2194: 快速傅立叶之二
2194: 快速傅立叶之二
分析:
把相乘的,列到纸上,看一看就明白了。
k为0的情况:
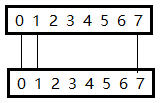
k为1的情况,7没有与它相连的点的了,于是可以加倍a数组。
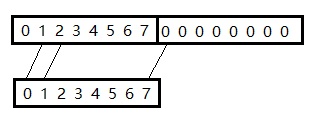
其他的同理,然后怎么快速求出这些位置的乘积之和。
将a数组翻转然后就是一个卷积的形式了,于是可以FFT。b数组后面填0即可。
代码:
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<cctype> #include<set> #include<queue> #include<vector> #include<map> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; inline int read() { int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();for(;!isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())if(ch=='-')f=-1; for(;isdigit(ch);ch=getchar())x=x*10+ch-'0';return x*f; } const int N = 270005; const double eps = 1e-10, Pi = acos(-1.0); struct Com{ double x, y; Com(double _x = 0,double _y = 0) { x = _x, y = _y; } }a[N], b[N]; Com operator + (const Com &A,const Com &B) { return Com(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); } Com operator - (const Com &A,const Com &B) { return Com(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y); } Com operator * (const Com &A,const Com &B) { return Com(A.x * B.x - A.y * B.y, A.x * B.y + A.y * B.x); } int x[N], y[N], f[N], rev[N]; void FFT(Com *a,int len,int ty) { for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) if (i < rev[i]) swap(a[i], a[rev[i]]); Com w1, w, u, t; for (int m = 2; m <= len; m <<= 1) { w1 = Com(cos(2 * Pi / m), ty * sin(2 * Pi / m)); for (int i = 0; i < len; i += m) { w = Com(1, 0); for (int k = 0; k < (m >> 1); ++k) { u = a[i + k], t = w * a[i + k + (m >> 1)]; a[i + k] = u + t, a[i + k + (m >> 1)] = u - t; w = w * w1; } } } } void mul(Com *a,Com *b,int len) { FFT(a, len, 1); FFT(b, len, 1); for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) a[i] = a[i] * b[i]; FFT(a, len, -1); for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i) f[i] = (int)(a[i].x / (double)len + 0.5); } int main() { int n = read(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) x[i] = read(), y[i] = read(); reverse(x, x + n + n); for (int i = 0; i < n + n; ++i) a[i] = Com(x[i], 0); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) b[i] = Com(y[i], 0); int len = 1, lg = 0; while (len < n + n) len <<= 1, lg ++; for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | ((i & 1) << (lg - 1)); mul(a, b, len); for (int i = n + n - 1; i > n - 1; --i) printf("%d\n", f[i]); return 0; }


