时效性
本篇撰写时间为2021.12.14,由于计算机技术日新月异,博客中所有内容都有时效和版本限制,具体做法不一定总行得通,链接可能改动失效,各种软件的用法可能有修改。但是其中透露的思想往往是值得学习的。
本篇前置:
- ExpRe[23] Oz[0] emacs初步,Hello world
https://www.cnblogs.com/minor-second/p/15689596.html
变量
Oz variables are single-assignment variables or more appropriately logic variables. In imperative languages like C and Java, a variable can be assigned multiple times. In contrast, single assignment variables can be assigned only once.
- variable只能赋值一次,bound之后就不能改变
- 更准确地,Oz的变量是logic variable,可以有相等关系
- 想“变化”?需要把变量绑定到
cell类型的值 - Oz是动态类型的。只有绑定了值才知道变量类型
示例
文档中用了Browse,但我们没有GUI,所以用Show
在上方窗口输入
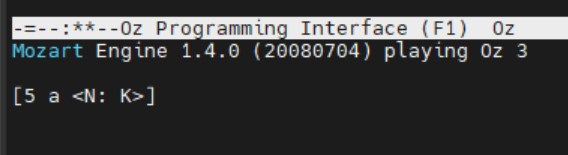
local I J K in
I = 5
J = 'a'
{NewName K}
{Show [I J K]}
end
按M-C-x,再按F10 O h e看到输出
record和tuple
Records are structured compound entities. A record has a label and a fixed number of components or arguments. There are also records with a variable number of arguments that are called open records. For now, we restrict ourselves to 'closed' records.
record类似于一个结构体。但具有一个标签
tuple相当于某种意义的“数组”(即结构体的"feature"是从1开始的数)
输入
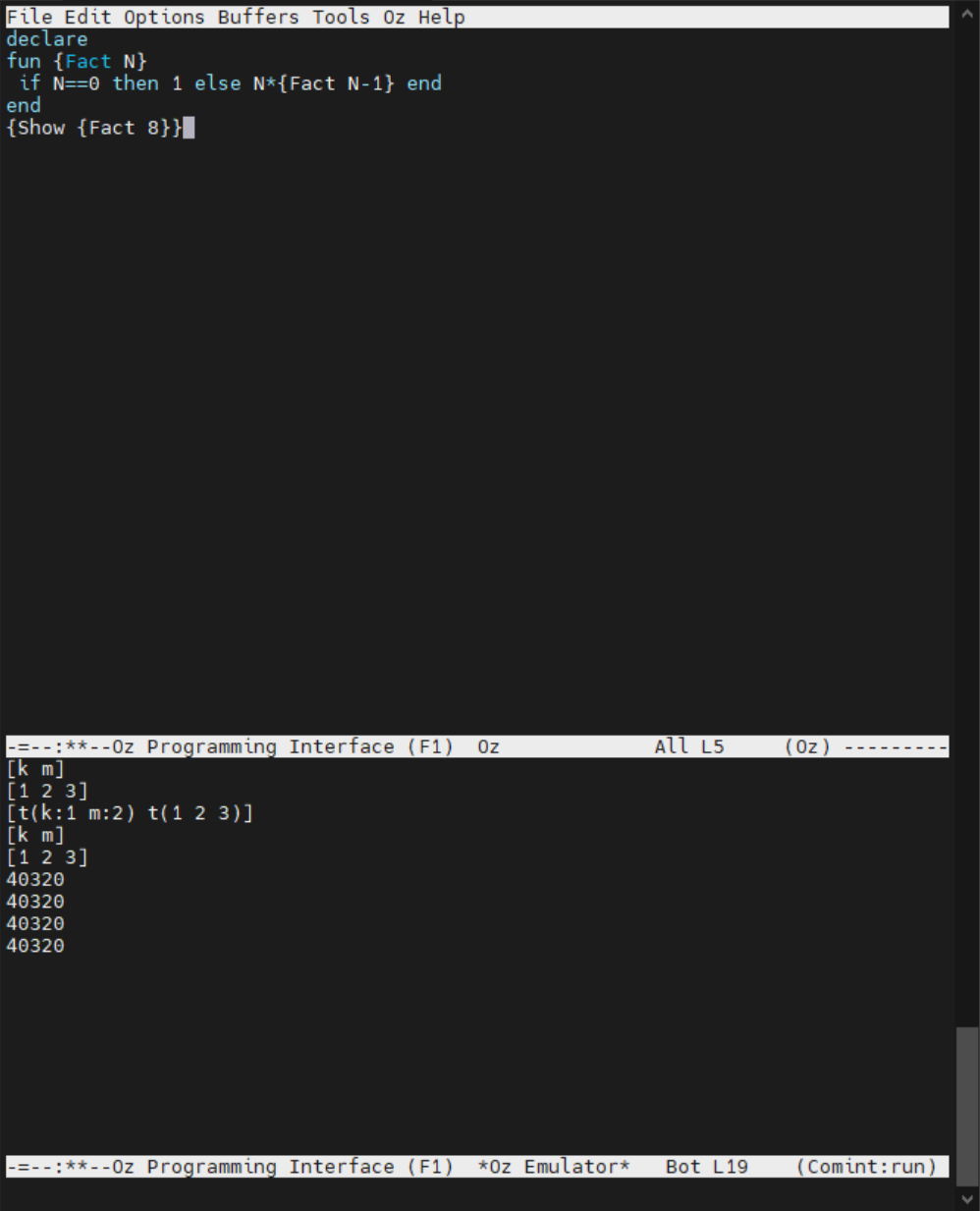
declare A B C X Y in
X = t(k:A m:B)
Y = t(A B C)
A = 1
B = 2
C = 3
{Show [X Y]}
declare Z W in
{Arity X Z}
{Show Z}
{Arity Y W}
{Show W}
输出
[1 2 3]
[t(k:1 m:2) t(1 2 3)]
[k m]
[1 2 3]
具体参见文档
- 注意
{Arity X Z}要求X已绑定,而Z未绑定,将把[k m]这种东西赋值给Z. 对于习惯“返回值”的人,可以理解成Z是“函数返回值” CondSelect同理
函数
一个简单的函数示例
declare
fun {Fact N}
if N==0 then 1 else N*{Fact N-1} end
end
定义了函数之后可以用{Show {Fact 8}}这种简单调用
注:Shift + Insert可以在MobaXterm中粘贴,即使在emacs中也可以,这很方便。
总结和问答练习
- Q: 定义一个函数并用它计算
88和77的最大公约数
A:
declare
fun {GCD A B}
if B==0 then A else {GCD B {Int.'mod' A B}} end
end
{Show {GCD 88 77}}
- 这里假设输入的前一个数比较大
Int.'mod'这种用法去官方文档http://mozart2.org/mozart-v1/doc-1.4.0/base/int.html#section.numbers.integers
可以查到


