 1.if ...else 语句 语法部分 不需要写分号 // 2.if ...else 语句 可以嵌套 if (false) { Console.WriteLine("满足if条件 做什么"); if (true) { } else { } } else { Console.WriteLine("不满足if条件 做什么"); } //其他的使用和if的使用是一样的 // 嵌套使用 也是和if语句 一样的 #endregion #region if...else if...else 语句 //作用:产生n条分支 多条道路选择 最先满足其中的一个条件 就做什么 // 语法: // if( bool类型值) // { // 满足条件执行的代码; // } // else if( bool类型值 ) // { // 满足条件执行的代码; // } // ...中间可以有n个 else if语句代码块 // else // { // 不满足条件执行的代码: // } // 注意: // 1.和前面两个是一样的 不需要写分号 // 2.是可以嵌套的 // 3.else 是可以省略的 // 4.注意 条件判断 从上到下执行 满足了第一个后 之后的都不会执行了 int a3 = 10; if (a3 >= 10) { Console.WriteLine("a大于等于10"); } else if (a3 > 5 && a3 < 10) { Console.WriteLine("a在6和9之间"); } else if (a3 >= 0 && a3 < 5) { Console.WriteLine("a在0和5之间"); } else { Console.WriteLine("a小于0"); } //if语句相关 if if...else if...else if...else // else if 和 else 是组合套餐 根据实际情况选择使用 #endregion } } }

第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入今日看唐老师视频花了多少分钟"); string a = Console.ReadLine(); int time = int.Parse(a); if (time > 60) { Console.WriteLine("今天看视频花了" + time + "分钟,看来你离成功又近了一步!"); } }
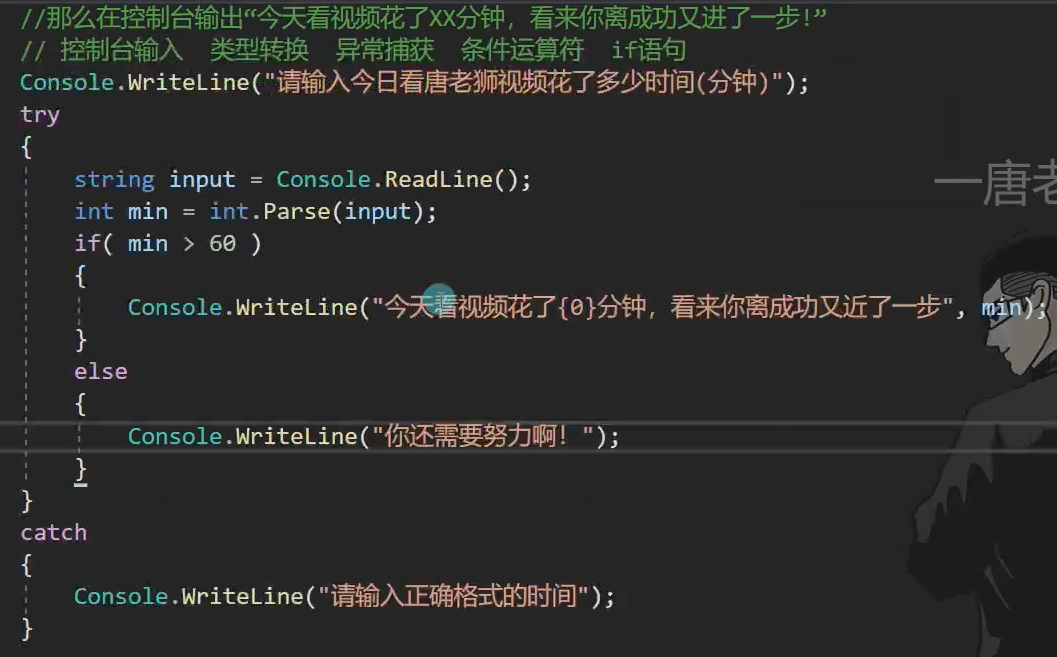
(注意占位符和异常捕获)
第二题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入你的语文成绩"); string a = Console.ReadLine(); int chinese = int.Parse(a); Console.WriteLine("请输入你的数学成绩"); string b = Console.ReadLine(); int math = int.Parse(b); Console.WriteLine("请输入你的英语成绩"); string c = Console.ReadLine(); int english = int.Parse(c); if (chinese>70&&math>80&&english>90) { Console.WriteLine("非常棒,请继续加油"); } else if (chinese==100||math==100||english==100) { Console.WriteLine("非常棒,请继续加油"); } else if (chinese>90&&(math>70||english>70)) { Console.WriteLine("非常棒,请继续加油"); } }
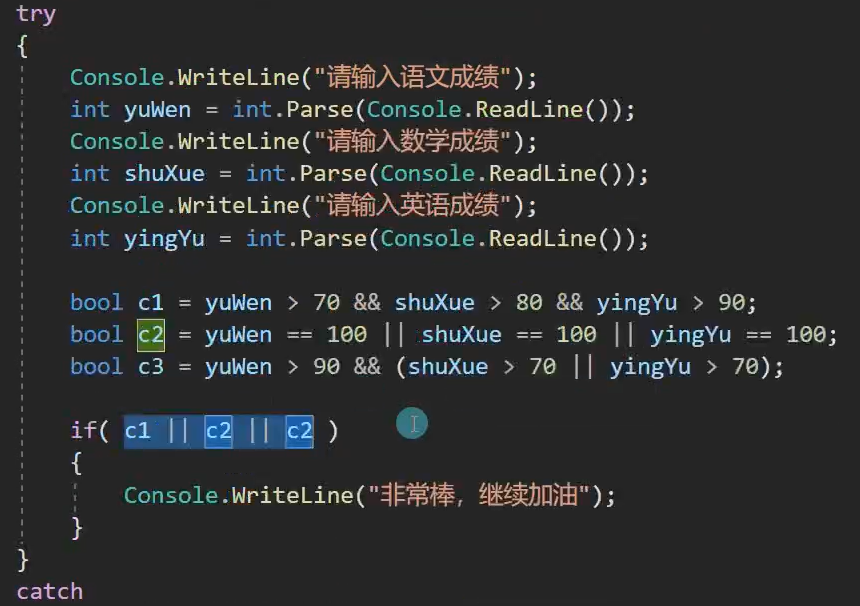
(if条件语句中的c2改成c3)
第三题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int score=90; if (score >= 90) { Console.WriteLine("爸爸奖励100元"); } else { Console.WriteLine("一个月不能玩游戏"); } }
