Java实战之03Spring-05Spring中的事务控制(基于AOP)
五、Spring中的事务控制(基于AOP)
1、Spring中事务有关的接口
1.1、明确:
JavaEE体系进行分层开发,事务处理位于业务层,Spring提供了分层设计业务层的事务处理解决方案
1.2、Spring事务管理主要包括3个接口
1.2.1、PlatformTransactionManager事务管理器

具体实现类:

1.2.2、TransactionDefinition事务定义信息

事务的隔离级别:

事务的传播行为:有时面试会问到
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)
MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常
REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。
NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常
NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行REQUIRED类似的操作。
超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置。
是否是只读事务:建议查询时设置为只读。
1.2.3、TransactionStatus事务具体运行状态

2、Spring中的事务控制
准备环境:
1.使用我们之前转账的案例。
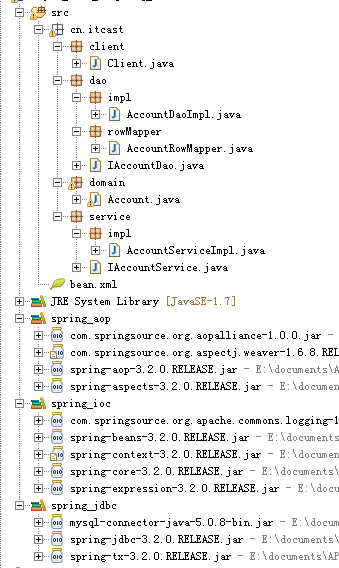
2.使用Spring容器来管理业务层和持久层对象的注入
1 public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { 2 3 4 private IAccountDao accountDao ; 5 6 7 8 public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) { 9 this.accountDao = accountDao; 10 } 11 12 13 public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) { 14 //1.根据名称获取账户信息 15 Account sourceAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);//转出账户 16 Account targetAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);//转入账户 17 //2.设置账户的金额 18 sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney()-money);//转出账户减钱 19 targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney()+money);//转入账户加钱 20 //3.更新账户信息 21 accountDao.updateAccount(sourceAccount); 22 //手动模拟一个异常 23 int i=1/0; 24 accountDao.updateAccount(targetAccount); 25 } 26 27 28 public Account findAccountById(Integer id) { 29 return accountDao.findAccountById(id); 30 } 31 32 }
1 public interface IAccountService { 2 3 /** 4 * 转账方法 5 * @param sourceAccountName 转出账户名称 6 * @param targetAccountName 转入账户名称 7 * @param money 转账金额 8 */ 9 void transfer(String sourceAccountName,String targetAccountName,Float money); 10 11 /** 12 * 根据id获取账户信息 13 * @param id 14 * @return 15 */ 16 Account findAccountById(Integer id); 17 }
3.使用Spring的jdbc模板(JdbcDaoSupport)来编写持久层。
1 public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements IAccountDao { 2 3 public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) { 4 List<Account> list = getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where name = ?", new AccountRowMapper(),accountName); 5 if(list.size() == 1){ 6 return list.get(0); 7 } 8 return null; 9 } 10 11 public void updateAccount(Account account) { 12 getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId()); 13 } 14 15 public Account findAccountById(Integer id) { 16 List<Account> list = getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where id = ?", new AccountRowMapper(),id); 17 if(list.size() == 1){ 18 return list.get(0); 19 } 20 return null; 21 } 22 }
1 public class AccountRowMapper implements RowMapper<Account> { 2 3 public Account mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException { 4 Account account = new Account(); 5 account.setId(rs.getInt("id")); 6 account.setName(rs.getString("name")); 7 account.setMoney(rs.getFloat("money")); 8 return account; 9 } 10 }
