Udemy AWS SAA - EBS, AMI, EFS
EBS (Elastic Block Store) Volume
- it is a network drive you can attach to you instances while they run
- it allows you instances to persist data, even after their termination. Just like a "network USB stick" (not physical)
- they can only be mounted to one instance at a time. And it is bound to a specific availability zone
EBS - Delete on Termination Attribute
- can control preserve root volume when instance is terminated
EBS Snapshots
- Make a backup (snapshot) of your EBS volume at a point in time
- You can copy snapshot from AZ to AZ
- You can archive it so cheaper, it take 24-72 hrs for restoring the archive
- You can recover deleted snapshots from recycle bin
- FSR (Fast Snapshot Restore): force full initialization of snapshot to have no latency on the first use, but very expensive
AMI
- Amazon Machine Image, a customization of an EC2 instance, you can add your own software, configuration, OS, monitoring, so that faster boot / config time bc all your software is pre-packaged
- Public AMI: AWS provided;
- Your own AMI: make and maintain them yourself;
- An AWS marketplace AMI: AMI made by someone else
AMI Process
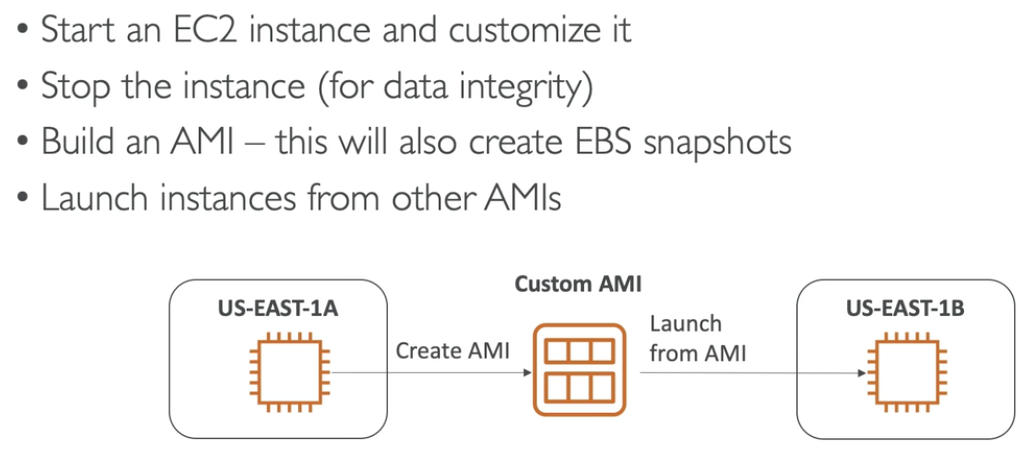
EC instance store
- EBS volumes are good but (it's network drive) limited performance
- So we need a high-performance in I/O hardware disk, use EC2 instance store. But it lose storage if they are stopped, so ephemeral, only good for buffer / cache / scratch data / temporary content
- risk of data loss if hardware fails, so need to backup and replicate
EBS Volume Types
-
gp2/gp3 (SSD): General purpose SSD volume that balances price and performance fora wide variety of workloads
-
iol /io2 (SSD): Highest-performance SSD volume for mission-critical low-latency or high-throughput workloads
-
stl (HDD): Low cost HDD volume designed for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads
-
scl (HDD): Lowest cost HDD volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads
-
only gp2 / gp3 and io1 / io2 can be used as boot volumes
EBS Volume Use Case
- GP: gp3 can increase IOPS and throughput independently, but gp2's volume size and IOPS are linked
- Provisioned IOPS SSD: great for database workload (sensitive to storage performance and consistency)
- HHD: hard disk drives, cannot be a boot volume
Multi-attach feature of EBS, only available to io1/io2
- It allows us attach same EBS volume to multiple EC2 instances in the same AZ
- it's up to 16 EC2 instances at a time
can achieve higher application availability in clustered linux app
EBS Encryption
- When you create an encrypted EBS volume, you get the following:
- Data at rest is encrypted inside the volume
- All the data in fight moving between the instance and the volume is encrypted
- All snapshots are encrypted
- All volumes created from the snapshot
- Encryption and decryption are handled transparently (you have nothing todo)
- Encryption has a minimal impact on latency
- EBS Encryption leverages keys from KMS (AES-256)
Amazon EFS- Elastic File System
- Managed NFS (network file system) that can be mounted on many EC2 EFS works with EC2 instances in multi-AZ
- Highly available, scalable, expensive (3x gp2), pay per use
- Use cases: content management, web serving, data sharing, Wordpress
- Uses NFSv4.l protocol
- Uses security group to control access to EFS
- Compatible with Linux based AMl (not Windows)
- Encryption at rest using KMS
- POSlX file system (~Linux) that has a standard file API
- File system scales automatically, pay-per-use, no capacity planning
EFS- Performance Classes
- EFS Scale
- 1000s of concurrent NFS clients, 10 GB+ /s throughput
- Grow to Petabyte-scale network file system, automatically
- Performance mode (set at EFS creation time)
- General purpose (default): latency-sensitive use cases (web server, CMS, etc...)Max 1/O- higher latency, throughput, highly parallel (big data, media processing)
- Throughput mode
- Bursting(lTB= 50MiB/s + burst ofup to 100MiB/s)
- Provisioned: set your throughput regardless of storage size, ex: l GiB/s for l TB storage
EFS- Storage Classes
-
Storage Tiers (lifecycle management feature -move file after N days)
- Standard: for frequently accessed files
- Infrequent Access (EFS-A): cost to retrieve fles,lower price to store. Enable EFS-lA with a Life cycle Policy
-
Availability and durability
- Standard: Multi-AZ, great for prod
- One Zone: One AZ, great for dev, backup enabled by default, compatible with lA (EFS One Zone-lA)
-
Mounting 100s of instances across AZ
-
EFS share website files (WordPress)
-
Only for Linux Instances (POSlx)
-
EFS has a higher price point than EBS
-
Can leverage EFS-IA for cost savings
EBS vs EFS
EBS
- EBS volumes..
- can be attached to only one instance at a time
- are locked at the Availability Zone (AZ) level
- gp2: 1O increases if the disk size increases
- iol: can increase lO independently
- To migrate an EBS volume across AZ
- Take a snapshot
- Restore the snapshot to another AZ
- EBS backups use lO and you shouldn't run them while your application is handling a lot of traffic
- Root EBS Volumes of instances get terminatedby default if the EC2 instance gets terminated.(you can disable that)
EFS
- Mounting 100s of instances across AZ
- EFS share website files (WordPress)
- Only for Linux Instances (POSlx)
- EFS has a higher price point than EBS
- Can leverage EFS-A for cost savings
Remember: EFS vs EBS vs Instance Store




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义