第四题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请给a赋值"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int a = int.Parse(str); Console.WriteLine("请给b赋值"); string str1 = Console.ReadLine(); int b = int.Parse(str1); if (a%b==0||a+b>100) { Console.WriteLine("a的值是:"+a); } else { Console.WriteLine("b的值是:"+b); } }
补充条件(b%a==0)
第五题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入一个数"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int a = int.Parse(str); if (a%2==0) { Console.WriteLine("Your input is even"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Your input is odd"); } }
第六题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int a = 1; int b = 2; int c = 3; if(a>b&&a>c) { Console.WriteLine("最大的整数是a:" + a); } else if (b > a && b > c) { Console.WriteLine("最大的整数是b:" + b); } else if (c > a && c > b) { Console.WriteLine("最大的整数是c:" + c); } }
第七题:
static void Main(string[] args) { try { Console.WriteLine("请输入一个字符"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); if (int.Parse(str) >= 0 && int.Parse(str) <= 9) { Console.WriteLine("您输入了一个数字"); } else { Console.WriteLine("这不是一个数字"); } } catch { Console.WriteLine("这不是一个数字"); } }
法一:
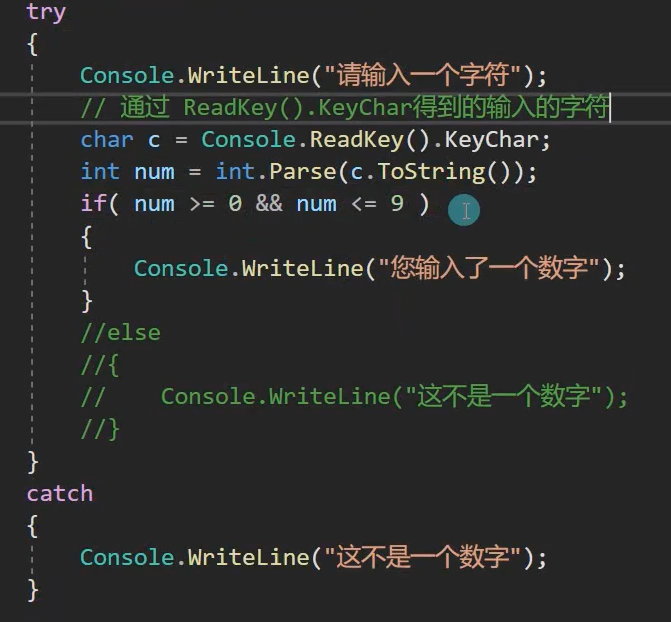

法二( 使用ASKII码来判断):

第八题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入用户名"); string username = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入密码"); string password = Console.ReadLine(); if (username=="admin"&&password=="8888") { Console.WriteLine("正确"); } else if (username != "admin") { Console.WriteLine("用户用户名不存在"); } else if (username=="admin"&&password!="8888") { Console.WriteLine("密码错误"); } }
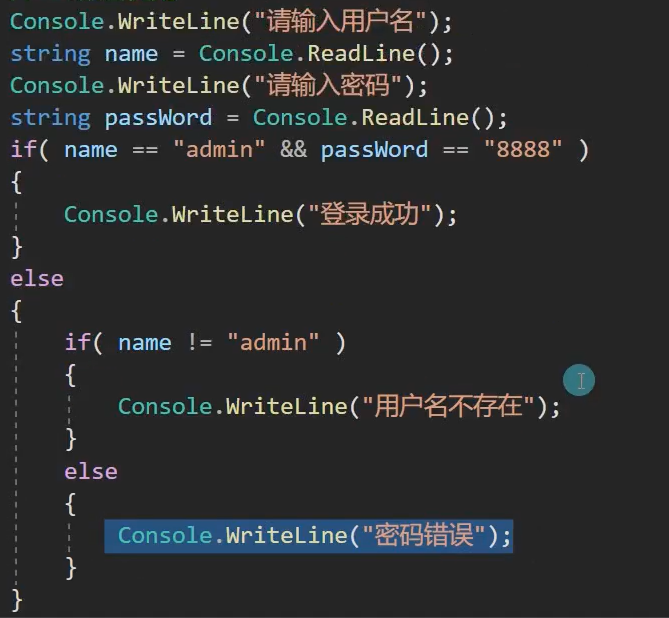
