MySql集群架构之MHA
1、MHA介绍
MHA(Master High Availability)是一款开源的 MySQL 的高可用程序,它为 MySQL 主从复制架构提供了 automating master failover 功能。在MySQL故障切换过程中,MHA能做到在30秒之内自动完成数据库的故障切换操作,并且在进行故障切换的过程中,MHA能在最大程度上保证数据的一致性,以达到真正意义上的高可用。MHA还支持在线快速将Master切换到其他主机,通常只需0.5-2秒。
目前MHA主要支持一主多从的架构,最少三台服务,即一主两从。
MHA的服务分两种:
MHA Manager(管理节点):通常单独部署在一台独立机器上管理多个 master/slave 集群(组),也可以部署在一台 slave节点上。负责检测master是否宕机、控制故障转移、检查MySQL复制状况等。
MHA Node(数据节点):运行在每台 MySQL 服务器上,不管是Master角色,还是Slave角色,都称为Node。Node都是被监控的对象,负责收集从节点服务器上所生成的bin-log日志并与新的主节点做差异话的复制,也将其差异的事件应用于其他的slave、清除中继日志,完成新主节点的提升。
MHA的原理总结:
- 把宕机的master二进制日志(binlog)保存下来
- 通过binlog记录的位置在从机中找出最新的slave
- 用最新的slave的中继日志(relay log)同步到其他slave
- 把从master中保存下来的binlog在最新的slave进行恢复
- 把最新的slave提升为master
- 将其它的slave重新指向新的master,并开启主从复制
2、环境介绍
- 使用虚拟机完成一主两从(主从搭建参考我之前的文章“搭建MySql主从复制”)
- 主(192.168.119.149)
- 从1(192.168.119.150)
- 从2(192.168.119.151)
- MySql版本:8.0.21
- CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
- mha4mysql-manager:https://github.com/yoshinorim/mha4mysql-manager
- mha4mysql-node:https://github.com/yoshinorim/mha4mysql-node/tree/v0.58
- 一般来说MHA Manager(管理节点)要单独布置的,不跟主从的数据库一个服务器,本文把MHA Manager(管理节点)安装到了从1(192.168.119.150)上
- 数据库主从的BinLog是row模式。
3、安装MHA
1、MHA需要依赖Perl,所以先安装Perl,结果如图一:
yum install perl*
2、安装 MHA-node,执行以下命令即可。
yum localinstall mha4mysql-node-0.58-0.el7.centos.noarch.rpm
3、安装 mha4mysql-manager,把下载好的manager包上传到从1(192.168.119.150)的服务器上。先进行解压,随后在进入目录使用perl安装manager。
#解压安装包 unzip mha4mysql-manager-master.zip cd mha4mysql-manager-master perl Makefile.PL make && make install
注意:在执行“perl Makefile.PL”命令的时候有几个依赖没有安装成功,如图二:
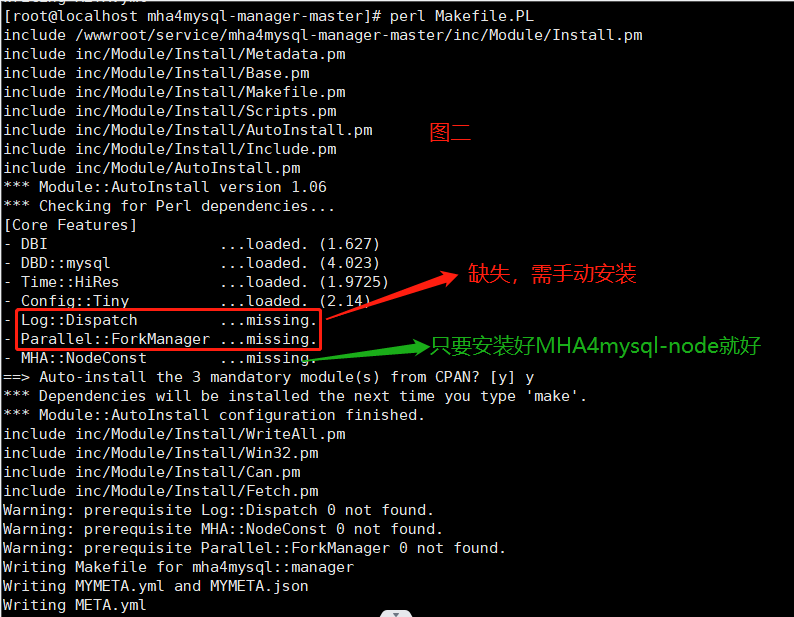
3.1、手动安装图二中缺失的两个依赖,要安装图二中的依赖需要安装 CPAN,所以我们先安装 CPAN。
#linux是RHEL,CentOS,执行下面的一个命令 yum install perl-CPAN -y #linux是Ubuntu,Debian,执行下面的一个命令 sudo apt-get install perl-modules
安装好后就这可以手动安装图二的依赖了,安装命令如下。
cpan install Log::Dispatch cpan install Parallel::ForkManager
在执行的时候一直超时下载不了所需的包,所以我就给 CPAN 加了两个源,命令如下。图三仅做参考。
#进入cpan命令模式 perl -MCPAN -e shell #查看配置文件所在路径,在接下来的交互中输入 yes 生成本地的配置文件,下次可以用 vim 命令直接修改本地配置文件 o conf init #多加入两个源:一个搜狐,一个阿里 o conf urllisthttp://mirrors.sohu.com/CPAN/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/CPAN/ #提交修改内容 o conf commit #退出命令模式 exit
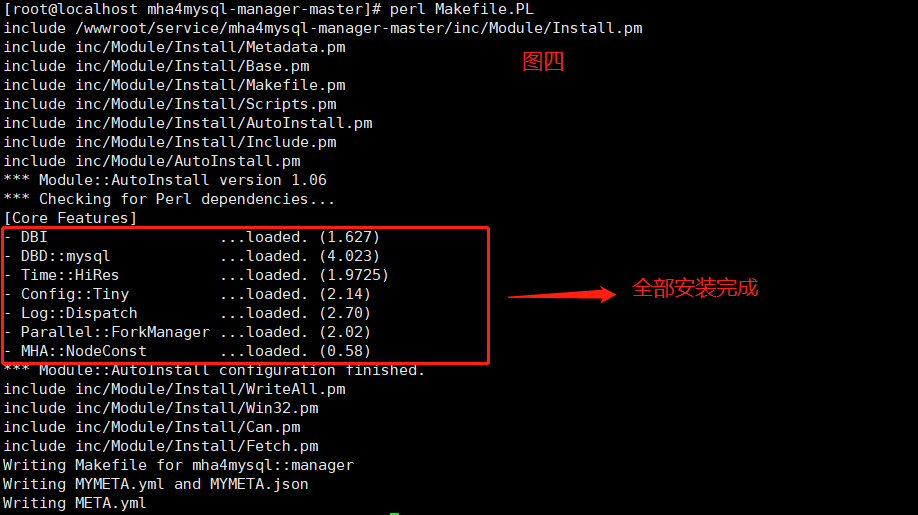
修改好源后再次执行以下两个命令,安装依赖。之后再执行命令安装mha4mysql-manager-master,结果如图四。安装成功后,系统会在 /usr/local/bin 目录下生成相应的脚本文件,如图五。
cpan install Log::Dispatch cpan install Parallel::ForkManager #以上两个依赖安装成功后,再次执行下面命令安装mha4mysql-manager-master perl Makefile.PL #安装MHA make && make install
4、配置MHA
4.1、将每个MHA集群节点,配置ssh无需密码访问,因为在MHA的管理节点在进行心跳检测等操作时他需要通过ssh登录验证。
