JAVA8新特性---函数式接口
一、什么是函数式接口?
-
只包含一个抽象方法的接口,称为函数式接口
-
可以使用@Functionallinterface注解,这样可以检验它是否是一个函数式接口。同时javadoc 也会包含一条声明
-
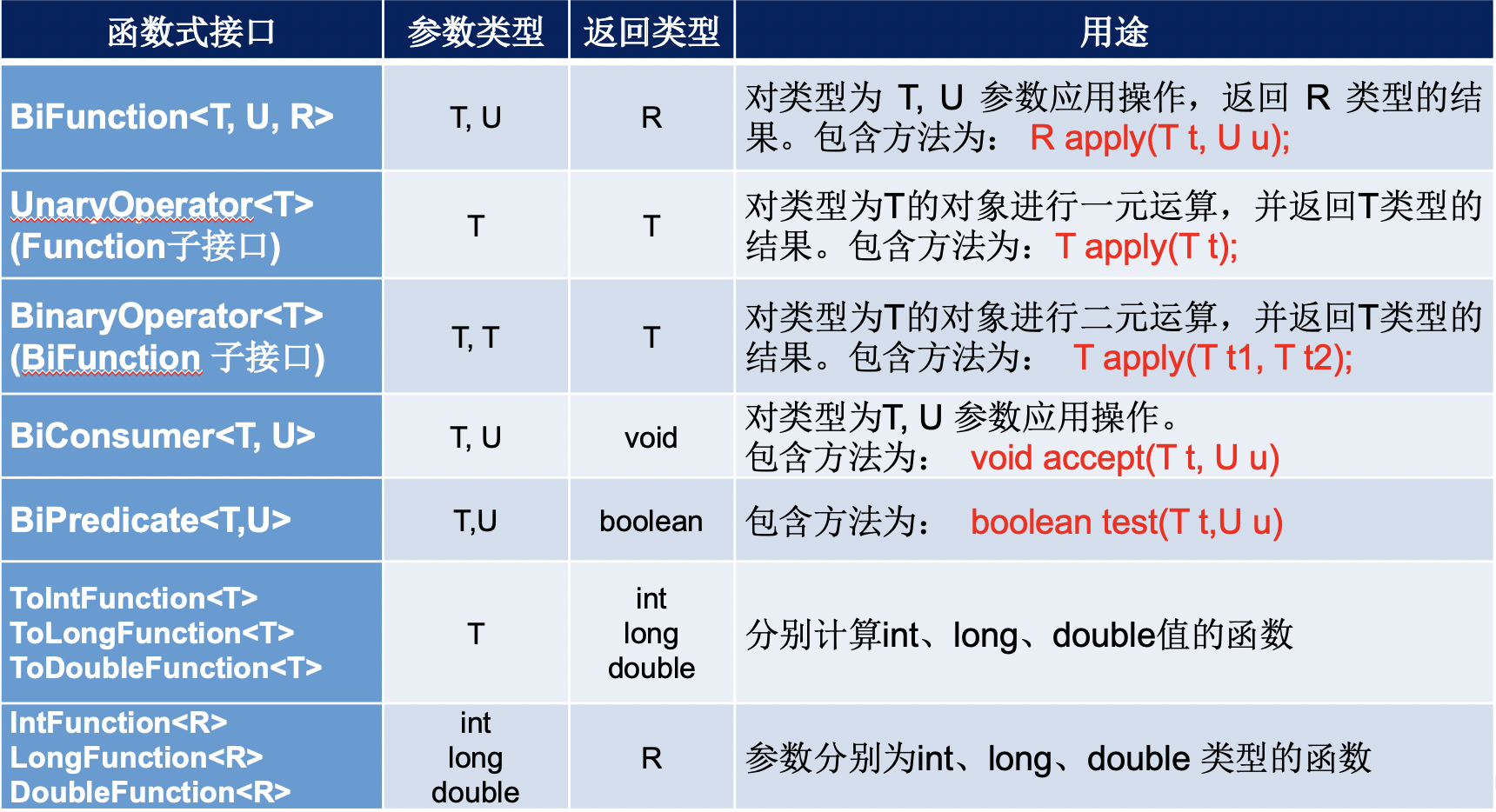
在java.util.function包下定义了java8的丰富的函数式接口
二、函数式接口举例
1、函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface public interface Runnable { /** * When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used * to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's * <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing * thread. * <p> * The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may * take any action whatsoever. * * @see java.lang.Thread#run() */ public abstract void run(); }
@FunctionalInterface public interface Comparator<T> { /** * * @param o1 the first object to be compared. * @param o2 the second object to be compared. * @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the * first argument is less than, equal to, or greater than the * second. * @throws NullPointerException if an argument is null and this * comparator does not permit null arguments * @throws ClassCastException if the arguments' types prevent them from * being compared by this comparator. */ int compare(T o1, T o2);