第九题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入年龄"); string str = Console.ReadLine(); int age = int.Parse(str); if (age>=18) { Console.WriteLine("可以查看"); } else if (age < 13) { Console.WriteLine("不允许查看"); } else if (age >= 13 && age < 18) { Console.WriteLine("是否继续查看"); Console.WriteLine("请输入yes或者no"); string answer = Console.ReadLine(); if (answer=="yes") { Console.WriteLine("请查看"); } else if (answer == "no") { Console.WriteLine("退出"); } } }
第十题:
5

正确答案是没有任何打印结果,直接报错
Lesson17_条件分支语句_switch
static void Main(string[] args) { #region 知识点一 作用 //让顺序执行的代码 产生分支 #endregion #region 知识点二 基本语法 //switch (变量) //{ // // 变量 == 常量 执行 case和 break之间的代码 // case 常量: // 满足条件执行的代码逻辑; // break; // case 常量: // 满足条件执行的代码逻辑; // break; // case 可以有无数个 // default: // 如果上面case的条件都不满足 就会执行 default中的代码 // break; //} // 注意: 常量!! 只能写一个值 不能去写一个范围 不能写条件运算符、逻辑运算符 // switch 只判断变量是否等于某一个固定值!!!! int a = 3; int a2 = 3; switch (a) { //这个条件一定是常量 case 1: Console.WriteLine("a等于1"); break; case 2: Console.WriteLine("a等于2"); break; case 3: Console.WriteLine("a等于3"); break; default: Console.WriteLine("什么条件都不满足,执行default中的内容"); break; } float f = 1.4f; //它一般是配合枚举使用 switch (f) { case 1.5f: Console.WriteLine("f等于1.5"); break; case 1: Console.WriteLine("f等于1"); break; default: Console.WriteLine("f什么条件都不满足,执行default中的内容"); break; } #endregion #region 知识点三 default可省略 string str = "123"; switch (str) { case "123": Console.WriteLine("等于123"); break; case "234": Console.WriteLine("等于234"); break; } #endregion #region 知识点四 可自定义常量 char c = 'A'; //1.必须初始化 2.不能修改 const char c2 = 'A'; switch (c) { case c2: Console.WriteLine("c等于A"); break; default: break; } #endregion #region 知识点五 贯穿 //作用: 满足某些条件时 做的事情是一样的 就可以使用贯穿 int aa = 1; switch (aa) { // 不写case后面配对的break 就叫做贯穿 // 满足 1 3 4 2其中一个条件 就会执行 之后的代码 case 1: case 3: case 4: case 2: // case和break之间可以写n句语句 // 并且可以嵌套使用 Console.WriteLine("是个数字"); if (aa == 1) { switch (aa) { default: break; } } break; default: break; } #endregion }