在从1(192.168.119.150)管理节点生成秘钥。之后再149、151的服务器上各自生成秘钥发到其他两台服务器上。这样就可以保证使用ssh登录其他服务器不需要密码。
#生成ssh秘钥,执行命令后遇到询问就按回车键 ssh-keygen -t rsa #将生成好的秘钥发给其他机器 ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.119.149 ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.119.151
4.2、配置MySql主从,主从架构的选择是没有固定形式的。你可以是多主多从,也可以是一主多从。
MySql主从搭建可以参考我的另一篇文章【搭建MySql主从复制】,在这里就不再赘述了。
4.3、配置MHA的相关文件。
4.3.1.在 MHA Manager(管理节点)的服务器上创建【/etc/masterha】目录,存放相应的配置文件和脚本。
#创建目录 mkdir /etc/masterha
4.3.2.把 mha4mysql-manager-master 解压后的【/samples/conf】目录下的 app1.cnf 文件复制到【/etc/masterha】目录下。
#复制 app1.cnf 文件到 masterha 目录下 cp app1.cnf /etc/masterha/
4.3.3.在【/etc/masterha】目录下编辑 app1.cnf 文件,清空文件中的内容,写入以下配置(注意:配置文件中的注释最好不要):
[server default] manager_workdir=/etc/masterha # mha管理节点工作目录 manager_log=/etc/masterha/manager.log # mha日志 master_binlog_dir=/wwwroot/service/mysql/data # mysql的二进制日志目录 master_ip_failover_script= /etc/masterha/script/master_ip_failover #转移脚本 master_ip_online_change_script= /etc/masterha/script/master_ip_online_change #在线切换管理节点的脚本 user=slave # 设置监控用户主mysql的用户 password=root # 主mysql的密码 repl_user=slave #设置复制环境中的复制用户名 repl_password=root #设置复制环境中的用户名密码 ping_interval=1 # 单位秒,探测心跳时间(如果3次ping不通,就认为主库宕机默认3次) remote_workdir=/usr/local/mysql/bin # 设置远端mysql在发生切换时binlog的保存位置 report_script=/etc/masterha/script/send_report # 设置发生切换后发送的报警的脚本 secondary_check_script= /usr/local/bin/masterha_secondary_check -s 192.168.119.150 -s 192.168.119.151 # 指定检查的从服务器IP地址 shutdown_script="" #设置ssh的登录用户名 ssh_user=root [server1] hostname=192.168.119.149 port=3306 [server2] hostname=192.168.119.150 port=3306 no_master=1 # 不管什么情况下都不会作为主 ignore_fail=1 #默认是0,当某个slave的ssh或者mysql宕机或者复制失败的时候,MHA manager不启动failover。但是有些环境下,你想要在某个特定的slave失败的时候继续执行failover,就把这个设置成ignore_fail=1,即时这个slave失败的时候,failover依然继续执行。 [server3] hostname=192.168.119.151 port=3306 candidate_master=1 # 配置为主的候选人 check_repl_delay=0 #默认情况下如果一个slave落后master 超过100M的relay logs的话,MHA将不会选择该slave作为一个新的master, 因为对于这个slave的恢复需要花费很长时间;通过设置check_repl_delay=0,MHA触发切换在选择一个新的master的时候将会忽略复制延时,这个参数对于设置了candidate_master=1的主机非常有用,因为这个候选主在切换的过程中一定是新的master。
4.3.4.配置MHA 转移脚本。在【/etc/masterha】目录下创建一个名叫 script 的目录,用来存放脚本。
#在 /etc/masterha 目录下创建script目录 mkdir script #进入 script 目录 cd script #创建 MHA 转移脚本文件master_ip_failover;在线切换管理节点的脚本master_ip_online_change;设置发生切换后发送的报警的脚本send_report vim master_ip_failover
vim master_ip_online_change
vim send_report
master_ip_failover文件的脚本内容如下,主要修改【$vip = '192.168.119.200';】自定义一个自己网内的IP地址;设置【$ssh_start_vip】和【$ssh_stop_vip】的网卡名称,我用的网卡是ens33。通过命令【ip a】可以查看。
