Python全栈day28(描述符应用)
描述符的使用
python是弱类型语言,及参数的赋值没有类型限制,下面通过描述符机制来实现类型限制功能
描述符应用1.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | class Typed: def __get__(self, instance, owner): print('get方法') print('instance是[%s]'%instance) print('owner是[%s]'%owner) def __set__(self, instance, value): print('set方法') #instance就是实例化出来的对象本身 print('instance是[%s]'%instance) print('value是[%s]'%value) def __delete__(self, instance): print('delete方法') print('instance是[%s]' % instance)class People: name = Typed() def __init__(self,name,age,salary): self.name = name self.age = age self.salary = salary#实例化触发了以下三个赋值操作#p1.__dict__['name'] = 'zhangsan'#p1.__dict__['age'] = 18#p1.__dict__['salary'] = 999999#但是数据属性被描述符描述了进行赋值操作调用的是描述类的set方法#因为set方法没有进行实际赋值操作所以字典的name属性为Nonep1 = People('zhangsan',18,999999)# set方法# instance是[<__main__.People object at 0x000001E527F67390>]# value是[zhangsan]print(p1)#<__main__.People object at 0x000001BF1B047390>print(p1.__dict__)#调用数据属性触发__get__方法输出p1.name# get方法# instance是[<__main__.People object at 0x000001F7F3ED8080>]# owner是[<class '__main__.People'>]#调用del删除数据属性,触发__delete__方法输出del p1.name# delete方法# instance是[<__main__.People object at 0x0000018239F274E0>] |
以上只是测试是否调用了描述符,但是对应的__get__,__set__,__delete__只是执行了打印操作没有进行返回值,设置值,删除值的操作所以只有打印输出
PS:根据优先级数据描述符大于实例所以优先调用数据描述符,假如进行了p1.name = ‘lisi’会执行set方法但是不会赋值,name依旧为空
下面在__get__,__set__,__delete__执行对应的返回值,设置值,删除值操作
描述符应用2.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | class Typed: def __init__(self,key): self.key=key def __get__(self, instance, owner): print('get方法') # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('owner是[%s]'%owner) #使用对应的key返回值 return instance.__dict__[self.key] def __set__(self, instance, value): print('set方法') #instance就是实例化出来的对象本身 # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('value是[%s]'%value) #对对应的key进行赋值设置操作 instance.__dict__[self.key] = value def __delete__(self, instance): print('delete方法') # print('instance是[%s]' % instance) #使用对应的key删除操作 instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)class People: name = Typed('name') def __init__(self,name,age,salary): self.name = name self.age = age self.salary = salary#实例化触发了以下三个赋值操作#p1.name = 'zhangsan'#p1.age = 18#p1.salary = 999999#其中p1.name = 'zhangsan'调用了描述符类Typed进行实例化#name = Typed('name')运行初始化函数__init__#self.name = 'name'p1 = People('zhangsan',18,999999)#set方法#打印字典name也赋值成功print(p1.__dict__)#{'age': 18, 'name': 'zhangsan', 'salary': 999999}p1.name#get方法del p1.name#delete方法#打印字典上一步的删除操作也成功删除了属性nameprint(p1.__dict__)#{'age': 18, 'salary': 999999} |
通过定义描述符类的初始化__init__函数获取字典需要修改对应的key值然后执行相应的返回值,设置值,删除值的操作
下面对用户实例化输入的信息进行判断,比如输入姓名只能是字符串格式不能是数字或者其他格式
描述符应用3.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | class Typed: def __init__(self,key): self.key=key def __get__(self, instance, owner): print('get方法') # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('owner是[%s]'%owner) #使用对应的key返回值 return instance.__dict__[self.key] def __set__(self, instance, value): print('set方法') #instance就是实例化出来的对象本身 # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('value是[%s]'%value) #对应的key进行赋值设置操作 if not isinstance(value,str): print('你输入是不是字符串类型,错误') return instance.__dict__[self.key] = value def __delete__(self, instance): print('delete方法') # print('instance是[%s]' % instance) #使用对应的key删除操作 instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)class People: name = Typed('name') def __init__(self,name,age,salary): self.name = name self.age = age self.salary = salaryp1=People(18,18,999999)#因为调用__set__方法的时候检测到输入的名字不是字符串,然后直接return了所以name没有赋值print(p1.__dict__) |
#set方法
#你输入是不是字符串类型,错误
#{'salary': 999999, 'age': 18}
可以把错误返回改的高端一点
描述符应用4.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | class Typed: def __init__(self,key): self.key=key def __get__(self, instance, owner): print('get方法') # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('owner是[%s]'%owner) #使用对应的key返回值 return instance.__dict__[self.key] def __set__(self, instance, value): print('set方法') #instance就是实例化出来的对象本身 # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('value是[%s]'%value) #对应的key进行赋值设置操作 if not isinstance(value,str): # print('你输入是不是字符串类型,错误') # return raise TypeError('%s你传入的不是字符串'%value) instance.__dict__[self.key] = value def __delete__(self, instance): print('delete方法') # print('instance是[%s]' % instance) #使用对应的key删除操作 instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)class People: name = Typed('name') def __init__(self,name,age,salary): self.name = name self.age = age self.salary = salaryp1=People(18,18,999999) |
运行直接报错
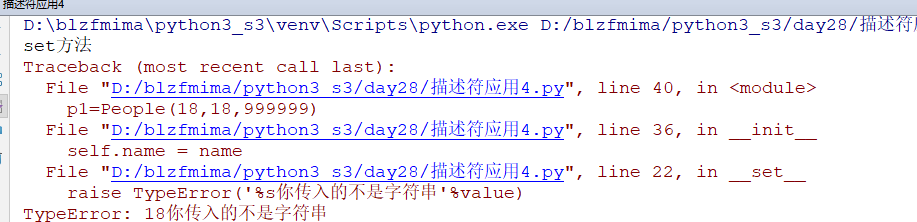
以上只是实现了输入的name必须是字符串,并没有对输入的age限制必须是整型
描述符应用5.py
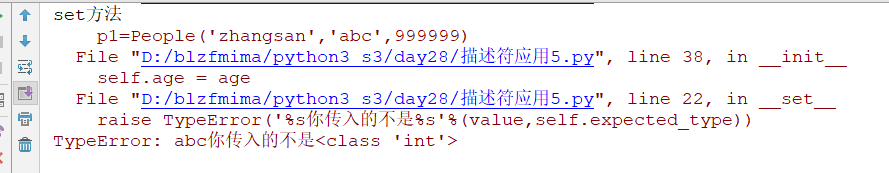
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | class Typed: def __init__(self,key,expected_type): self.key=key self.expected_type=expected_type def __get__(self, instance, owner): print('get方法') # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('owner是[%s]'%owner) #使用对应的key返回值 return instance.__dict__[self.key] def __set__(self, instance, value): print('set方法') #instance就是实例化出来的对象本身 # print('instance是[%s]'%instance) # print('value是[%s]'%value) #对应的key进行赋值设置操作 if not isinstance(value,self.expected_type): # print('你输入是不是字符串类型,错误') # return raise TypeError('%s你传入的不是%s'%(value,self.expected_type)) instance.__dict__[self.key] = value def __delete__(self, instance): print('delete方法') # print('instance是[%s]' % instance) #使用对应的key删除操作 instance.__dict__.pop(self.key)class People: name = Typed('name',str) age = Typed('age',int) def __init__(self,name,age,salary): self.name = name self.age = age self.salary = salaryp1=People('zhangsan','abc',999999)print(p1.__dict__) |
因为age输入的是字符串所以报错





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!