第七章 Kubernetes进阶之Ingress
Ingress
1.Pod与Ingress的关系
- 通过service相关联
- 通过Ingress Controller实现Pod负载均衡
- 支持TCP/UDP 4层和7层
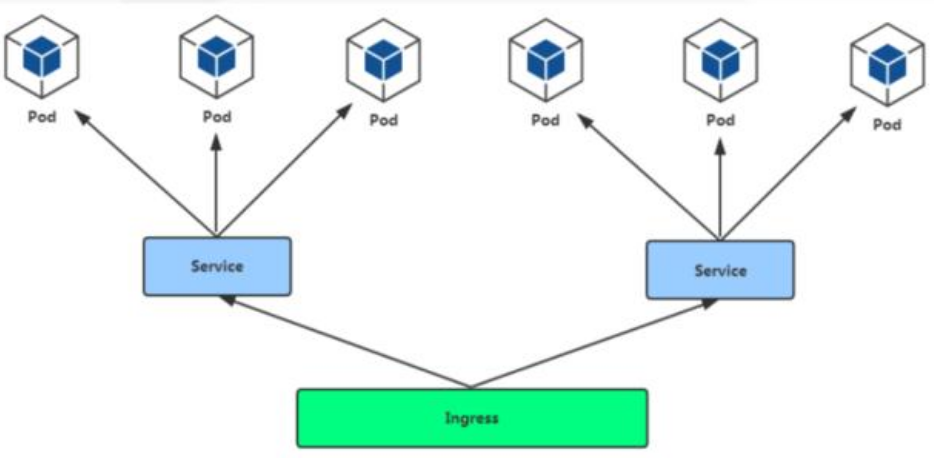
访问流程
用户->Ingress controller->Pod
部署参考文档:https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/blob/master/docs/deploy/index.md
下载ingress-nginx配置文件
1 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/static/mandatory.yaml |
PS:如果无法下载在本机hosts添加一行配置
1 | 151.101.108.133 raw.githubusercontent.com |
下载后修改
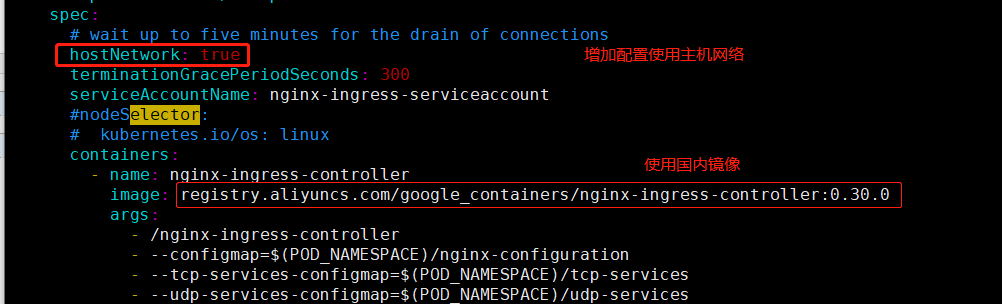
应用
1 | kubectl apply -f mandatory.yaml |
排错:应用以后使用命令查看显示为空 本次拍错参考文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/Dev0ps/p/10778328.html
1 2 | # kubectl get pod -n ingress-nginxNo resources found. |
修改kube-controller-manager配置文件记录日志
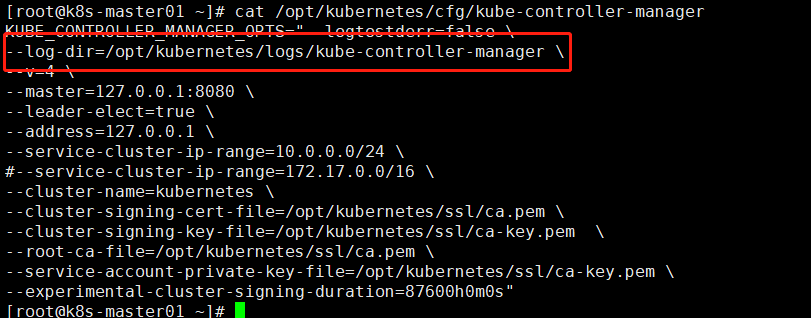
查看错误日志kube-controller-manager.ERROR发现以下报错
1 | E0310 08:55:56.869874 13765 replica_set.go:450] Sync "ingress-nginx/nginx-ingress-controller-5648d4586f" failed with pods "nginx-ingress-controller-5648d4586f-884bb" is forbidden: SecurityContext.RunAsUser is forbidden |
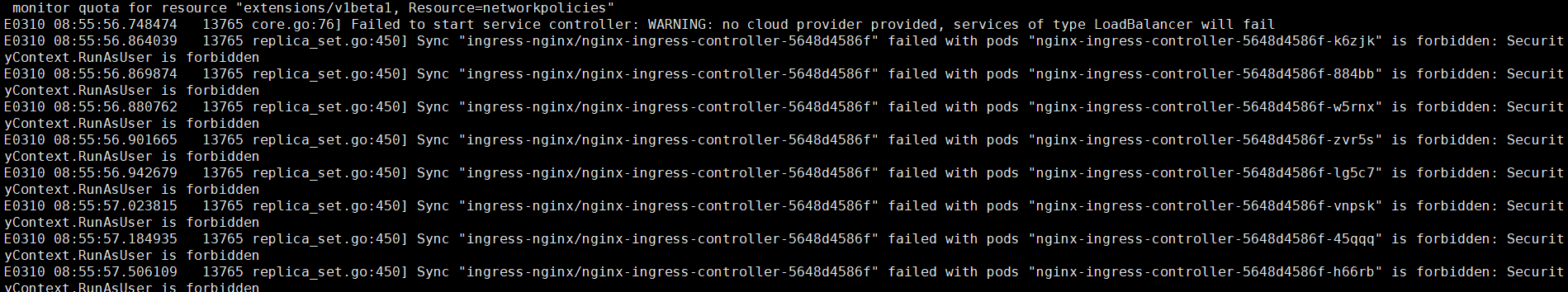
修改kube-apiserver配置文件增加配置
1 | --enable-admission-plugins=NamespaceLifecycle,LimitRanger,ServiceAccount,ResourceQuota,NodeRestriction \ |
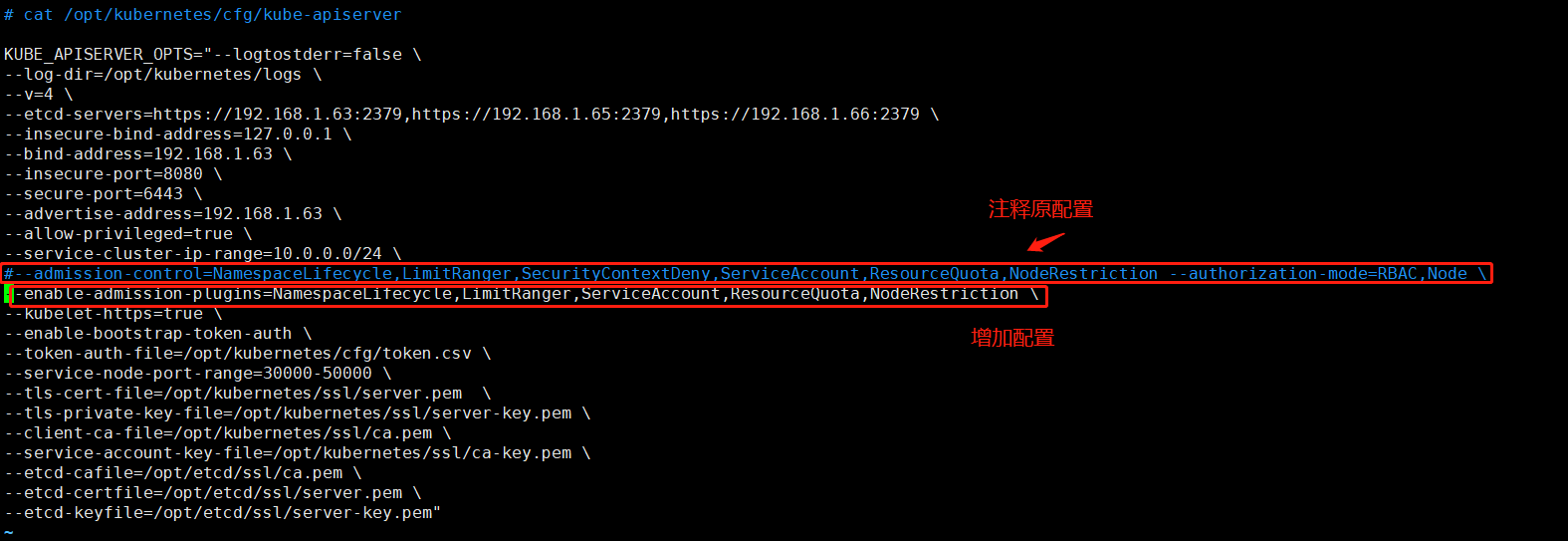
重启kube-apiserver
1 | systemctl restart kube-apiserver |
应用以后查看
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | # kubectl get pod,ns -n ingress-nginxNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEpod/nginx-ingress-controller-5648d4586f-nhzm5 1/1 Running 0 20sNAME STATUS AGEnamespace/default Active 15hnamespace/ingress-nginx Active 20snamespace/kube-public Active 15hnamespace/kube-system Active 15h |
查看该pod分配到哪个node节点上

因为配置文件配置hostNetwork=true使用宿主机网络所以在对应节点会监听80和443端口
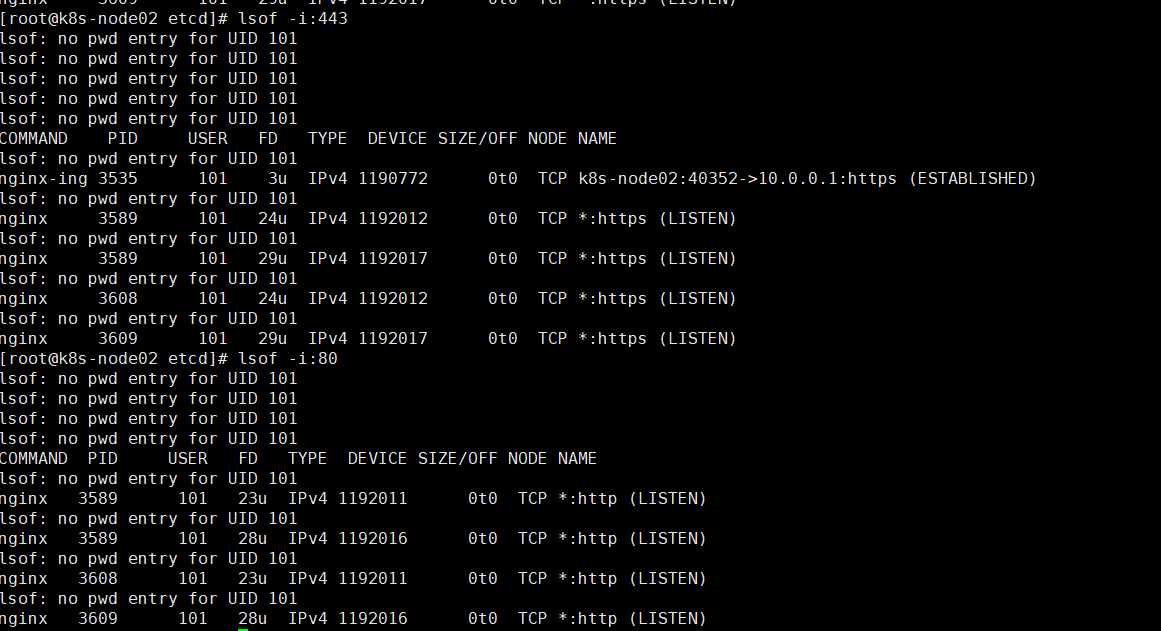
对应节点不要有其他应用程序占用这两个端口
2.Ingress Controller
控制器已经部署好了,需要定义ingress规则定义域名访问
创建测试示例,最小示例可以在官方网站下载https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | # cat ingress.yaml apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1kind: Ingressmetadata: name: simple-fanout-example annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /spec: rules: #定义访问域名 - host: foo.bar.com http: paths: #访问根目录 - path: / backend: #转发到哪个server下 serviceName: my-service servicePort: 80 |
该ingrss对应的service必须存在,如果没有使用以下命令创建,service端口也需要对应80
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | #创建deploymentkubectl run my-service --image=nginx --port=80#创建service对应刚刚创建的deployment my-servicekubectl expose deployment my-service --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort#查看是否创建成功# kubectl get svcNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEkubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 17hmy-service NodePort 10.0.0.130 <none> 80:42291/TCP 99s |