#!/usr/bin/env perl use strict; use warnings FATAL => 'all'; use Getopt::Long; use MHA::DBHelper; my ( $command, $ssh_user, $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip, $orig_master_port, $new_master_host, $new_master_ip, $new_master_port, $new_master_user, $new_master_password ); my $vip = '192.168.119.200'; my $key = '1'; my $ssh_start_vip = "sudo /sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key $vip netmask 255.255.255.0"; my $ssh_stop_vip = "sudo /sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key down"; GetOptions( 'command=s' => \$command, 'ssh_user=s' => \$ssh_user, 'orig_master_host=s' => \$orig_master_host, 'orig_master_ip=s' => \$orig_master_ip, 'orig_master_port=i' => \$orig_master_port, 'new_master_host=s' => \$new_master_host, 'new_master_ip=s' => \$new_master_ip, 'new_master_port=i' => \$new_master_port, 'new_master_user=s' => \$new_master_user, 'new_master_password=s' => \$new_master_password, ); exit &main(); sub main { print "\n\n VIP Command: start=$ssh_start_vip stop=$ssh_stop_vip\n\n"; if ( $command eq "stop" || $command eq "stopssh" ) { # $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip, $orig_master_port are passed. # If you manage master ip address at global catalog database, # invalidate orig_master_ip here. my $exit_code = 1; eval { print "Disabling the VIP on old master: $orig_master_host \n"; &stop_vip(); # updating global catalog, etc $exit_code = 0; }; if ($@) { warn "Got Error: $@\n"; exit $exit_code; } exit $exit_code; } elsif ( $command eq "start" ) { # all arguments are passed. # If you manage master ip address at global catalog database, # activate new_master_ip here. # You can also grant write access (create user, set read_only=0, etc) here. my $exit_code = 10; eval { my $new_master_handler = new MHA::DBHelper(); # args: hostname, port, user, password, raise_error_or_not $new_master_handler->connect( $new_master_ip, $new_master_port, $new_master_user, $new_master_password, 1 ); ## Set read_only=0 on the new master $new_master_handler->disable_log_bin_local(); print "Set read_only=0 on the new master.\n"; $new_master_handler->disable_read_only(); $new_master_handler->disconnect(); print "Enabling the VIP - $vip on the new master - $new_master_host \n"; &start_vip(); $exit_code = 0; }; if ($@) { warn $@; # If you want to continue failover, exit 10. exit $exit_code; } exit $exit_code; } elsif ( $command eq "status" ) { print "Check script.. OK \n"; # do nothing exit 0; } else { &usage(); exit 1; } } sub start_vip() { `ssh $ssh_user\@$new_master_host \" $ssh_start_vip \"`; } sub stop_vip() { return 0 unless ($ssh_user); `ssh $ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \" $ssh_stop_vip \"`; } sub usage { print "Usage: master_ip_failover --command=start|stop|stopssh|status --orig_master_host=host --orig_master_ip=ip --orig_master_port=port --new_master_host=host --new_master_ip=ip --new_master_port=port\n"; }