第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int salary = 4000; Console.WriteLine("请输入唐老师的评级:"); string level = Console.ReadLine(); switch (level) { case "A": Console.WriteLine("唐老师的工资是:" + (salary + 500)); break; case "B": Console.WriteLine("唐老师的工资是:" + salary); break; case "C": Console.WriteLine("唐老师的工资是:" + (salary - 300)); break; case "D": Console.WriteLine("唐老师的工资是:" + (salary - 500)); break; case "E": Console.WriteLine("唐老师的工资是" + (salary - 800)); break; default: Console.WriteLine("请输入A~E之间的一个字母"); break; } }
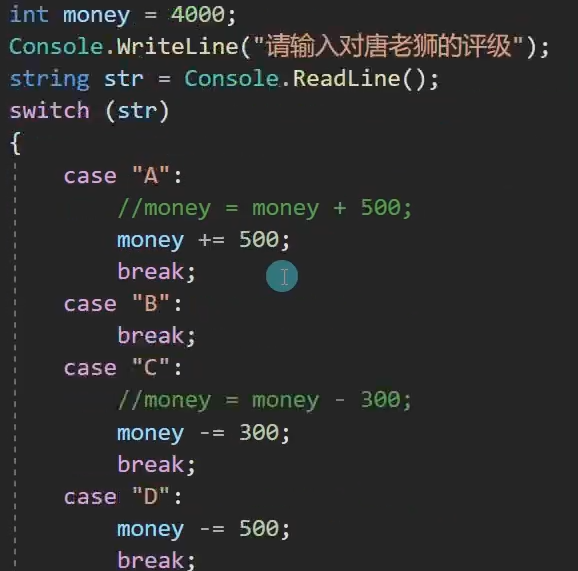
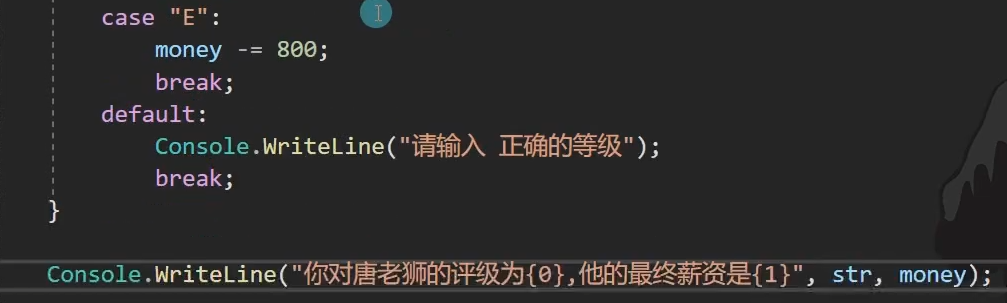
第二题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int money = 10; Console.WriteLine("请输入选择的型号:"); string type = Console.ReadLine(); switch (type) { case "1": Console.WriteLine("钱够,中杯购买成功,小王最后还剩{0}元", money - 5); break; case "2": Console.WriteLine("钱够,大杯购买成功,小王最后还剩{0}元", money - 7); break; case "3": Console.WriteLine("钱不够,请换其他型号"); break; default: Console.WriteLine("请输入数字1~3"); break; } }
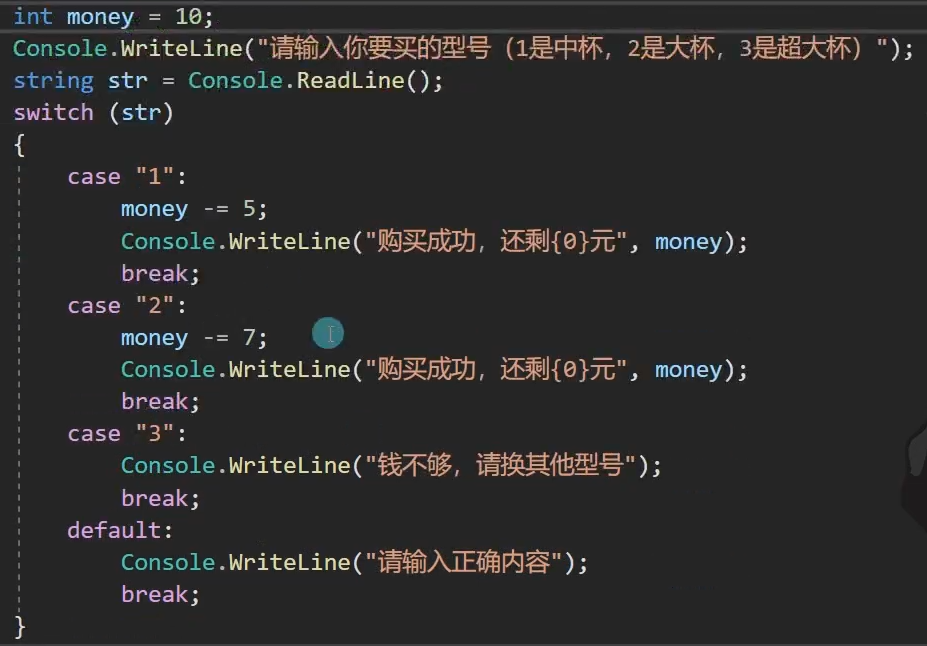
第三题:
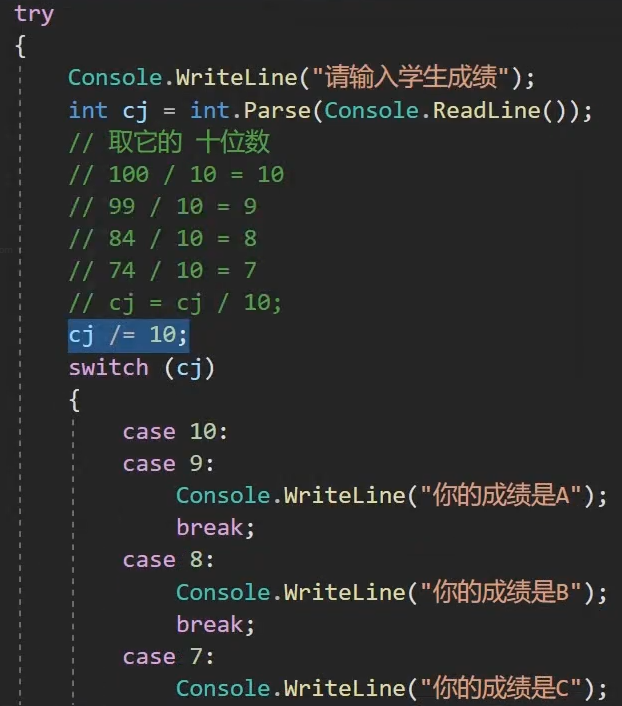

第四题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入一个0~9的数"); string num = Console.ReadLine(); switch (num) { case "0": Console.WriteLine("零"); break; case "1": Console.WriteLine("一"); break; case "2": Console.WriteLine("二"); break; case "3": Console.WriteLine("三"); break; case "4": Console.WriteLine("四"); break; case "5": Console.WriteLine("五"); break; case "6": Console.WriteLine("六"); break; case "7": Console.WriteLine("七"); break; case "8": Console.WriteLine("八"); break; case "9": Console.WriteLine("九"); break; default: break; } }
Lesson18_条件分支语句_while
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("while语句"); #region 知识点一 作用 // 让顺序执行的代码 可以不停的循环执行某一代码块的内容 // 条件分支语句 是 让代码产生分支 // 循环语句 是 让代码可以被重复执行 #endregion #region 知识点二 语法相关 // bool类型变量 条件运算符 逻辑运算符 //while (bool类型的值) //{ // 当满足条件时 就会执行while语句块中的内容 // ...... // ...... // ...... // ...... // 当代码逻辑执行完 会回到while循环开头 // 再次进行条件判断 //} //Console.WriteLine("主代码逻辑"); //死循环 //就不停的执行循环中的逻辑"直到死为止" //死循环只有在目前我们学习 控制台程序时 会频繁使用 //之后进入 Unity过后 基本不会使用死循环 //1.