应用ingress
1 2 | # kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml ingress.extensions/simple-fanout-example created |
查看
1 2 3 | # kubectl get ingressNAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGEsimple-fanout-example foo.bar.com 80 62s |
对应的name是 simple-fanout-example
对应的域名是 foo.bar.com
对应的ADDRESS为空 是转发到backend对应的后端
在主机设置hosts即可使用域名访问nginx
ingress控制器使用nginx进行负载均衡,进入控制器
1 | kubectl exec -it nginx-ingress-controller-74cf54575-gt9mm bash -n ingress-nginx |
1 | ps -ef|grep nginx |
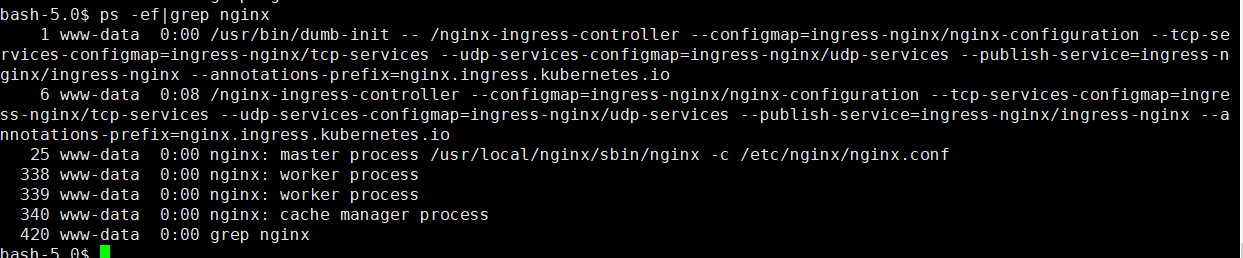
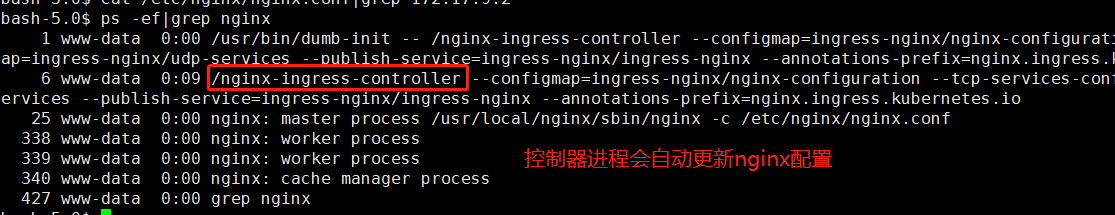
查看nginx配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 | # Configuration checksum: 4424420289189243736# setup custom paths that do not require root accesspid /tmp/nginx.pid;daemon off;worker_processes 2;worker_rlimit_nofile 523264;worker_shutdown_timeout 240s ;events { multi_accept on; worker_connections 16384; use epoll;}http { lua_package_path "/etc/nginx/lua/?.lua;;"; lua_shared_dict balancer_ewma 10M; lua_shared_dict balancer_ewma_last_touched_at 10M; lua_shared_dict balancer_ewma_locks 1M; lua_shared_dict certificate_data 20M; lua_shared_dict certificate_servers 5M; lua_shared_dict configuration_data 20M; init_by_lua_block { collectgarbage("collect") -- init modules local ok, res ok, res = pcall(require, "lua_ingress") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else lua_ingress = res lua_ingress.set_config({ use_forwarded_headers = false, use_proxy_protocol = false, is_ssl_passthrough_enabled = false, http_redirect_code = 308, listen_ports = { ssl_proxy = "442", https = "443" }, hsts = true, hsts_max_age = 15724800, hsts_include_subdomains = true, hsts_preload = false, }) end ok, res = pcall(require, "configuration") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else configuration = res end ok, res = pcall(require, "balancer") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else balancer = res end ok, res = pcall(require, "monitor") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else monitor = res end ok, res = pcall(require, "certificate") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else certificate = res end ok, res = pcall(require, "plugins") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else plugins = res end -- load all plugins that'll be used here plugins.init({}) } init_worker_by_lua_block { lua_ingress.init_worker() balancer.init_worker() monitor.init_worker() plugins.run() } geoip_country /etc/nginx/geoip/GeoIP.dat; geoip_city /etc/nginx/geoip/GeoLiteCity.dat; geoip_org /etc/nginx/geoip/GeoIPASNum.dat; geoip_proxy_recursive on; aio threads; aio_write on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; log_subrequest on; reset_timedout_connection on; keepalive_timeout 75s; keepalive_requests 100; client_body_temp_path /tmp/client-body; fastcgi_temp_path /tmp/fastcgi-temp; proxy_temp_path /tmp/proxy-temp; ajp_temp_path /tmp/ajp-temp; client_header_buffer_size 1k; client_header_timeout 60s; large_client_header_buffers 4 8k; client_body_buffer_size 8k; client_body_timeout 60s; http2_max_field_size 4k; http2_max_header_size 16k; http2_max_requests 1000; http2_max_concurrent_streams 128; types_hash_max_size 2048; server_names_hash_max_size 1024; server_names_hash_bucket_size 32; map_hash_bucket_size 64; proxy_headers_hash_max_size 512; proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 64; variables_hash_bucket_size 256; variables_hash_max_size 2048; underscores_in_headers off; ignore_invalid_headers on; limit_req_status 503; limit_conn_status 503; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type text/html; gzip on; gzip_comp_level 5; gzip_http_version 1.1; gzip_min_length 256; gzip_types application/atom+xml application/javascript application/x-javascript application/json application/rss+xml application/vnd.ms-fontobject application/x-font-ttf application/x-web-app-manifest+json application/xhtml+xml application/xml font/opentype image/svg+xml image/x-icon text/css text/javascript text/plain text/x-component; gzip_proxied any; gzip_vary on; # Custom headers for response server_tokens on; # disable warnings uninitialized_variable_warn off; # Additional available variables: # $namespace # $ingress_name # $service_name # $service_port log_format upstreaminfo '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" $request_length $request_time [$proxy_upstream_name] [$proxy_alternative_upstream_name] $upstream_addr $upstream_response_length $upstream_response_time $upstream_status $req_id'; map $request_uri $loggable { default 1; } access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log upstreaminfo if=$loggable; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice; resolver 114.114.114.114 8.8.8.8 valid=30s ipv6=off; # See https://www.nginx.com/blog/websocket-nginx map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade { default upgrade; # See http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_upstream_module.html#keepalive '' ''; } # Reverse proxies can detect if a client provides a X-Request-ID header, and pass it on to the backend server. # If no such header is provided, it can provide a random value. map $http_x_request_id $req_id { default $http_x_request_id; "" $request_id; } # Create a variable that contains the literal $ character. # This works because the geo module will not resolve variables. geo $literal_dollar { default "$"; } server_name_in_redirect off; port_in_redirect off; ssl_protocols TLSv1.2; ssl_early_data off; # turn on session caching to drastically improve performance ssl_session_cache builtin:1000 shared:SSL:10m; ssl_session_timeout 10m; # allow configuring ssl session tickets ssl_session_tickets on; # slightly reduce the time-to-first-byte ssl_buffer_size 4k; # allow configuring custom ssl ciphers ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384'; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; ssl_ecdh_curve auto; # PEM sha: 9f4bba529d99741566ce35e96beba9d3da375481 ssl_certificate /etc/ingress-controller/ssl/default-fake-certificate.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/ingress-controller/ssl/default-fake-certificate.pem; proxy_ssl_session_reuse on; upstream upstream_balancer { ### Attention!!! # # We no longer create "upstream" section for every backend. # Backends are handled dynamically using Lua. If you would like to debug # and see what backends ingress-nginx has in its memory you can # install our kubectl plugin https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/kubectl-plugin. # Once you have the plugin you can use "kubectl ingress-nginx backends" command to # inspect current backends. # ### server 0.0.0.1; # placeholder balancer_by_lua_block { balancer.balance() } keepalive 32; keepalive_timeout 60s; keepalive_requests 100; } # Cache for internal auth checks proxy_cache_path /tmp/nginx-cache-auth levels=1:2 keys_zone=auth_cache:10m max_size=128m inactive=30m use_temp_path=off; # Global filters ## start server _ server { server_name _ ; listen 80 default_server reuseport backlog=511 ; listen 443 default_server reuseport backlog=511 ssl http2 ; set $proxy_upstream_name "-"; ssl_certificate_by_lua_block { certificate.call() } location / { set $namespace ""; set $ingress_name ""; set $service_name ""; set $service_port ""; set $location_path "/"; rewrite_by_lua_block { lua_ingress.rewrite({ force_ssl_redirect = false, ssl_redirect = false, force_no_ssl_redirect = false, use_port_in_redirects = false, }) balancer.rewrite() plugins.run() } # be