master_ip_online_change 文件的脚本内容如下,主要修改【$vip = '192.168.119.200';】自定义一个自己网内的IP地址;设置【$ssh_start_vip】和【$ssh_stop_vip】的网卡名称,我用的网卡是ens33。通过命令【ip a】可以查看。
opyright (C) 2011 DeNA Co.,Ltd. # # This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify # it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by # the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or # (at your option) any later version. # # This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, # but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of # MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the # GNU General Public License for more details. # # You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License # along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software # Foundation, Inc., # 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA ## Note: This is a sample script and is not complete. Modify the script based on your environment. use strict; use warnings FATAL => 'all'; use Getopt::Long; use MHA::DBHelper; use MHA::NodeUtil; use Time::HiRes qw( sleep gettimeofday tv_interval ); use Data::Dumper; my $_tstart; my $_running_interval = 0.1; my ( $command, $orig_master_is_new_slave, $orig_master_host, $orig_master_ip, $orig_master_port, $orig_master_user, $orig_master_password, $orig_master_ssh_user, $new_master_host, $new_master_ip, $new_master_port, $new_master_user, $new_master_password, $new_master_ssh_user ); GetOptions( 'command=s' => \$command, 'orig_master_is_new_slave' => \$orig_master_is_new_slave, 'orig_master_host=s' => \$orig_master_host, 'orig_master_ip=s' => \$orig_master_ip, 'orig_master_port=i' => \$orig_master_port, 'orig_master_user=s' => \$orig_master_user, 'orig_master_password=s' => \$orig_master_password, 'orig_master_ssh_user=s' => \$orig_master_ssh_user, 'new_master_host=s' => \$new_master_host, 'new_master_ip=s' => \$new_master_ip, 'new_master_port=i' => \$new_master_port, 'new_master_user=s' => \$new_master_user, 'new_master_password=s' => \$new_master_password, 'new_master_ssh_user=s' => \$new_master_ssh_user, ); my $vip = '192.168.119.200'; my $key = '1'; my $ssh_start_vip = "sudo /sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key $vip netmask 255.255.255.0"; my $ssh_stop_vip = "sudo /sbin/ifconfig ens33:$key down"; exit &main(); sub current_time_us { my ( $sec, $microsec ) = gettimeofday(); my $curdate = localtime($sec); return $curdate . " " . sprintf( "%06d", $microsec ); } sub sleep_until { my $elapsed = tv_interval($_tstart); if ( $_running_interval > $elapsed ) { sleep( $_running_interval - $elapsed ); } } sub get_threads_util { my $dbh = shift; my $my_connection_id = shift; my $running_time_threshold = shift; my $type = shift; $running_time_threshold = 0 unless ($running_time_threshold); $type = 0 unless ($type); my @threads; my $sth = $dbh->prepare("SHOW PROCESSLIST"); $sth->execute(); while ( my $ref = $sth->fetchrow_hashref() ) { my $id = $ref->{Id}; my $user = $ref->{User}; my $host = $ref->{Host}; my $command = $ref->{Command}; my $state = $ref->{State}; my $query_time = $ref->{Time}; my $info = $ref->{Info}; $info =~ s/^\s*(.*?)\s*$/$1/ if defined($info); next if ( $my_connection_id == $id ); next if ( defined($query_time) && $query_time < $running_time_threshold ); next if ( defined($command) && $command eq "Binlog Dump" ); next if ( defined($user) && $user eq "system user" ); next if ( defined($command) && $command eq "Sleep" && defined($query_time) && $query_time >= 1 ); if ( $type >= 1 ) { next if ( defined($command) && $command eq "Sleep" ); next if ( defined($command) && $command eq "Connect" ); } if ( $type >= 2 ) { next if ( defined($info) && $info =~ m/^select/i ); next if ( defined($info) && $info =~ m/^show/i ); } push @threads, $ref; } return @threads; } sub main { if ( $command eq "stop" ) { ## Gracefully killing connections on the current master # 1. Set read_only= 1 on the new master # 2. DROP USER so that no app user can establish new connections # 3. Set read_only= 1 on the current master # 4. Kill current queries # * Any database access failure will result in script die. my $exit_code = 1; eval { ## Setting read_only=1 on the new master (to avoid accident) my $new_master_handler = new MHA::DBHelper(); # args: hostname, port, user, password, raise_error(die_on_error)_or_not $new_master_handler->connect( $new_master_ip, $new_master_port, $new_master_user, $new_master_password, 1 ); print current_time_us() . " Set read_only on the new master.. "; $new_master_handler->enable_read_only(); if ( $new_master_handler->is_read_only() ) { print "ok.\n"; } else { die "Failed!