可能因为内存问题 造成程序崩溃 闪退 //2.造成程序卡死 while (true) { //Console.WriteLine("*************"); //Console.WriteLine("请玩家输入用户名密码"); //Console.ReadKey(); } //计算一个为0的整形变量 让它只能累加1 不停的加到10为止 int i = 0; //bool类型的值 还可以用逻辑运算符 && || ! 条件运算符 算术运算结合运算 while (i < 10) { ++i; } Console.WriteLine(i); #endregion #region 知识点三 嵌套使用 // 不仅可以嵌套 if switch 还可以嵌套 while int a = 0; int b = 0; while (a < 10) { ++a; while (b < 10) { ++b; } } a = 0; b = 0; while (a < 10) { ++a; if (b < 10) { ++b; } } int a2 = 0; while (a2 < 10) { ++a2; //每次从外层循环进来时 //b2和上一次的b2有没有关系 是不是一个变量 //切记 没有关系 int b2 = 0; while (b2 < 10) { ++b2; } } #endregion #region 知识点四 流程控制关键词 //作用 : 控制循环逻辑的关键词 // break: 跳出循环 while (true) { Console.WriteLine("break之前的代码"); break; Console.WriteLine("break之后的代码"); } Console.WriteLine("循环外的代码"); int i2 = 0; while (true) { ++i2; Console.WriteLine(i2); if (i2 == 10) { break; } } Console.WriteLine(i2); // continue: 回到循环开始 继续执行 while (true) { Console.WriteLine("continue前的代码"); continue; Console.WriteLine("continue后的代码"); } Console.WriteLine("循环外的代码"); //打印1到20之间的 奇数 int index = 0; while (index < 20) { ++index; //什么样的数是奇数 //不能被2整除的数——>% if (index % 2 == 0) { continue; } Console.WriteLine(index); } //注意:break和continue主要是和循环配合使用的 和if语句无关 // break在switch中的作用 和 while循环中的作用有异曲同工之妙 //while (true) //{ // int a3 = 1; // switch (a3) // { // default: // continue; // break; // } // Console.WriteLine("11111"); //} #endregion }

第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int a=0; while (a<100) { a++; Console.WriteLine(a); } }
第二题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int a=0; int b=0; while (a<100) { a++; b = b + a; } Console.WriteLine(b); }
第三题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int a = 0; int b = 0; while (a<100) { a++; if (a % 7 == 0) { continue; } b = b + a; } Console.WriteLine(b); }