careful with `access_by_lua_block` and `satisfy any` directives as satisfy any # will always succeed when there's `access_by_lua_block` that does not have any lua code doing `ngx.exit(ngx.DECLINED)` # other authentication method such as basic auth or external auth useless - all requests will be allowed. #access_by_lua_block { #} header_filter_by_lua_block { lua_ingress.header() plugins.run() } body_filter_by_lua_block { } log_by_lua_block { balancer.log() monitor.call() plugins.run() } access_log off; port_in_redirect off; set $balancer_ewma_score -1; set $proxy_upstream_name "upstream-default-backend"; set $proxy_host $proxy_upstream_name; set $pass_access_scheme $scheme; set $pass_server_port $server_port; set $best_http_host $http_host; set $pass_port $pass_server_port; set $proxy_alternative_upstream_name ""; client_max_body_size 1m; proxy_set_header Host $best_http_host; # Pass the extracted client certificate to the backend # Allow websocket connections proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade; proxy_set_header X-Request-ID $req_id; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $best_http_host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $pass_port; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $pass_access_scheme; proxy_set_header X-Scheme $pass_access_scheme; # Pass the original X-Forwarded-For proxy_set_header X-Original-Forwarded-For $http_x_forwarded_for; # mitigate HTTPoxy Vulnerability # https://www.nginx.com/blog/mitigating-the-httpoxy-vulnerability-with-nginx/ proxy_set_header Proxy ""; # Custom headers to proxied server proxy_connect_timeout 5s; proxy_send_timeout 60s; proxy_read_timeout 60s; proxy_buffering off; proxy_buffer_size 4k; proxy_buffers 4 4k; proxy_max_temp_file_size 1024m; proxy_request_buffering on; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_cookie_domain off; proxy_cookie_path off; # In case of errors try the next upstream server before returning an error proxy_next_upstream error timeout; proxy_next_upstream_timeout 0; proxy_next_upstream_tries 3; proxy_pass http://upstream_balancer; proxy_redirect off; } # health checks in cloud providers require the use of port 80 location /healthz { access_log off; return 200; } # this is required to avoid error if nginx is being monitored # with an external software (like sysdig) location /nginx_status { allow 127.0.0.1; deny all; access_log off; stub_status on; } } ## end server _ ## start server foo.bar.com server { server_name foo.bar.com ; listen 80 ; listen 443 ssl http2 ; set $proxy_upstream_name "-"; ssl_certificate_by_lua_block { certificate.call() } location / { set $namespace "default"; set $ingress_name "simple-fanout-example"; set $service_name "my-service"; set $service_port "80"; set $location_path "/"; rewrite_by_lua_block { lua_ingress.rewrite({ force_ssl_redirect = false, ssl_redirect = true, force_no_ssl_redirect = false, use_port_in_redirects = false, }) balancer.rewrite() plugins.run() } # be careful with `access_by_lua_block` and `satisfy any` directives as satisfy any # will always succeed when there's `access_by_lua_block` that does not have any lua code doing `ngx.exit(ngx.DECLINED)` # other authentication method such as basic auth or external auth useless - all requests will be allowed. #access_by_lua_block { #} header_filter_by_lua_block { lua_ingress.header() plugins.run() } body_filter_by_lua_block { } log_by_lua_block { balancer.log() monitor.call() plugins.run() } port_in_redirect off; set $balancer_ewma_score -1; set $proxy_upstream_name "default-my-service-80"; set $proxy_host $proxy_upstream_name; set $pass_access_scheme $scheme; set $pass_server_port $server_port; set $best_http_host $http_host; set $pass_port $pass_server_port; set $proxy_alternative_upstream_name ""; client_max_body_size 1m; proxy_set_header Host $best_http_host; # Pass the extracted client certificate to the backend # Allow websocket connections proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade; proxy_set_header X-Request-ID $req_id; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $best_http_host; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $pass_port; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $pass_access_scheme; proxy_set_header X-Scheme $pass_access_scheme; # Pass the original X-Forwarded-For proxy_set_header X-Original-Forwarded-For $http_x_forwarded_for; # mitigate HTTPoxy Vulnerability # https://www.nginx.com/blog/mitigating-the-httpoxy-vulnerability-with-nginx/ proxy_set_header Proxy ""; # Custom headers to proxied server proxy_connect_timeout 5s; proxy_send_timeout 60s; proxy_read_timeout 60s; proxy_buffering off; proxy_buffer_size 4k; proxy_buffers 4 4k; proxy_max_temp_file_size 1024m; proxy_request_buffering on; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_cookie_domain off; proxy_cookie_path off; # In case of errors try the next upstream server before returning an error proxy_next_upstream error timeout; proxy_next_upstream_timeout 0; proxy_next_upstream_tries 3; proxy_pass http://upstream_balancer; proxy_redirect off; } } ## end server foo.bar.com # backend for