Udemy AWS SAA - Scalability & Availability
1.Udemy AWS SAA - Intro and IAM2.Udemy AWS SAA - Private vs Public IP (IPv4)3.Udemy AWS SAA - EC2
4.Udemy AWS SAA - Scalability & Availability
5.Udemy AWS SAA - RDSScalability: an application / system can handle greater loads by adapting.
There are two kinds of scalability
- Vertical Scalability (=scale up / down)
- increasing the size of the instance, like better laptop, or from t2.micro to t2.large
- Horizontal Scalability(= elasticity)(= scale out / in)
- increasing the number of instances or systems for your application. This implies distributed systems
- Auto Scaling Group
- Load Balancer
Availability (= run instances for the same app across multi AZs)
- High Availability usually goes hand inhand with horizontal scaling
- High availability means running your application /system in at least 2 data centers (== vailability Zones)
- The goal of high availability is to survive a data center loss
- The high availability can be passive (forRDS Multi AZ for example)
Load balancing:
servers that forward traffic to multiple servers (ex. EC2 instances) downstream
Why use a load balancer?
- Spread load across multiple downstream instances
- Expose a single point of access (DNS) to your application
- Seamlessly handle failures of downstream instances
- Do regular health checks to your instances
- Provide SSL termination (HTTPS) for your websites
- Enforce stickiness with cookies
- High availability across zones
- Separate public traffic from private traffic
Elastic load balancer
- a managed load balancer
- cheaper that creating your own load balancer, and integrate with many AWS offerings
Health Checks
- Crucial for load balancers
- They enable the load balancer to know if instances it forwards traffic to are available to reply to requests
- The health check is done on a port and a route (/health is common)
- If the response is not 200 (OK), then the instance is unhealthy
4 kinds of managed load balancers
-
classic load balancer
- support TCP HTTP HTTPS
- fixed hostname
-
application load balancer
- HTTP only, Load balancing to multiple HTTP applications across machines (target groups)
- = CLB + multiple target groups (can apply diff rules to diff groups)
- fixed hostname, app server don't see the IP of client directly
- target group could be EC@ instances, ECS tasks, Lambda Functions, private IP addresses