第四题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入一个数"); int num = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); int a = 1; if (num == 1) { Console.WriteLine("1不是质数"); } if (num == 2) { Console.WriteLine("2是质数"); } while (a<num-1) { a++; if (num % a == 0) { Console.WriteLine("{0}不是素数", num); Console.WriteLine("{0}除以{1}", num, a); continue; } } }
没做出来,只想到不是素数怎么求
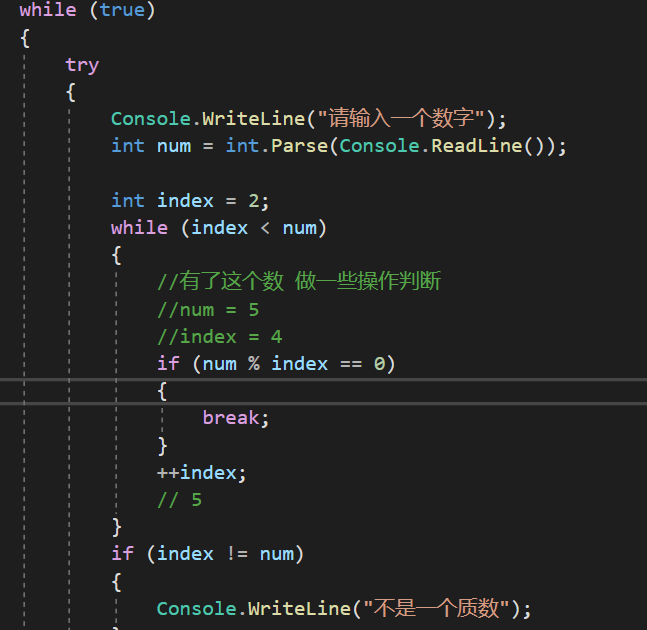
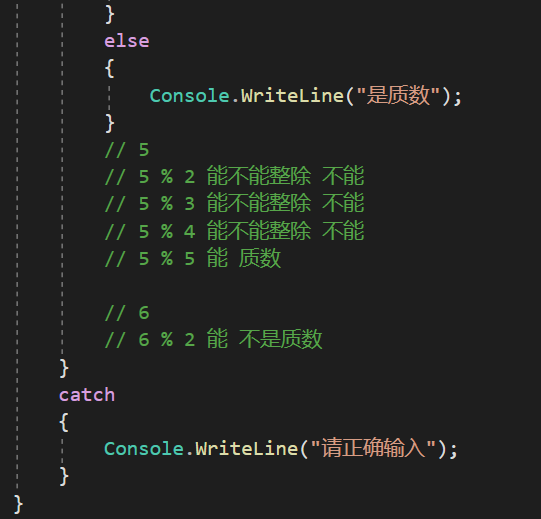
第五题:
static void Main(string[] args) { while (true) { Console.WriteLine("请输入用户名"); string name = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入密码"); string password = Console.ReadLine(); if (name == "admin" && password == "8888") { Console.WriteLine("用户名和密码正确"); break; } else { Console.WriteLine("用户名或密码错误"); continue; } } }
第六题:
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("输入班级人数"); int num = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); int a = 0; int b = 0; int average; int total = 0; while (a<num) { a++; b++; Console.WriteLine("输入成绩,当前是第{0}个学员",b); int score = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); total = total + score; } Console.WriteLine("班级学员的总成绩是{0}",total); average = total / num; Console.WriteLine("班级学员的平均成绩是{0}",average); }
第七题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int sum = 0; int a = 0; while (a<100) { a++; sum = sum + a; if (sum > 500) { Console.WriteLine("累加到第{0}个数字就可以使sum大于500", a); break; } } }
第八题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int basic = 100; int month = 0; while (basic<=1000) { month++; basic = (int)(basic + basic * 0.2); } Console.WriteLine("经历{0}个月看唐老师视频的同学能达到1000人", month); }
第九题:
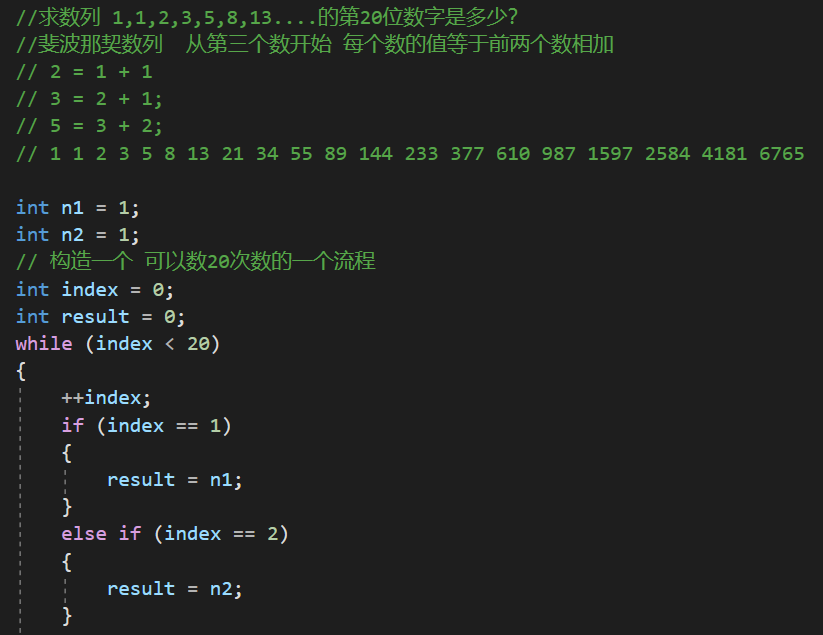

第十题:
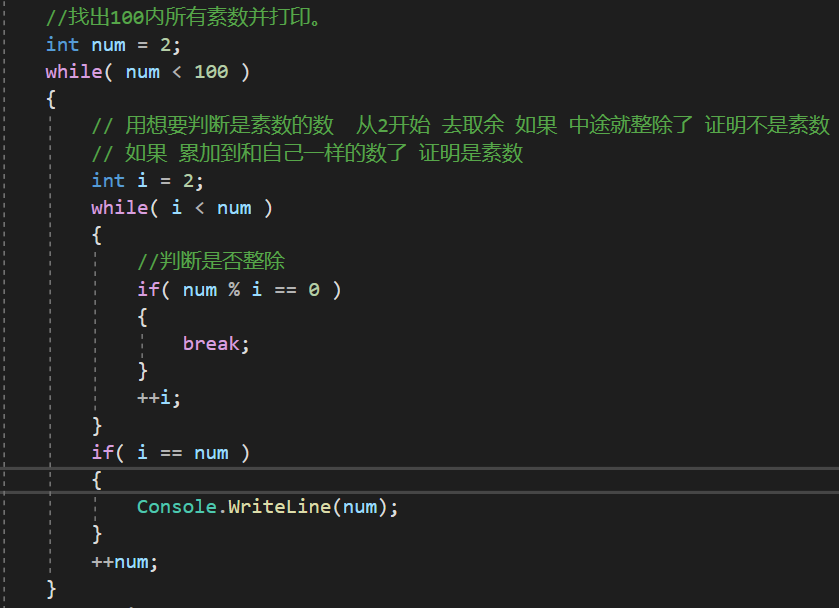
Lesson19_条件分支语句_do...while