when default-backend-service is not configured or it does not have endpoints server { listen 8181 default_server reuseport backlog=511; set $proxy_upstream_name "internal"; access_log off; location / { return 404; } } # default server, used for NGINX healthcheck and access to nginx stats server { listen 127.0.0.1:10246; set $proxy_upstream_name "internal"; keepalive_timeout 0; gzip off; access_log off; location /healthz { return 200; } location /is-dynamic-lb-initialized { content_by_lua_block { local configuration = require("configuration") local backend_data = configuration.get_backends_data() if not backend_data then ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) return end ngx.say("OK") ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK) } } location /nginx_status { stub_status on; } location /configuration { client_max_body_size 21m; client_body_buffer_size 21m; proxy_buffering off; content_by_lua_block { configuration.call() } } location / { content_by_lua_block { ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_NOT_FOUND) } } }}stream { lua_package_path "/etc/nginx/lua/?.lua;/etc/nginx/lua/vendor/?.lua;;"; lua_shared_dict tcp_udp_configuration_data 5M; init_by_lua_block { collectgarbage("collect") -- init modules local ok, res ok, res = pcall(require, "configuration") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else configuration = res end ok, res = pcall(require, "tcp_udp_configuration") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else tcp_udp_configuration = res end ok, res = pcall(require, "tcp_udp_balancer") if not ok then error("require failed: " .. tostring(res)) else tcp_udp_balancer = res end } init_worker_by_lua_block { tcp_udp_balancer.init_worker() } lua_add_variable $proxy_upstream_name; log_format log_stream '[$remote_addr] [$time_local] $protocol $status $bytes_sent $bytes_received $session_time'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log log_stream ; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; upstream upstream_balancer { server 0.0.0.1:1234; # placeholder balancer_by_lua_block { tcp_udp_balancer.balance() } } server { listen 127.0.0.1:10247; access_log off; content_by_lua_block { tcp_udp_configuration.call() } } # TCP services # UDP services } |
3.Ingress(HTTP与HTTPS)
实现基于https需要定义ssl
生成自签名证书
