Python之MySQL数据库连接驱动pymysql的使用
本文介绍python数据库MySQL连接驱动pymysql的简单使用
1,安装pymysql模块
未安装模块首先使用pip安装
1 | pip3 install pymysql |
2,创建数据库连接
使用模块pymysql创建数据库连接的语法为
传递的参数为host主机,user用户名 password密码,db数据库名称
1 | conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='www-data',password='www-data',db='awesome') |
以键值对方法传递,也可以把这些键值对存储为一个dict使用以下方式传递
1 | conn = pymysql.connect(**kw) |
3,创建数据库浮标
使用以下方法创建浮标,使用数据库连接对象conn加方法cursor创建一个数据库连接浮标
1 | cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) |
4,执行sql语句
有了数据库浮标cursor就可以执行sql语句了,执行语法如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 | cursor.execute(sql,args)sql # 需要执行的sql语句例如'select * from table_name'args # 替换sql语句的格式化字符串,即sql语句可以使用%s代表一个字符串,然后在args中使用对应的变量或参数替换,args为一个list或元组,即是一个有序的序列需要和sql中的%s一一对应# 例如sql='select * from table_name where id=%s' args=['12345']# 相当于使用args中的参数替换sql中的%s # select * from table_name where id='12345' |
5,实践执行sql语句
实践执行sql语句前我们首先在本机创建一个数据库和对应的表用于测试
数据库对应的主机,用户名,密码,库名,表名如下
1 2 3 4 5 | host: localhostuser: www-datapassword: www-datadb:awesometable_name: users |
创建表名的sql语句如下,需要在数据库中创建好对应的表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `email` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `passwd` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `admin` tinyint(1) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `image` varchar(500) NOT NULL, `created_at` double NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `idx_email` (`email`), KEY `idx_created_at` (`created_at`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
创建好的表对应的结构如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | mysql> desc users;+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+| id | varchar(50) | NO | PRI | NULL | || email | varchar(50) | NO | UNI | NULL | || passwd | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | || admin | tinyint(1) | NO | | NULL | || name | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | || image | varchar(500) | NO | | NULL | || created_at | double | NO | MUL | NULL | |+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+7 rows in set (2.68 sec) |
①执行insert操作
往数据库插入一条数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | import time# insert startsql = 'insert into `users` (`email`, `passwd`, `admin`, `name`, `image`, `created_at`, `id`) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)'args = ['test@qq.com','password',1,'test','about:blank',time.time(),'111111']# 使用replace 把'?'替换成'%s'cursor.execute(sql.replace('?','%s'),args)conn.commit()# insert end |
插入以下代码
use_pymysql.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | import time# insert startsql = 'insert into `users` (`email`, `passwd`, `admin`, `name`, `image`, `created_at`, `id`) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)'args = ['test@qq.com','password',1,'test','about:blank',time.time(),'111111']# 使用replace 把'?'替换成'%s'cursor.execute(sql.replace('?','%s'),args)conn.commit()# insert end |
注意:执行修改操作需要使用conn.commit()提交,否则修改不生效
在MySQL数据库查询可以看到插入的数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | mysql> select * from users;+--------+-------------+----------+-------+------+-------------+------------------+| id | email | passwd | admin | name | image | created_at |+--------+-------------+----------+-------+------+-------------+------------------+| 111111 | test@qq.com | password | 1 | test | about:blank | 1637723096.69565 |+--------+-------------+----------+-------+------+-------------+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