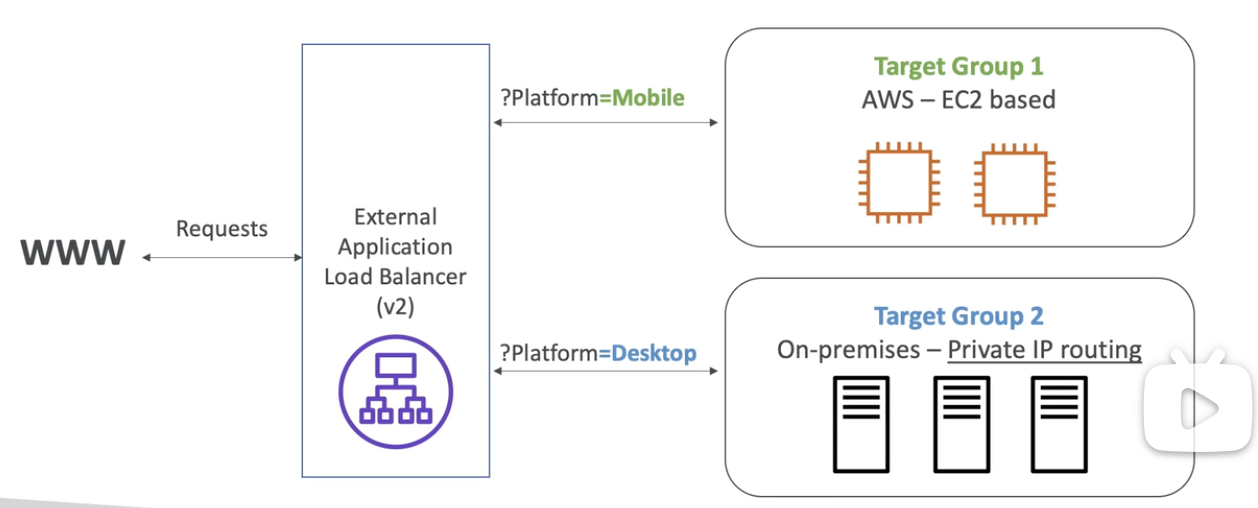
- Load balancing to multiple applications on the same machine (ex: containers)
- Support for HTTP/2 and WebSocket, Support redirects (from HTTP to HT TPS for example)
- can route base on path/hostname/Query String, headers in URL
-
network load balancer
- allow to forward TCP&UDP traffic to your instances for extreme performance, can handle millions of request per sec, less latency, and has one static IP per AZ and supporting assigning elastic IP
- just like ALB, apply to target group
-
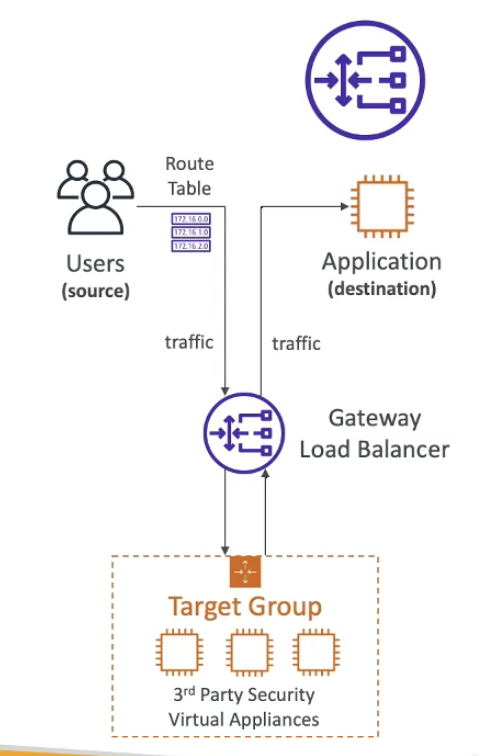
Gateway Load Balancer
- reply a fleet of third party network virtual appliances in AWS
- transfer IP packets, GENEVE protocol on port 608
Elastic Load Balancer
Sticky sessions (session affinity)
- make same client always redirected to the same instance behind a load balancer
- a cookie is used for stickiness, make sure user doesn't lose their session data
Application-based cookies
- custom cookie: generated by the target, can include any custom attributes required by the application
- application cookie: generated by load balancer
Duration-based cookie - generated by load balancer
Cross-zone load balancing
- each load balancer instances distributes evenly across all registered instances in all AZ
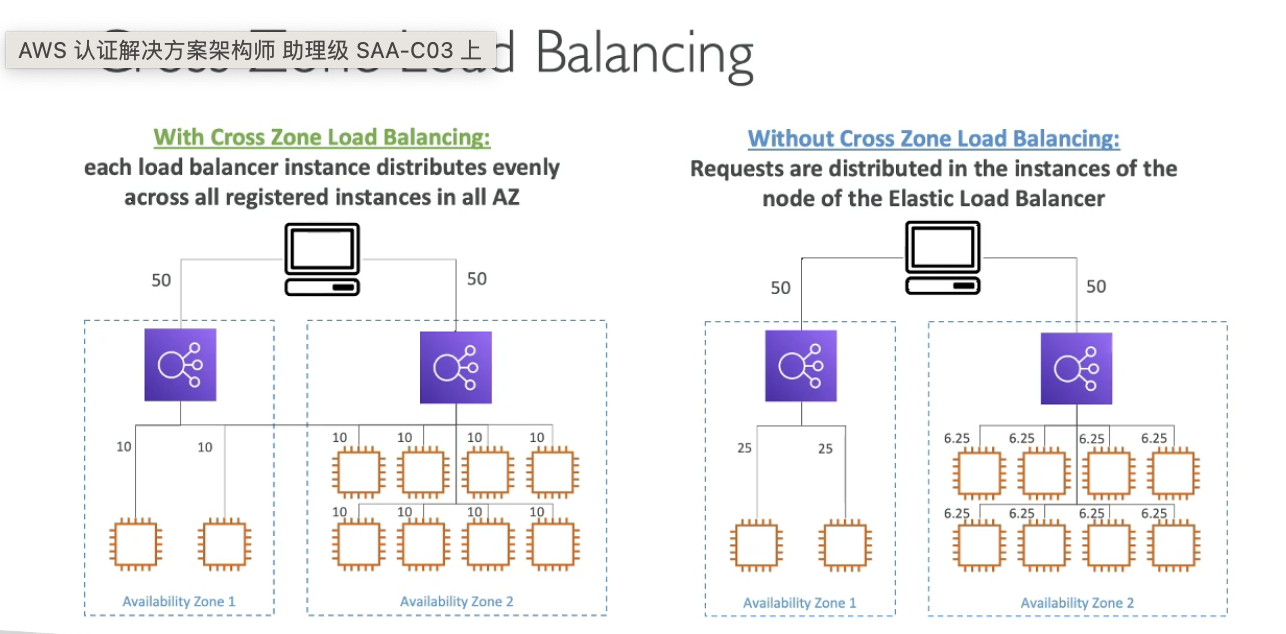
- application load balancer: always on, no extra charge
- network load balancer: disabled by default, have extra charge
- classic load balancer
SSL/TLS
- encrypt traffic
- Public SSL certificates are issued by CA
- TLS is newer version of SSL
Connection draining
- feature naming, give some time to complete in flight requests while instance is de-registering or unhealthy
Auto Scaling Group
- scale out and in to match an increased/decreased load
- possible to scale an ASG based on CloudWatch alarm, alarm monitors a metric
- scaling policies
- target tracking scaling: simple and easy, I want avg CPU stay at 40%
- simple / step scaling: when Cloudwatch triggered, add 2 units
- scheduled actions: when Friday night, add 2 units
predictive scaling is the future
Good metrics:
- CPU Utilizations
- Request count per Target
- Average Network In / Out
- any custom metric
Scaling cooldowns
- default 300 seconds, then not launch or terminate additional instances




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?