[CV] Mnist手写数字分类
数据集
手写数字Mnist数据集Mnist(lecun.com)
- 每张手写数字图片包含28*28个灰度像素点
- 包含从0~9十个数字
任务
使用SVM对手写数字进行分类
步骤
- 对图像提取特征
- 划分数据集,分为训练集和测试集7:3
- 使用SVM对图像进行分类
- 输出混淆矩阵和精确度
方法
-
由于原图片只有28*28,直接使用像素作为特征送入SVM分类器
# 直接对28*28像素进行svm分类 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix import numpy as np from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn import svm import cv2 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml # 获取数据集 X, y = fetch_openml('mnist_784', data_home="./data", as_frame=False, return_X_y=True) # 数据集的格式是每行是一张图片(一维数组numpy.dnarray总长度是28*28) print(X[0]) assert X[0].shape[0] == 28*28 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0) svc = svm.SVC() svc.fit(X_train, y_train) predicts = svc.predict(X_test) # 打印出混淆矩阵 print(confusion_matrix(predicts, y_test)) print("accuracy : {}".format(accuracy_score(predicts, y_test)))运行结果:
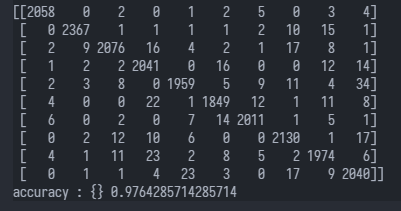
P.S. 直接送入分类器进行分类准确度就已经可以达到0.976了
-
由之前学习的Sobel等梯度算子(边缘信息),同时为了旋转不变性就联想到数据增强——多角度提取边缘特征。基于梯度方向直方图(HOG)进行特征提取,再送入SVM分类器进行分类
# 使用HOG特征提取 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix import numpy as np from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn import svm import cv2 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml # 获取数据集 X, y = fetch_openml('mnist_784', data_home="./data", as_frame=False, return_X_y=True) winSize = (4, 4) blockSize = (4, 4) blockStride = (8, 8) cellSize = (4, 4) nbins = 9 derivAperture = 1 winSigma = 4. histogramNormType = 0 L2HysThreshold = 2.0000000000000001e-01 gammaCorrection = 0 nlevels = 64 hog = cv2.HOGDescriptor(winSize, blockSize, blockStride, cellSize, nbins, derivAperture, winSigma, histogramNormType, L2HysThreshold, gammaCorrection, nlevels) print(hog.compute(X[0].reshape(28,28).astype(np.uint8)).flatten().shape) # 计算提取HOG特征 new_X = np.asarray([hog.compute(x.reshape(28,28).astype(np.uint8)).flatten() for x in X]) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( new_X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0) svc = svm.SVC() svc.fit(X_train, y_train) predicts = svc.predict(X_test) # 打印出混淆矩阵 print(confusion_matrix(predicts, y_test)) print("accuracy : {}".format(accuracy_score(predicts, y_test)))
使用HOG提取特征后,特征由28*28维度降到441维度,同时准确率也提升接近0.01。