注意:执行操作也是有返回的,返回结果是本次操作影响的数据库条数,如果把返回结果打印,本次输出为1
1 2 3 | rs = cursor.execute(sql.replace('?','%s'),args)conn.commit()print(rs) |
②执行update操作
修改数据我们根据条件id修改刚刚插入的数据
执行修改前需要把刚刚执行的插入语句注释,否则因为建值重复会报错
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # update startsql = 'update `users` set `email`=?, `passwd`=?, `admin`=?, `name`=?, `image`=?, `created_at`=? where `id`=?'args = ['test2@qq.com','password',1,'test2','about:blank',time.time(),'111111'] print(cursor.execute(sql.replace('?','%s'),args))conn.commit()# update end |
执行以后把email和name修改了
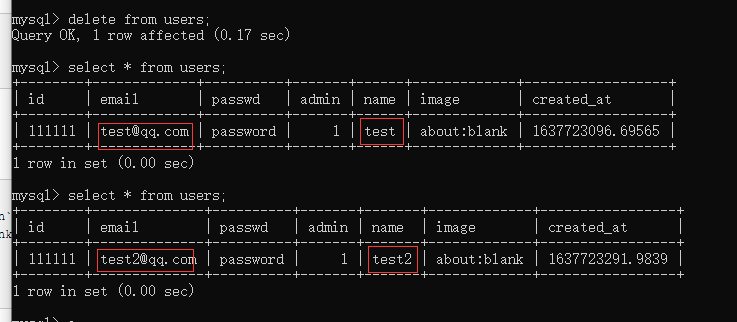
③执行delete操作
执行删除操作把刚刚插入的数据删除
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # delete startsql = 'delete from `users` where `id`=?'args = ['111111'] print(cursor.execute(sql.replace('?','%s'),args))conn.commit()# delete end |
同样根据关键字id指定的值删除了这条数据
④执行select操作
在执行select操作前我们保证数据库里面至少有一条数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)sql = 'select * from users'args = []# 执行查询返回结果数量# 执行查询rs=cursor.execute(sql,args)# 获取查询结果# 获取查询的第一条结果,返回一个dict,dict元素是查询对应的键值对# 如果查询结果有多条则执行一次,游标移动到下一条数据,在执行一次又返回一条数据print(cursor.fetchone()) |
同样执行select操作返回结果也是本次操作影响了几行数据,即根据条件查询到几条数据,本次为1条
要想获得结果使用游标的fetchone(),fetchall(),fetehmant(num)来获取,他们的区别在于
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | # 获取查询的第一条结果,返回一个dict,dict元素是查询对应的键值对# 如果查询结果有多条则执行一次,游标移动到下一条数据,再执行一次又返回一条数据print(cursor.fetchone())# 获取查询的所有结果,返回一个list,list元素是dict,dict元素是查询对应的键值对print(cursor.fetchall())# 获取查询的前几条结果,返回一个list,list元素是dict,dict元素是查询对应的键值对print(cursor.fetchmany(1)) |
fetchone()获取的是dict
fetchall()和fecthmany(num)获取的是list,list的元素是是dict
他们对应的结果如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | print(cursor.fetchone())# {'id': '111111', 'email': 'test@qq.com', 'passwd': 'password', 'admin': 1, 'name': 'test', 'image': 'about:blank', 'created_at': 1637723578.5734}print(cursor.fetchall())# [{'id': '111111', 'email': 'test@qq.com', 'passwd': 'password', 'admin': 1, 'name': 'test', 'image': 'about:blank', 'created_at': 1637723578.5734}]print(cursor.fetchmany(1))# [{'id': '111111', 'email': 'test@qq.com', 'passwd': 'password', 'admin': 1, 'name': 'test', 'image': 'about:blank', 'created_at': 1637723578.5734}] |
注意:cursor的一个浮标,当获取数据以后浮标会移动,假如查询的数据只有一条已经使用cursor.fetchone()方法取出这一条数据,浮标已经移动到没有数据,再使用fetchone(),fetchall() ,fetchmany(num)去获取则会返回None或者是空列表[]
浮标处没有数据了再使用fetchone()返回None,使用fetchall(),fetchmany(num)返回[]
⑥写成函数使用
为了方便调用可以把执行sql语句写成函数来使用,分两个函数,一个函数执行select把结果返回,一个函数执行insert,update,delete把影响的行数返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | def select(sql,args,size=None): log(sql,args) cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) cursor.execute(sql.replace('?','%s'),args or ()) if size: rs = cursor.fetchmany(size) else: rs = cursor.fetchall() cursor.close logging.info('rows returned: %s' % len(rs)) return rsdef execute(sql,args): cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) try: cursor.execute(sql.replace('?','%s'),args) # rowcount方法把影响函数返回 rs = cursor.rowcount cursor.close() conn.commit() except: raise return rs |
其中select函数加一个默认参数size即返回查询的数据条数,需要传递一个整数返回这个整数的个数的条数,如果不传递则返回所有查询结果,结果是一个list,这个list的元素是查询结果键值对组成的dict
执行修改操作的函数把影响的条数返回,如果返回为0则代表没有影响数据库,代表修改失败,修改操作不要忘记conn.commit()提交修改结果,否则修改不生效





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
2020-11-24 Web开发基础之Bootstrap