2、自定义函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyNumber<T> {
public boolean compare(Integer a,Integer b); }
@Test public void test2(){ MyNumber<Integer> myNumber = (Integer a,Integer b) -> a>b; System.out.println(myNumber.compare(1,2)); }
三、JAVA内置的四大核心函数式接口
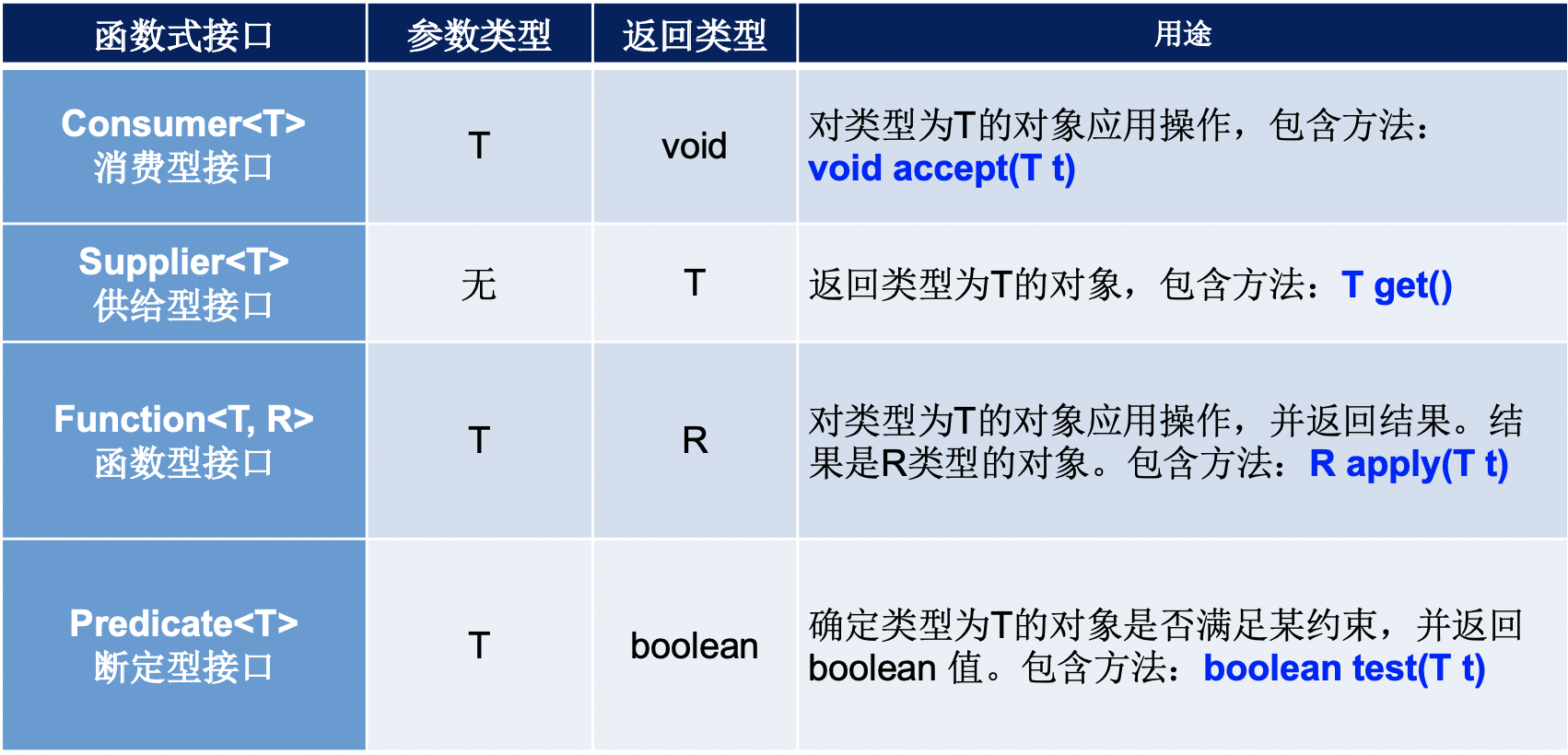
1、例子1
@Test public void test() { System.out.println(studytime(()->"studyTime")); } //供给型函数,无参有返回值 public String studytime(Supplier<String> supplier){ return supplier.get(); }
2、例子2
@Test public void test2(){ String goodOneDay = goodDay("goodOneDay", (s -> s)); System.out.println(goodOneDay); } public String goodDay(String s, Function<String,String> function){ return function.apply(s); }
3、例子3
@Test public void test3(){ List<String> list = Arrays.asList("杏鲍菇","金针菇","大枣","平菇"); List<String> filterList = new ArrayList<>(); list.forEach((s)-> { if(s.contains("菇")) { filterList.add(s); } }); System.out.println("filterList:"+filterList); }
四、其他接口