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 | # cat certs.sh cat > ca-config.json <<EOF{ "signing": { "default": { "expiry": "87600h" }, "profiles": { "kubernetes": { "expiry": "87600h", "usages": [ "signing", "key encipherment", "server auth", "client auth" ] } } }}EOFcat > ca-csr.json <<EOF{ "CN": "kubernetes", "key": { "algo": "rsa", "size": 2048 }, "names": [ { "C": "CN", "L": "Beijing", "ST": "Beijing", "O": "k8s", "OU": "System" } ]}EOFcfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca -#-----------------------cat > sslexample.foo.com-csr.json <<EOF{ "CN": "sslexample.foo.com", "hosts": [], "key": { "algo": "rsa", "size": 2048 }, "names": [ { "C": "CN", "L": "BeiJing", "ST": "BeiJing", "O": "k8s", "OU": "System" } ]}EOFcfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=kubernetes sslexample.foo.com-csr.json | cfssljson -bare sslexample.foo.com |
运行脚本生成
1 | sh cert.sh |
创建的以下证书
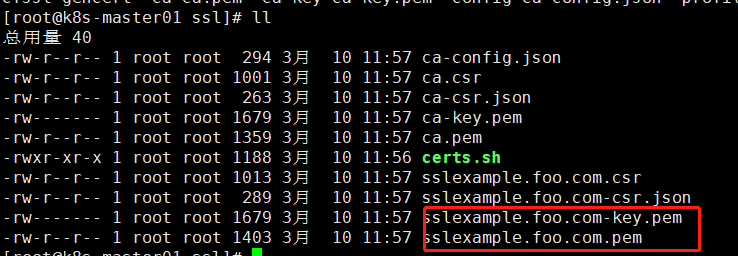
创建证书至k8s
1 | kubectl create secret tls sslexample-foo-com --cert=sslexample.foo.com.pem --key=sslexample.foo.com-key.pem |
查看,是在默认命名空间default
1 2 3 4 | # kubectl get secretNAME TYPE DATA AGEdefault-token-ctcb9 kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 20hsslexample-foo-com kubernetes.io/tls 2 3m20s |
创建ingrss配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | # cat ingress-https.yaml apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1kind: Ingressmetadata: name: tls-example-ingressspec: tls: - hosts: - sslexample.foo.com #证书名,需要和刚刚导入的证书名对应 secretName: sslexample-foo-com rules: - host: sslexample.foo.com http: paths: - path: / backend: serviceName: my-service servicePort: 80 |
应用
1 | kubectl apply -f ingress-https.yaml |
查看
1 2 3 4 | # kubectl get ingressNAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGEsimple-fanout-example foo.bar.com 80 171mtls-example-ingress sslexample.foo.com 80, 443 4m7s |
设置hosts以后使用https://域名 访问,因为是自签名证书不受浏览器信任,需要添加信任
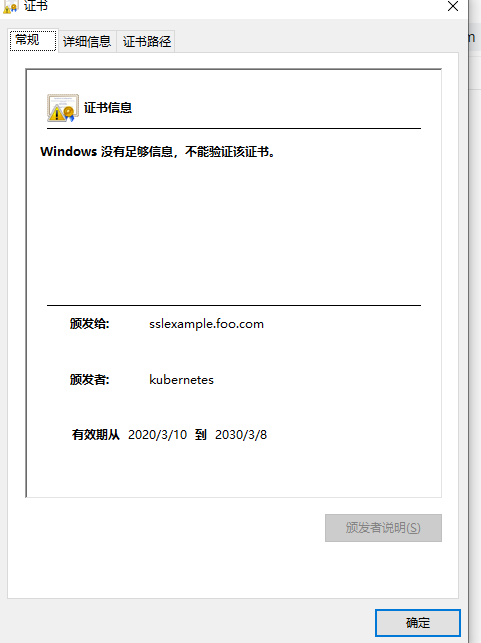
如果指定的证书没有,则k8s会自动颁发一个证书
Ingress高可用
上面配置的副本数为1个那么启动该pod的node只会是集群中的一台node主机,也只会在该主机启动80 443端口,无法实现高可用
我们只是解决了集群对外提供服务的功能,并没有对ingress进行高可用的部署,Ingress高可用,我们可以通过修改deploment的副本数来实现高可用,但是对于ingress承载着整个集群流量的接入,所以在生产环境中,建议把ingres通过DaemonSet的方式部署集群,而且该节点打上污点不允许业务pod进行调度,以避免业务应用于Ingress服务发生资源争抢。然后通过SLB把ingress节点主机添加为后端服务器,进行流量转发。
高可用配置参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/minseo/p/12171687.html
小结
Ingress
1,四层,七层负载均衡
2,支持自定义Serverice访问策略
3,只支持域名的网站访问
4,支持TLS
2024-02-04补充
设置了一个ingress对应的是禅道应用在访问的时候页面出现503,后台看禅道访问日志是没有收到请求的
1 | 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable |
原因:之前在不同的命名空间设置了相同的ingress,删除之前设置的ingress即可,在设置相同的ingress使用apply应用配置文件时没有报错,导致排查困难
2024-02-29补充
如果ingress从一个命名空间迁移至另外一个命名空间则原ingress需要删除即使不在同一个命名空间也需要删除否则外网无法访问





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
2018-03-10 Cobbler自动化安装