Java 多线程的基本概念
一、线程介绍
多线程同时运行时,单CPU系统实际上是分给每个线程固定的时间片,用这种方式使得线程“看起来像是并行的”。在多CPU系统中,每个CPU可以单独运行一个线程,实现真正意义上的并行,但是如果线程数多于CPU数目,每个CPU仍然采用分时间片的方式。
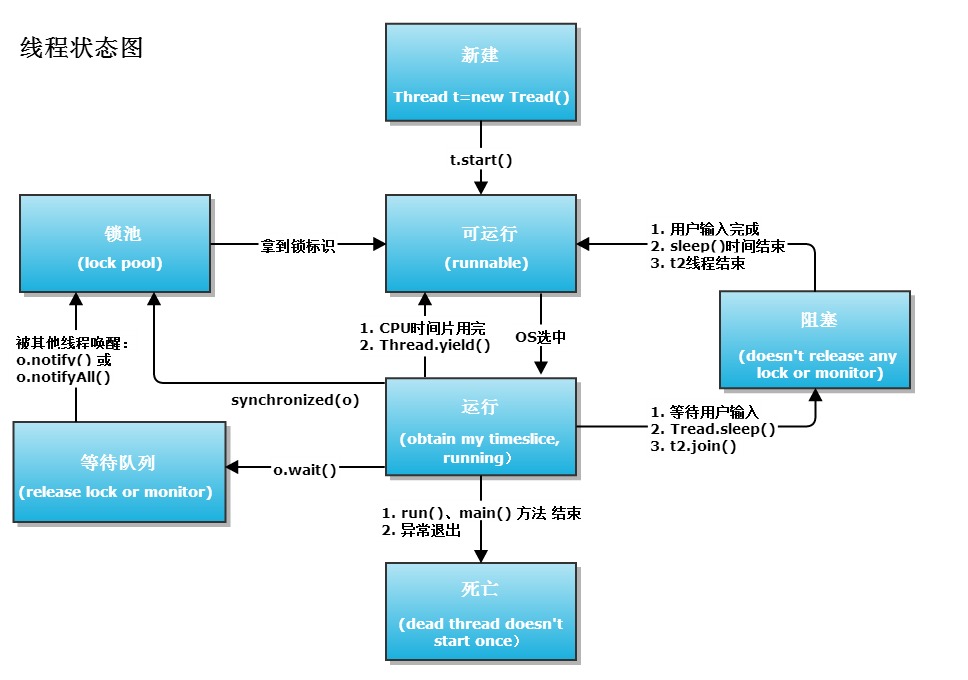
上图是线程状态转移图,稍微解释一下其中的几个点
1、阻塞状态,类似于自旋锁,当条件满足的时候,会立即试图抢占CPU
2、处于等待状态后,需要收到通知之后,从等待集合中出队,才具备了抢占CPU的条件
二、两种实现线程的方式
1、继承自Thread
class IphoneThread extends Thread { public int iphone = 5; public String user; public IphoneThread(String str) { user = str; } @Override public void run() { while (iphone != 0) { iphone--; System.out.println(user + " get one and left iphone num=" + iphone); } } } public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] arg) { IphoneThread t1 = new IphoneThread("Toms"); t1.start(); IphoneThread t2 = new IphoneThread("Jack"); t2.start(); IphoneThread t3 = new IphoneThread("Boom"); t3.start(); } }
2、实现Runnable接口
class IphoneRunable implements Runnable { public int iphone = 5; @Override public void run() { while (iphone != 0) { iphone--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " get one and left iphone num=" + iphone); } } } public class RunableTest { public static void main(String[] arg) { IphoneRunable runable = new IphoneRunable(); Thread t1 = new Thread(runable, "Toms"); t1.start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(runable, "Jack"); t2.start(); Thread t3 = new Thread(runable, "Boom"); t3.start(); } }
参考资料:
《Java核心技术I 基础知识》



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号