\n"; } $new_master_handler->disconnect(); # Connecting to the orig master, die if any database error happens my $orig_master_handler = new MHA::DBHelper(); $orig_master_handler->connect( $orig_master_ip, $orig_master_port, $orig_master_user, $orig_master_password, 1 ); $orig_master_handler->disable_log_bin_local(); ## Waiting for N * 100 milliseconds so that current connections can exit my $time_until_read_only = 15; $_tstart = [gettimeofday]; my @threads = get_threads_util( $orig_master_handler->{dbh}, $orig_master_handler->{connection_id} ); while ( $time_until_read_only > 0 && $#threads >= 0 ) { if ( $time_until_read_only % 5 == 0 ) { printf "%s Waiting all running %d threads are disconnected.. (max %d milliseconds)\n", current_time_us(), $#threads + 1, $time_until_read_only * 100; if ( $#threads < 5 ) { print Data::Dumper->new( [$_] )->Indent(0)->Terse(1)->Dump . "\n" foreach (@threads); } } sleep_until(); $_tstart = [gettimeofday]; $time_until_read_only--; @threads = get_threads_util( $orig_master_handler->{dbh}, $orig_master_handler->{connection_id} ); } ## Setting read_only=1 on the current master so that nobody(except SUPER) can write print current_time_us() . " Set read_only=1 on the orig master.. "; $orig_master_handler->enable_read_only(); if ( $orig_master_handler->is_read_only() ) { print "ok.\n"; } else { die "Failed!\n"; } ## Waiting for M * 100 milliseconds so that current update queries can complete my $time_until_kill_threads = 5; @threads = get_threads_util( $orig_master_handler->{dbh}, $orig_master_handler->{connection_id} ); while ( $time_until_kill_threads > 0 && $#threads >= 0 ) { if ( $time_until_kill_threads % 5 == 0 ) { printf "%s Waiting all running %d queries are disconnected.. (max %d milliseconds)\n", current_time_us(), $#threads + 1, $time_until_kill_threads * 100; if ( $#threads < 5 ) { print Data::Dumper->new( [$_] )->Indent(0)->Terse(1)->Dump . "\n" foreach (@threads); } } sleep_until(); $_tstart = [gettimeofday]; $time_until_kill_threads--; @threads = get_threads_util( $orig_master_handler->{dbh}, $orig_master_handler->{connection_id} ); } ## Terminating all threads print current_time_us() . " Killing all application threads..\n"; $orig_master_handler->kill_threads(@threads) if ( $#threads >= 0 ); print current_time_us() . " done.\n"; $orig_master_handler->enable_log_bin_local(); $orig_master_handler->disconnect(); print "Disabling the VIP on old master: $orig_master_host \n"; &stop_vip(); ## After finishing the script, MHA executes FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK $exit_code = 0; }; if ($@) { warn "Got Error: $@\n"; exit $exit_code; } exit $exit_code; } elsif ( $command eq "start" ) { ## Activating master ip on the new master # 1. Create app user with write privileges # 2. Moving backup script if needed # 3. Register new master's ip to the catalog database # We don't return error even though activating