多线程之CAS和ABA
前言
文章主线
CAS -> UnSafe -> CAS底层思想 -> ABA -> 原子引用更新 -> 如何规避ABA问题
原理图
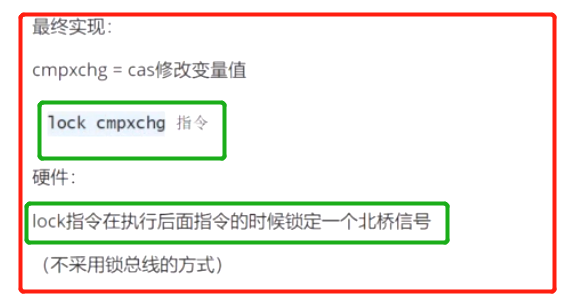
CAS 最底层 汇编与硬件
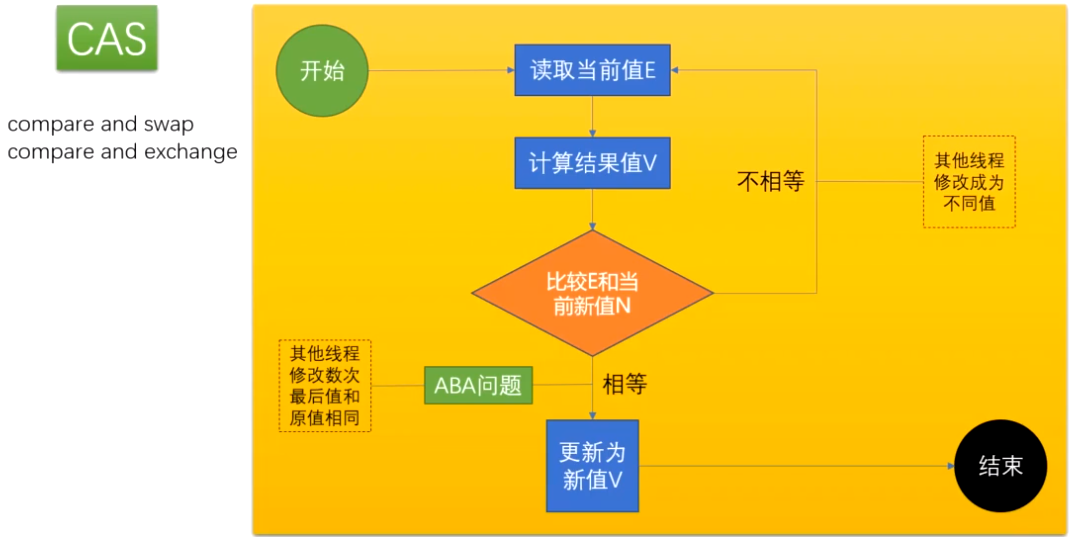
(一) CAS 比较相等就修改 不相等就不修改
为什么用CAS 不用synchronized (并发性不好,每次加锁操作完成后,才能进行下一步操作)
CAS 核心类 为Unsafe
由于Java方法无法直接访问底层系统,需要通过本地(native)方法来访问,Unsafe相当于一个后门,甚至该类可以直接操作特定内存的数据。
Unsafe类存在于sun.misc包中,其内部方法操作可以像C指针一样直接操作内存,因为Java中CAS操作的执行依赖于Unsafe类的方法
注意: Unsafe类中的所有方法都是native修饰的,也就是说Unsafe类中的方法都直接调用操作系统底层资源执行相应的任务
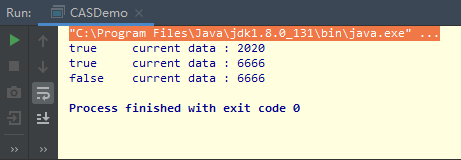
代码示例
1 package com.Interview.study.thread; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 4 5 /** 6 * @author zhangchaocai 7 * @create 2020-04-16 13:40 8 */ 9 public class CASDemo { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 13 AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(5); 14 15 System.out.println( atomicInteger.compareAndSet(5,2020) + "\t current data : " + atomicInteger.get()); 16 17 //看了源码 compareAndSet 和 weakCompareAndSet 是一样的 18 //底层都是 unsafe.compareAndSwapInt 19 System.out.println( atomicInteger.weakCompareAndSet(2020,6666) + "\t current data : " + atomicInteger.get()); 20 21 System.out.println( atomicInteger.weakCompareAndSet(2020,77777) + "\t current data : " + atomicInteger.get()); 22 } 23 }
运行结果
CAS 缺点
例如 unSafe 中的getAndAddInt方法 中有个do while
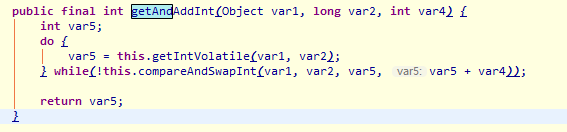
如果CAS 失败,会一直尝试。如果CAS 长时间不成功,可能会给CPU带来很大的开销
(二) CAS 引出ABA 问题
ABA 释义 : 狸猫换太子
CAS 算法实现一个重要前提需要取出内存中某时刻的数据并在当下时刻比较并替换,那么在这个时间差之间会导致数据的变化。
比如说一个线程one从内存位置V取出A,这个时候另一个线程two也从内存中取出A,并且线程two进行进行了一些操作将值变味了B,
然后线程two又将V位置的数据变成A,这时候线程one进行CAS操作发现内存中仍然是A,然后线程one操作成功
尽管线程one的CAS操作成功,但是不代表这个过程就是没有问题的
解决ABA 问题 加版本号!!!(AtomicStampedReference)
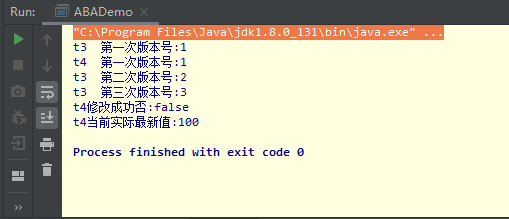
1 package com.Interview.study.thread; 2 3 import java.sql.Time; 4 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 5 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference; 6 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference; 7 8 /** 9 * @author zhangchaocai 10 * @create 2020-04-16 13:35 11 */ 12 public class ABADemo { //ABA问题解决 AtomicStampedReference 13 14 15 static AtomicReference<Integer> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>(100); 16 static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(100,1); 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 20 new Thread(() -> { 21 int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp(); 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t第一次版本号:" + stamp); 23 24 //T3线程暂停1秒 25 try{ 26 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 27 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100,101,atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1); 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t第二次版本号:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); 32 atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(101,100,atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1); 33 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t第三次版本号:" + atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); 34 },"t3").start(); 35 36 new Thread(() -> { 37 int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp(); 38 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t第一次版本号:" + stamp); 39 40 //T4线程暂停1秒 41 try{ 42 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); 43 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } 46 boolean result = atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(100,2020,stamp,stamp+1); 47 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "修改成功否:" + result); 48 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "当前实际最新值:" + atomicStampedReference.getReference()); 49 },"t4").start(); 50 51 } 52 53 }
运行结果
后来遇见他....