1 import cn.itcast.domain.Account; 2 3 /** 4 * 账户的持久层接口 5 * @author zhy 6 * 7 */ 8 public interface IAccountDao { 9 10 /** 11 * 根据账户名称,查询账户信息 12 * @param accountName 13 * @return 14 */ 15 Account findAccountByName(String accountName); 16 17 /** 18 * 更新账户信息 19 * @param account 20 */ 21 void updateAccount(Account account); 22 23 /** 24 * 根据id查询账户信息 25 * @param id 26 * @return 27 */ 28 Account findAccountById(Integer id); 29 }
4.使用Spring的内置数据源。
1 <!-- 配置数据源 --> 2 <bean id="driverManagerDataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> 3 <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> 4 <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ee0413_spring_day37"></property> 5 <property name="username" value="root"></property> 6 <property name="password" value="1234"></property> 7 </bean>
2.1、编程式事务控制(了解)
1 public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { 2 3 private IAccountDao accountDao ; 4 //定义一个事务模板 5 private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate; 6 7 public void setTransactionTemplate(TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate) { 8 this.transactionTemplate = transactionTemplate; 9 } 10 11 public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) { 12 this.accountDao = accountDao; 13 } 14 15 public void transfer(final String sourceName,final String targetName,final Float money) { 16 //定义一个TransactionCallback 17 TransactionCallback action = new TransactionCallback<Account>() { 18 //此方法内部,写需要事务控制的代码 19 public Account doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) { 20 //1.根据名称获取账户信息 21 Account sourceAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);//转出账户 22 Account targetAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);//转入账户 23 //2.设置账户的金额 24 sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney()-money);//转出账户减钱 25 targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney()+money);//转入账户加钱 26 //3.更新账户信息 27 accountDao.updateAccount(sourceAccount); 28 //手动模拟一个异常 29 int i=1/0; 30 accountDao.updateAccount(targetAccount); 31 return null; 32 } 33 }; 34 //事务控制的方法 35 transactionTemplate.execute(action); 36 } 37 38 public Account findAccountById(final Integer id) { 39 TransactionCallback action = new TransactionCallback<Account>() { 40 //此方法内部,写需要事务控制的代码 41 public Account doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) { 42 return accountDao.findAccountById(id); 43 } 44 }; 45 //事务控制的方法 46 return transactionTemplate.execute(action); 47 } 48 }
弊端:我们发现,其实就是编写了一个环绕通知,但是当我们业务代码很多时,每个都得向这样编写,很繁琐。
<!-- 把业务层的创建交给spring容器 --> <bean id="accountService" class="cn.itcast.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property> <!-- 注入事务管理模板 --> <property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置一个事务模板 --> <bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <!-- 注入事务管理器 --> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- 注入数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="driverManagerDataSource"></property> </bean>
2.2、声明式事务控制(重点)
编程式事务管理将数据层提交事务的代码加入到逻辑层,与Spring无侵入式编程的主思想有冲突,实际开发过程中,往往采用声明式事务管理形式
通过编程式事务管理的代码不难看出,在业务逻辑层对应的业务上添加某些代码即可完成整体事务管理的操作,使用SpringAOP的思想,将公共的代码加入后,即可完成对应的工作,这就是声明式事务管理的核心机制。
2.2.1、基于XML的声明式事务配置
a、导入spring事务支持的jar包