updatable accounts/ip failed so that we don't interrupt slaves' recovery. # If exit code is 0 or 10, MHA does not abort my $exit_code = 10; eval { my $new_master_handler = new MHA::DBHelper(); # args: hostname, port, user, password, raise_error_or_not $new_master_handler->connect( $new_master_ip, $new_master_port, $new_master_user, $new_master_password, 1 ); ## Set read_only=0 on the new master $new_master_handler->disable_log_bin_local(); print current_time_us() . " Set read_only=0 on the new master.\n"; $new_master_handler->disable_read_only(); $new_master_handler->enable_log_bin_local(); $new_master_handler->disconnect(); print "Enabling the VIP - $vip on the new master - $new_master_host \n"; &start_vip(); ## Update master ip on the catalog database, etc $exit_code = 0; }; if ($@) { warn "Got Error: $@\n"; exit $exit_code; } exit $exit_code; } elsif ( $command eq "status" ) { # do nothing exit 0; } else { &usage(); exit 1; } } sub start_vip() { return 0 unless ($new_master_ssh_user); `ssh $new_master_ssh_user\@$new_master_host \" $ssh_start_vip \"`; } sub stop_vip() { return 0 unless ($orig_master_ssh_user); `ssh $orig_master_ssh_user\@$orig_master_host \" $ssh_stop_vip \"`; } sub usage { print "Usage: master_ip_online_change --command=start|stop|status --orig_master_host=host --orig_master_ip=ip --orig_master_port=port --new_master_host=host --new_master_ip=ip --new_master_port=port\n"; die; }
send_report 文件的脚本内容如下。
#!/usr/bin/perl use strict; use warnings FATAL => 'all'; use Getopt::Long; #new_master_host and new_slave_hosts are set only when recovering master succeeded my ( $dead_master_host, $new_master_host, $new_slave_hosts, $subject, $body, $title, $content); GetOptions( 'orig_master_host=s' => \$dead_master_host, 'new_master_host=s' => \$new_master_host, 'new_slave_hosts=s' => \$new_slave_hosts, 'subject=s' => \$subject, 'body=s' => \$body, ); # 调用外部脚本 $title="[mha switch]"; $content="`date +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M'` old_master=".$dead_master_host." new_master=".$new_master_host; system("sh /etc/masterha/script/send_report.sh $title $content"); exit 0;
4.3.5.切换到 /usr/local/bin 目录下,检测ssh的配置是否有用,输入以下命令,结果如图七表示正确配置。
masterha_check_ssh --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf

4.3.6.切换到 /usr/local/bin 目录下,检测数据库主从是否有用,输入以下命令,结果如下图表示正确配置。
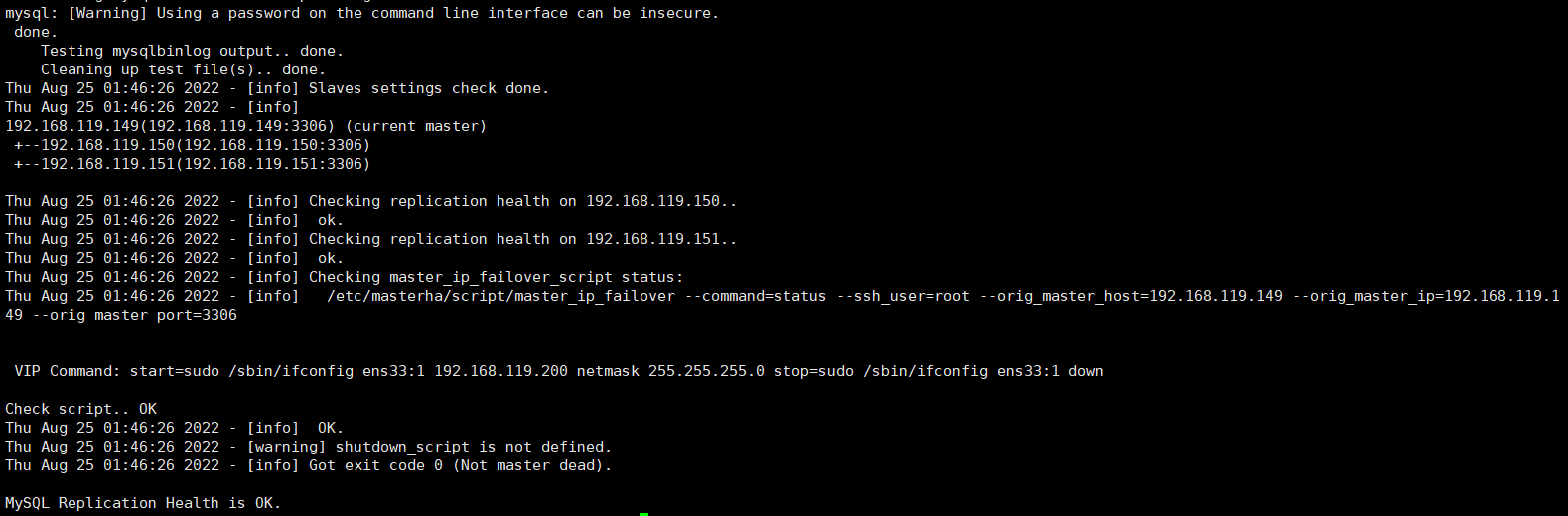
#检测主从的配置是否正确 masterha_check_repl --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf
问题:检查主从配置时碰到的一些问题:
(1)出现下图中的问题是因为在本文章的【4.3.3】步骤中,我把app1.cnf文件中配置写错了,用于主从复制的数据库帐号应该是【slave】,我写成【root】 。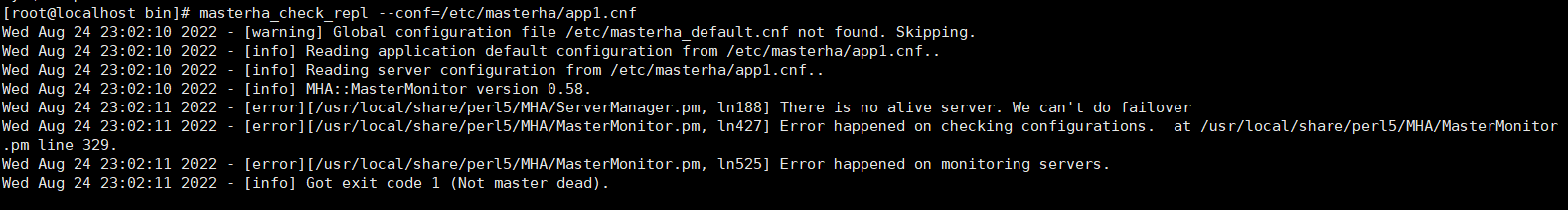