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("do...while循环"); #region 知识点一 基本语法 // while循环 是先判断条件再执行 // do while 循环 是先斩后奏 先至少执行一次循环语句块中的逻辑 再判断是否继续 //do //{ // do while 循环语句块; //} while (bool类型的值); // 注意 do while 语句 存在一个重要的分号 #endregion #region 知识点二 实际使用 // do while 使用较少 //do //{ // Console.WriteLine("do while 循环语句块"); //} while (true); //int a = 0; //do //{ // Console.WriteLine(a); // ++a; //} while (a<2); #endregion #region 知识点三 嵌套使用 // if switch while do while do { if (true) { } while (true) { } int i = 1; switch (i) { default: break; } //break; Console.WriteLine("111"); continue; // Console.WriteLine("111"); } while (false); #endregion }

第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) { do { Console.WriteLine("输入用户名"); string name = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("输入密码"); string password = Console.ReadLine(); if (name=="admin"&&password=="8888") { Console.WriteLine("正确"); break; } else { Console.WriteLine("用户名或密码错误,请重新输入"); } } while (true); }

第二题:
static void Main(string[] args) { do { Console.WriteLine("请输入你的姓名"); string name = Console.ReadLine(); if (name=="q") { Console.WriteLine("OVER"); break; } } while (true); }
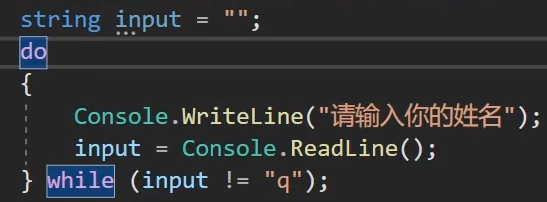
Lesson19_条件分支语句_do...while
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("for循环"); #region 知识点一 基本语法 //for(/*初始表达式*/;/*条件表达式*/;/* 增量表达式*/) //{ // //循环代码逻辑; //} // 第一个空 (初始表达式): 一般声明一个临时变量,用来计数用 // 第二个空 (条件表达式): 表明进入循环的条件 一个bool类型的结果 (bool变量 条件运算符 逻辑运算符) // 第三个空 (增量表达式): 用第一个空中的变量 进行 自增减运算 // 第一次进入循环时 才会调用 第一个空中的代码 // 每次进入循环之前 都会判断第二个空中的条件 满足才会进入循环逻辑 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.WriteLine(i); //执行完循环语句块中的逻辑后 //最后执行第三个空中的代码 } for (int i = 10; i >=0; i--) { Console.WriteLine(i); } //每个空位 可以按照规则进行书写 //第一个空位 就是声明变量 所以可以连续声明 //第二个空位 就是进入条件 只要是bool结果的表达式 都可以 //第三个空位 就是执行一次循环逻辑过后要做的事情 做啥都行 //for (int i = 0,j = 0; i < 10 && j < 0; ++i, j = j + 1) //{ //} #endregion #region 知识点二 支持嵌套 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { Console.WriteLine(i + "_" + j); } while (true) { } if (true) { } do { } while (true); } #endregion #region 知识点三 特殊写法 //for循环 这三个空位 可以都空着 可以根据需求去填写 // for循环可以写死循环 for (; ; ) { Console.WriteLine("for循环的死循环"); } int k = 0; for (; k<10; ) { ++k;//k++,k+=1; } for (k = 0; ; ++k) { if (k >= 10) { break; } } #endregion #region 知识点四 对比while循环 //for循环 一般用来可以准确得到 一个范围中的所有数 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { } int j = 0; while (j<10) { //....................... ++j; } #endregion }

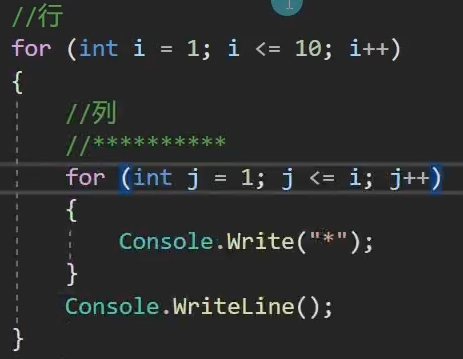
第一题:
static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { Console.WriteLine(i); } }
第二题:
static void Main(string[] args) { int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { if (i % 2 == 0) { sum = sum + i; } } Console.WriteLine(sum); }
第三题:
static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 100; i <= 999; i++) { int a = i / 100; int b = (i-100*a)/10; int c = i - 100 * a - 10 * b; if (i == a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c) { Console.WriteLine(i); } } }
第四题:
static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 1; i <=9; i++) { for (int a = i; a <=9; a++) { int b = a * i; Console.WriteLine("{0}x{1}={2}", i, a, b); } } }
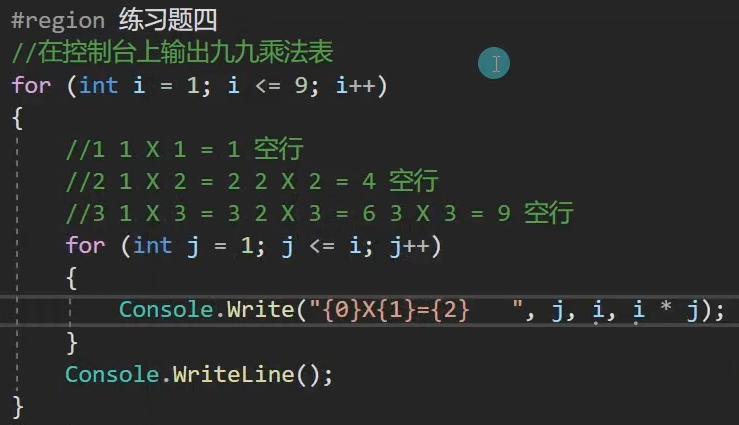
第五题:
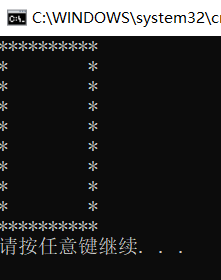
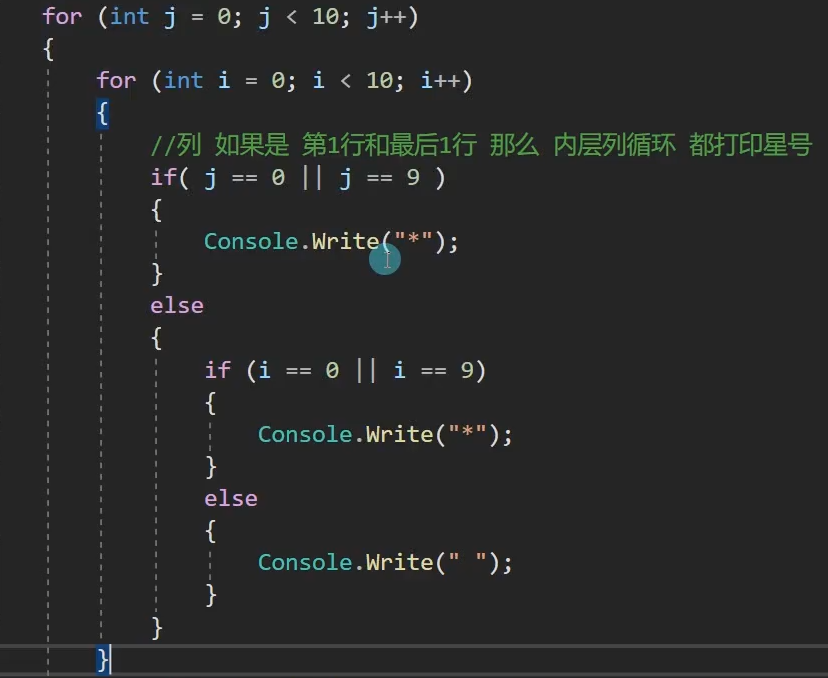
static void Main(string[] args) { for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) { if (i>=2&&i<=9) { Console.WriteLine("* *"); } else { Console.WriteLine("**********"); } } }
第六题:
static void Main(string[] args) { string str = "*"; for (int i = 1; i <=10; i++) { Console.WriteLine(str); str = str + "*"; } }
第七题:
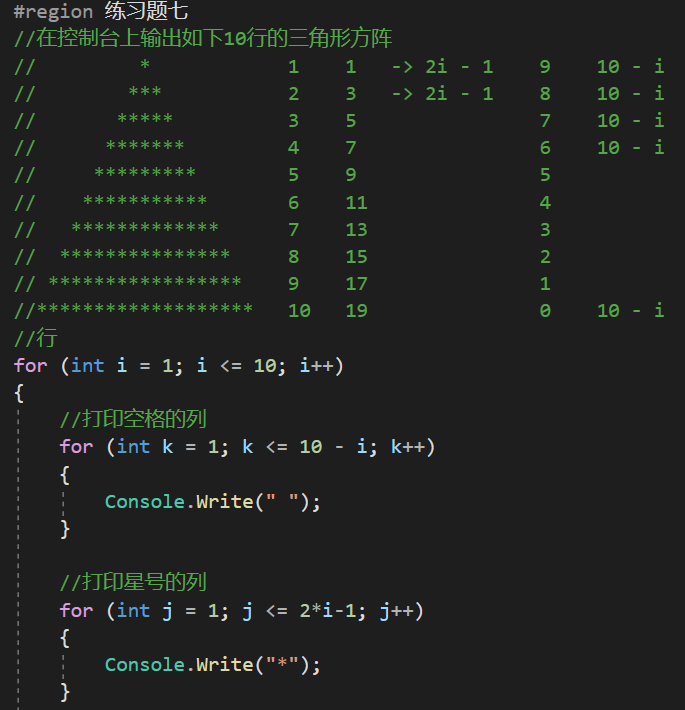


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号