b、引入spring事务的名称空间
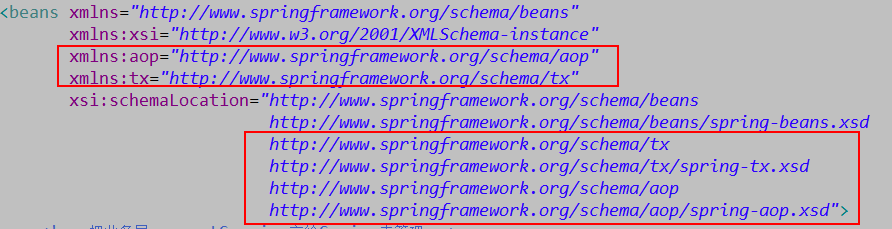
c、配置spring的事务支持
1 <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> 2 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> 3 <!-- 注入数据源 --> 4 <property name="dataSource" ref="driverManagerDataSource"></property> 5 </bean>
1 <!-- 配置通知,通知中要引用事务管理器。因为事务管理器中有公共的代码:提交事务和回滚事务 --> 2 <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> 3 <!-- 事务的属性设置 --> 4 <tx:attributes> 5 <!-- 指定需要事务的方法 6 常用属性: 7 isolation:指定事务的隔离级别 8 propagation:指定事务的传播行为 9 read-only:是否是只读事务 10 timeout:事务的超时时间 11 no-rollback-for:当产生指定异常时,不回滚。其他异常回滚。没有默认值 12 rollback-for:当产生指定异常时回滚,产生其他异常时,不回滚。没有默认值 13 14 --> 15 <!-- 查询方法 --> 16 <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" propagation="SUPPORTS"/> 17 <tx:method name="*" read-only="false" propagation="REQUIRED"/> 18 </tx:attributes> 19 </tx:advice>
1 <!-- 指定通知和切入点表达式 --> 2 <aop:config> 3 <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* cn.itcast.service.impl.*.*(..))"/> 4 </aop:config>
2.2.2、基于注解的声明式事务配置
a、把spring容器管理改为注解配置的方式
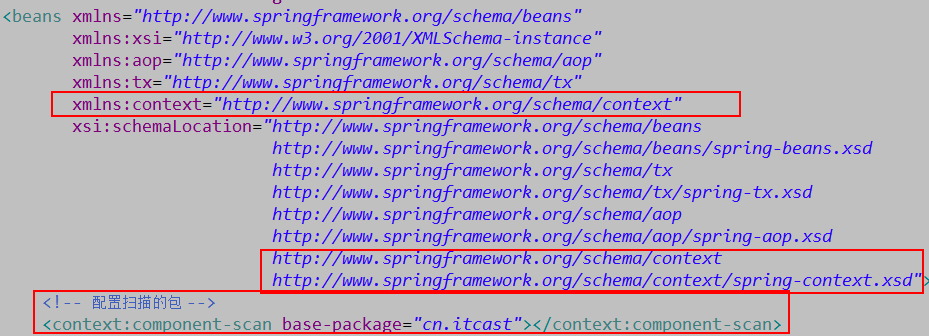
1 <!-- 配置一个JdbcTemplate的bean --> 2 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> 3 <property name="dataSource" ref="driverManagerDataSource"></property> 4 </bean>
1 public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { 2 3 @Autowired 4 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; 5 6 public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) { 7 List<Account> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where name = ?", new AccountRowMapper(),accountName); 8 if(list.size() == 1){ 9 return list.get(0); 10 } 11 return null; 12 } 13 14 public void updateAccount(Account account) { 15 jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId()); 16 } 17 18 public Account findAccountById(Integer id) { 19 List<Account> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?", new AccountRowMapper(),id); 20 if(list.size() == 1){ 21 return list.get(0); 22 } 23 return null; 24 } 25 }
1 @Component("accountService") 2 @Transactional 3 public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { 4 5 @Autowired 6 private IAccountDao accountDao ; 7 8 public void transfer(final String sourceName,final String targetName,final Float money) { 9 //1.根据名称获取账户信息 10 Account sourceAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);//转出账户 11 Account targetAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);//转入账户 12 //2.设置账户的金额 13 sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney()-money);//转出账户减钱 14 targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney()+money);//转入账户加钱 15 //3.更新账户信息 16 accountDao.updateAccount(sourceAccount); 17 //手动模拟一个异常 18 int i=1/0; 19 accountDao.updateAccount(targetAccount); 20 } 21 22 @Transactional(readOnly=true,propagation=Propagation.SUPPORTS) 23 public Account findAccountById(final Integer id) { 24 return accountDao.findAccountById(id); 25 } 26 27 }
b、开启注解事务的支持
1 <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> 2 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> 3 <!-- 注入数据源 --> 4 <property name="dataSource" ref="driverManagerDataSource"></property> 5 </bean>
c、在需要事务支持的地方加入@Transactional注解
1 @Component("accountService") 2 public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { 3 4 @Autowired 5 private IAccountDao accountDao ; 6 7 @Transactional 8 public void transfer(final String sourceName,final String targetName,final Float money) { 9 //1.根据名称获取账户信息 10 Account sourceAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);//转出账户 11 Account targetAccount = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);//转入账户 12 //2.设置账户的金额 13 sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney()-money);//转出账户减钱 14 targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney()+money);//转入账户加钱 15 //3.更新账户信息 16 accountDao.updateAccount(sourceAccount); 17 //手动模拟一个异常 18 int i=1/0; 19 accountDao.updateAccount(targetAccount); 20 } 21 22 @Transactional(readOnly=true,propagation=Propagation.SUPPORTS) 23 public Account findAccountById(final Integer id) { 24 return accountDao.findAccountById(id); 25 } 26 27 }
d、@Transactional注解配置的位置
l 用在业务实现类上:该类所有的方法都在事务的控制范围

l 用在业务接口上:该接口的所有实现类都起作用
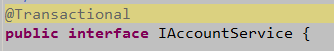
l 通过注解指定事务的定义信息



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号