(2)是因为manager的配置文件【/etc/masterha/app1.cnf】中的【master_binlog_dir=/usr/local/mysql/data】项与manager所在服务器的mysql自己的配置文件【/etc/my.cnf】中的【datadir=/wwwroot/service/mysql/data】项配置的不一样,这两个地方应该配置成一样的,我粗心写错了,造成了如下的问题。
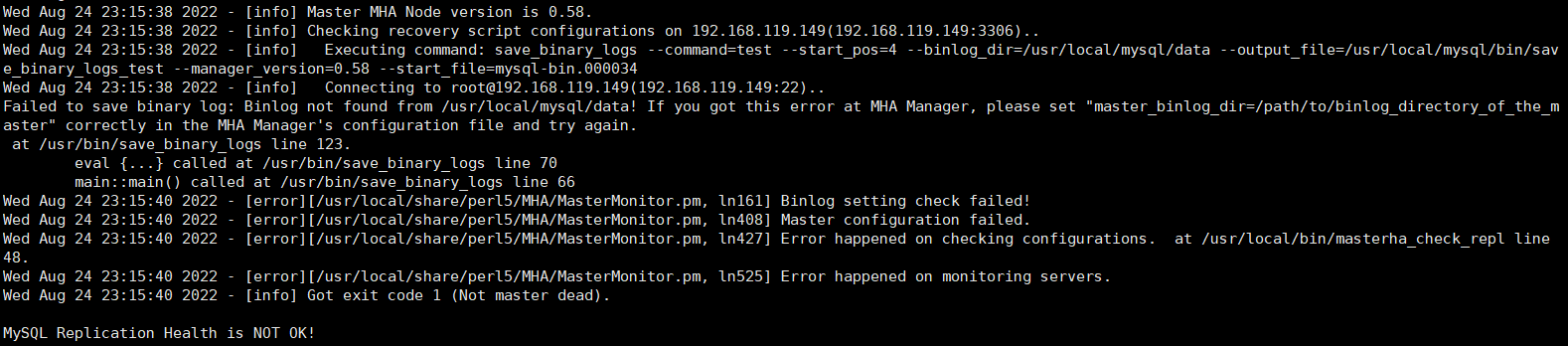
(3)主从所有服务器下的mysql的bin目录都已经加入环境变量中了,但还是没有起到作用,就在各自的服务器上做了一个软连接 【ln -s /wwwroot/service/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog /usr/local/bin/】解决了如下的问题。
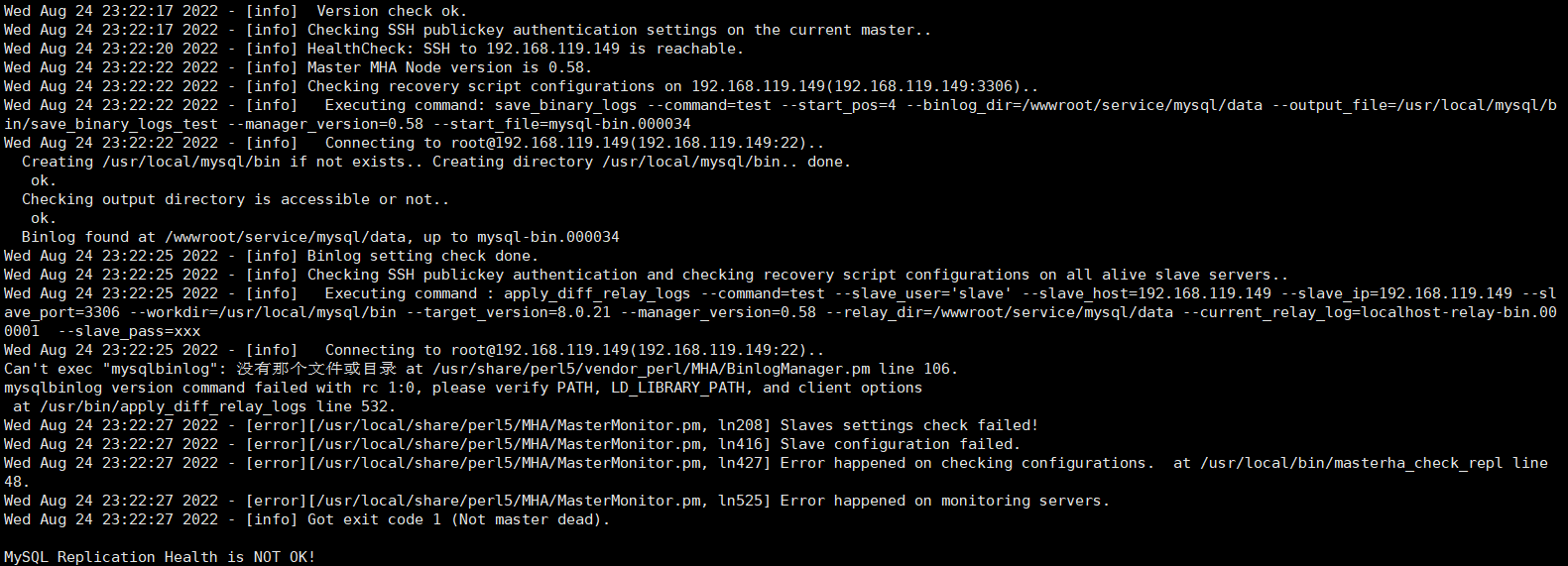
(4)把所有主从数据库的mysql配置文件中的关于字符集的设置都去掉,就可以解决下图中的问题。
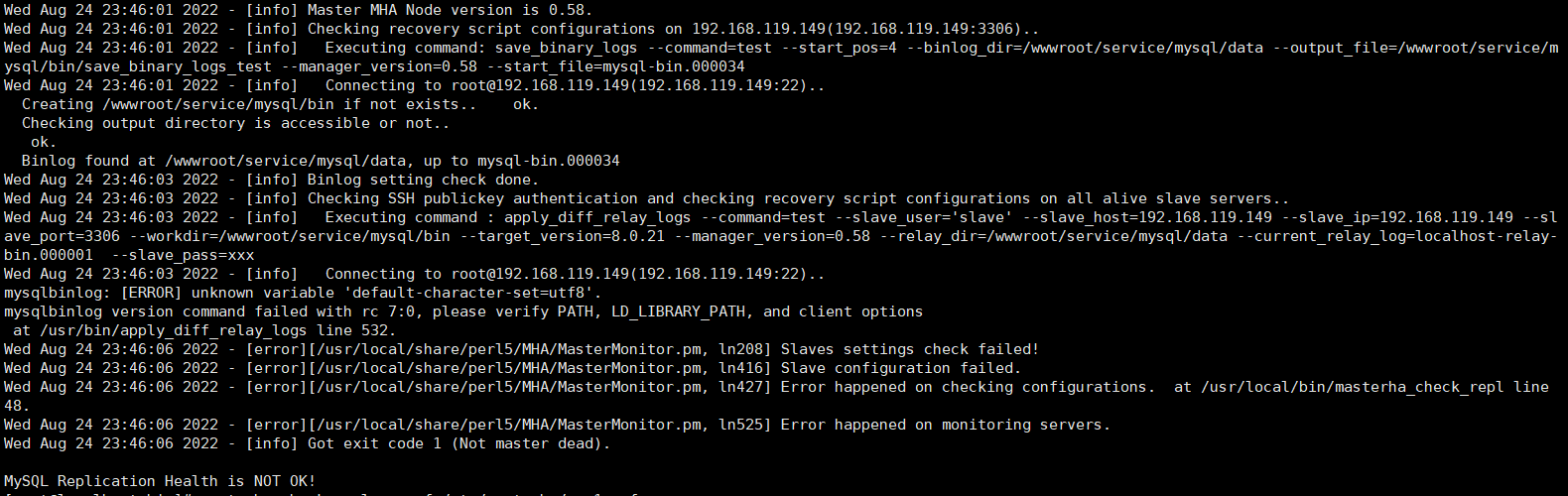
(5)这个问题跟第(3)个问题一样,只是软链接的对象不一样。主从所有服务器下的mysql的bin目录都已经加入环境变量中了,但还是没有起到作用,就在各自的服务器上做了一个软连接 【ln -s /wwwroot/service/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/local/bin/】解决了如下的问题。
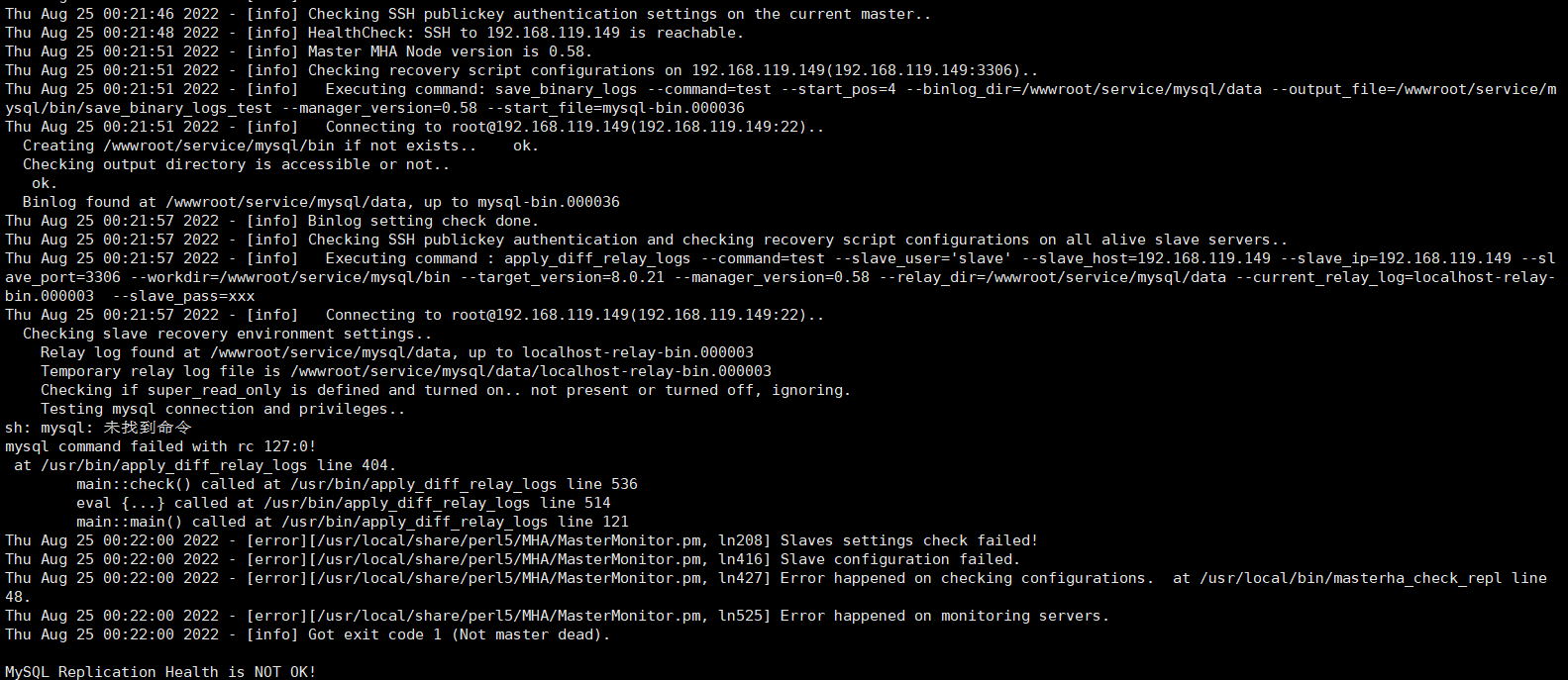
(6)主从复制的主库也执行了【start slave;】命令所以出现了下图的问题。解决:先在主库【stop slave;】 再执行【reset slave all;】
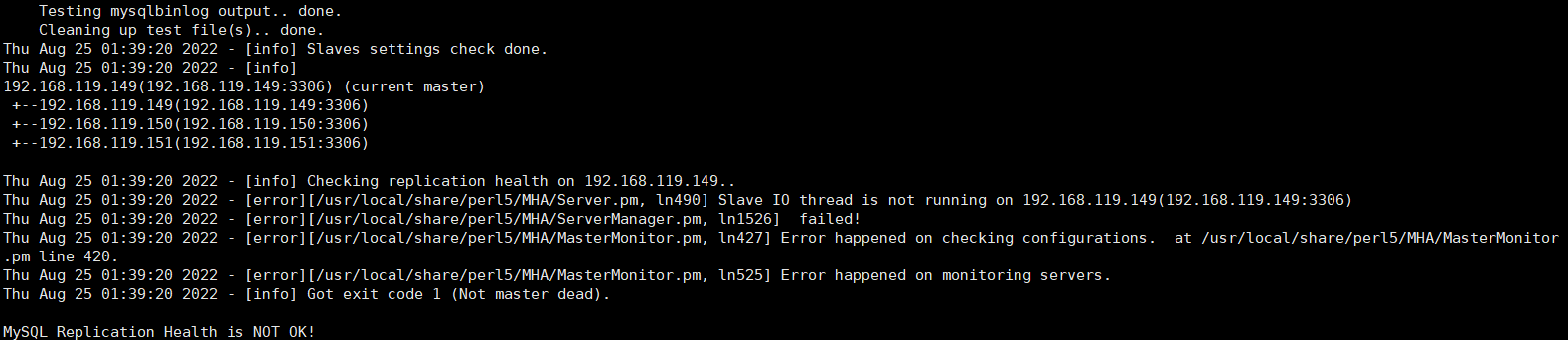
5、测试
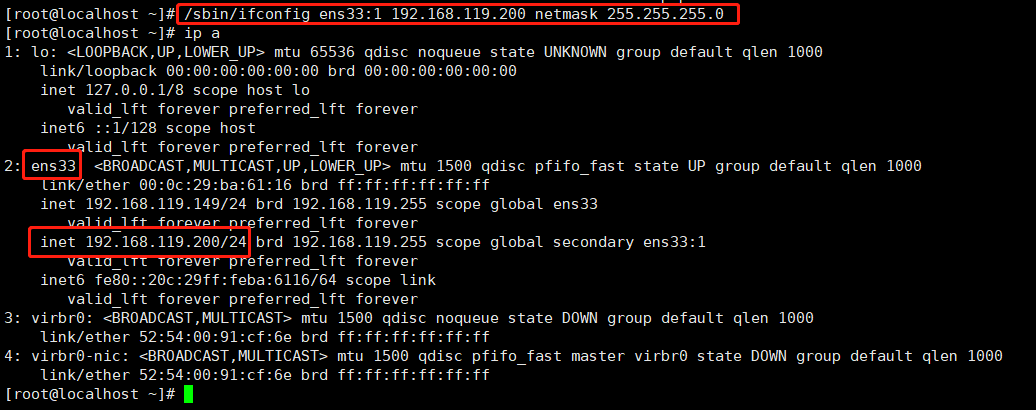
5.1、先给主库生成一个虚拟IP【192.168.119.200】,就是之前在【4.3.4】步骤中的【master_ip_failover】文件中配置【$vip=192.168.119.200】项,结果如下图。
#配置虚拟IP /sbin/ifconfig ens33:1 192.168.119.200 netmask 255.255.255.0
5.2、在MHA Manager(管理节点)的服务器上启动监控。
#启动管理节点的监控 nohup /usr/local/bin/masterha_manager --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.cnf --ignore_last_failover &
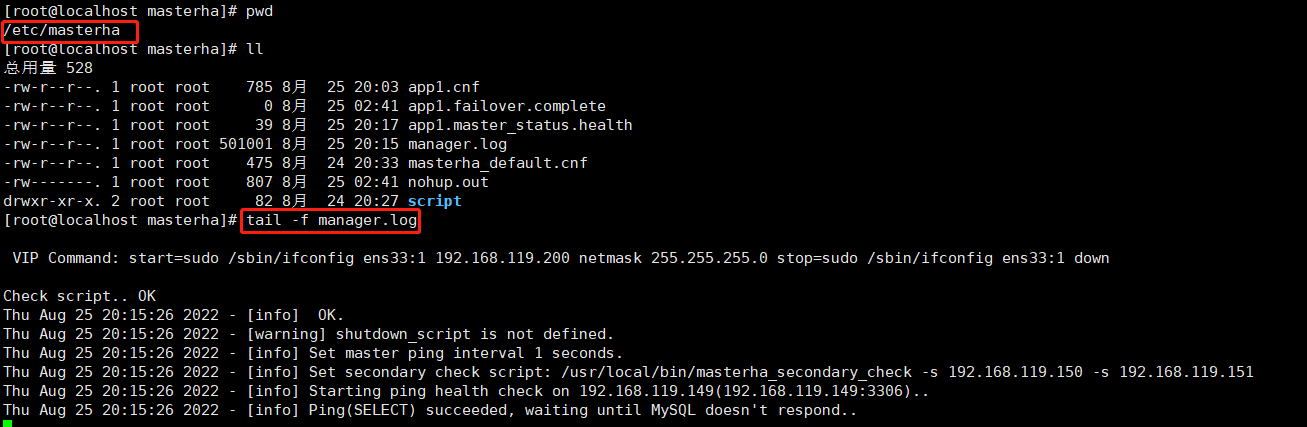
5.3、另开一个MHA Manager(管理节点)的窗口,在【/etc/masterha】目录下监听查看【manager.log】日志,通过日志来查看工作状态。
#监听查看 tail -f manager.log
5.4、打开Windows的dos窗口,输入以下命令查看当前连接的数据库是哪个。
#通过连接之前创建的虚拟IP=192.168.119.200来查看目前的主库是哪个,在下图中可以看见,现在主库是server_id=1的,也就是192.168.119.149的服务器。 mysql -uslave -proot -P3306 -h192.168.119.200 -e "show variables like 'server_id'"

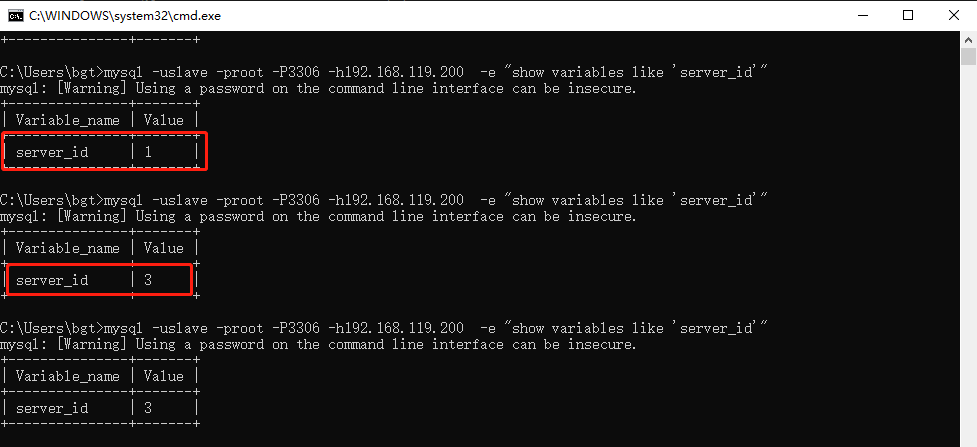
5.5、现在开始停掉主数据库,看他是否能选举出新的主数据库,并正常运行主从结构。从下图中可以发现【192.168.119.200】已经转移连接到【server_id=3】上面了,也就是【192.168.119.151】的服务器。
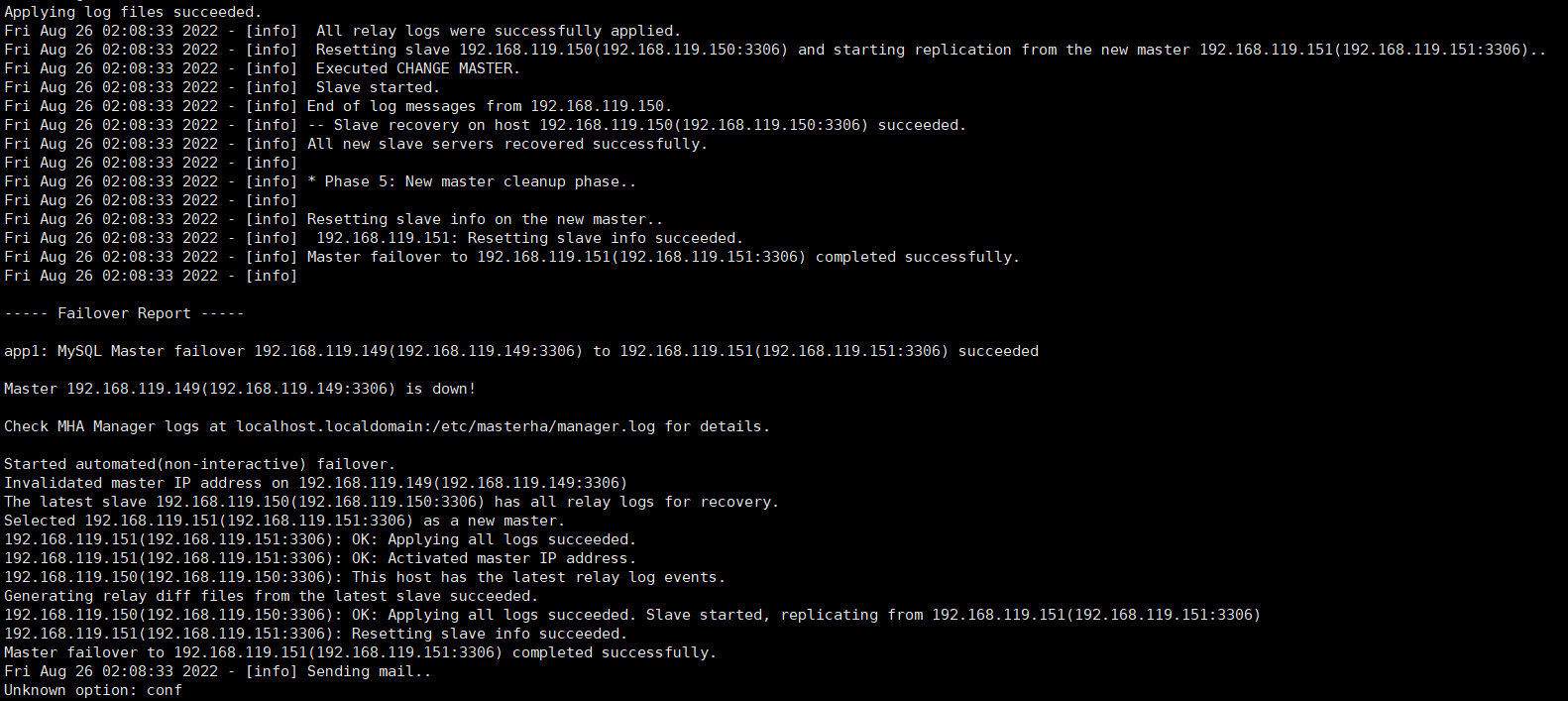
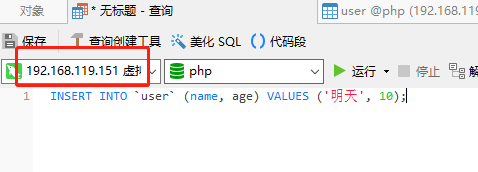
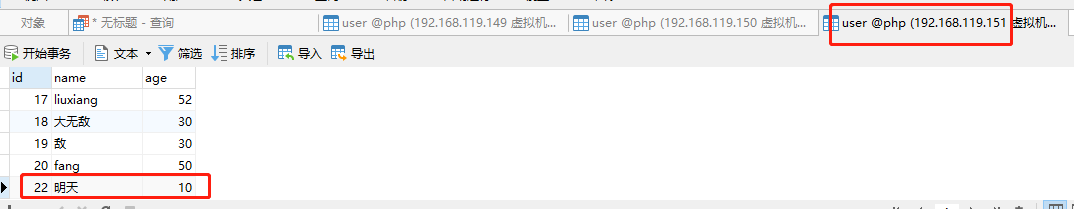
5.6、现在【192.168.119.151】数据库已经成为主库了,在其上插入一条新的数据,并查看【192.168.119.150】的从库是否同步了新数据。由下面几张图可得知,主库新增的数据同步到了从库。
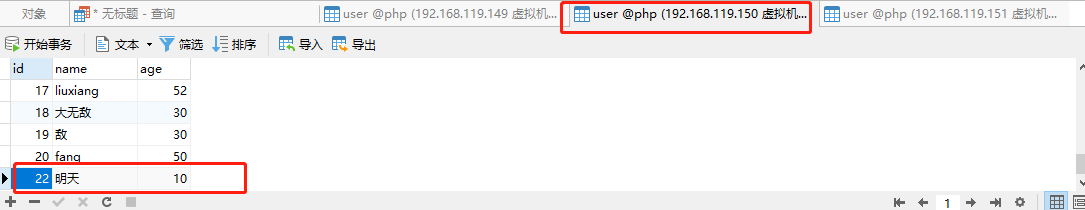
5.7、用主从同步的账号登录【192.168.119.150】的数据库,使用命令【show slave status\G;】查看此服务器上的数据库所连接的主库是否发生了变化。
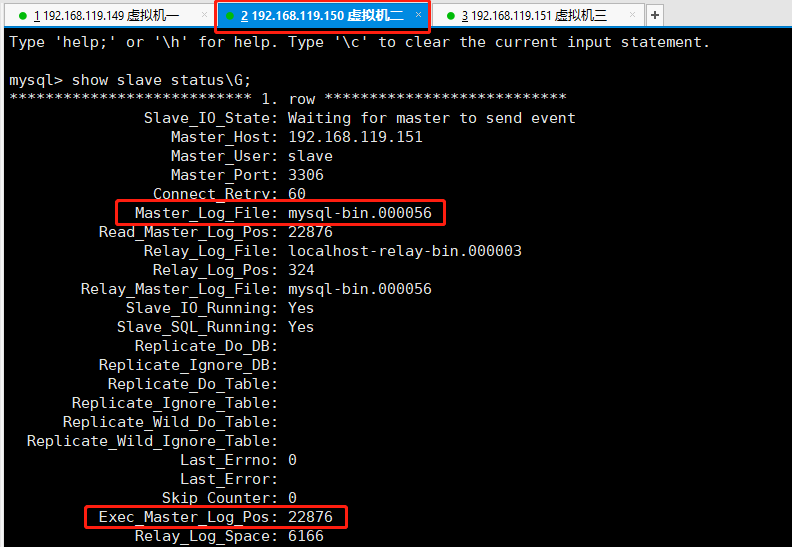
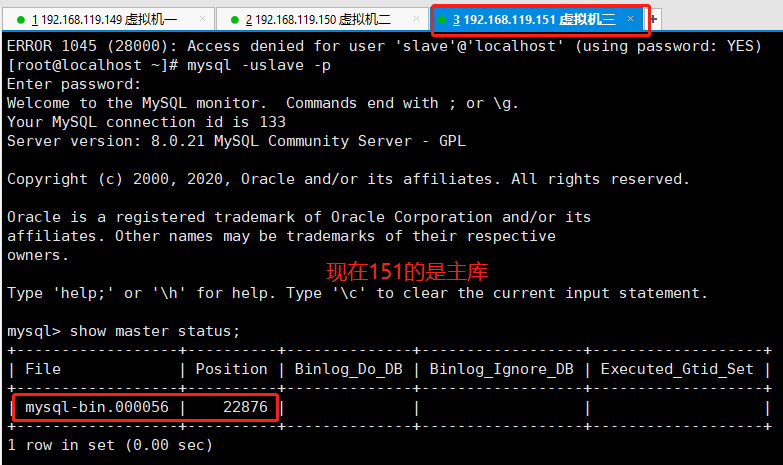
5.8、通过以上的验证已经说明我们的测试是成功的。如果要使原主【192.168.119.149】重新加入到新的主从中,就必须在启动后手动【change master】设置主从关系。重新启动后的原主数据库不会出现抢主的行为。
6、总结
优点:
- 主库宕机后能在从库中选举出新的主库,保障运行。
- 提供了主从切换和故障转移功能,在进行故障转移时不易产生数据的丢失。
缺点:
- 需要自己写故障转换的脚本。
- MHA只对主库进行监控,不能监控从库。
本文来自博客园,作者:疯子丶pony,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/mklblog/articles/16407903.html



