Programming Assignment 4: 8 Puzzle
编程作业四
我的代码:Board.java & Solver.java
问题简介
借助优先队列,实现解决八数码(8puzzle)问题的 A* 算法。
八数码问题就是下面这样,移动方块重排数字,最后使其有序,希望找到最少的移动次数。
1 3 1 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
4 2 5 => 4 2 5 => 4 5 => 4 5 => 4 5 6
7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8 6 7 8
initial 1 left 2 up 5 left goal
A* 算法是一种最优搜索(Best-first search),评价(或启发或优先级,反正就那意思)函数依实际问题而设计,搜索拓展节点时选最优,这里介绍了两个:
-
Hamming priority function. 定义为:不在正确位置上的方块数目加上目前移动的次数。直观上来说,在错误位置上的方块数目少,也就越接近目标,而且我们也希望移动次数少。
-
Manhattan priority function. 定义为:错误方块到正确位置需要的曼哈顿距离(水平加垂直格子数)之和加上目前移动的次数。
举例来说:
8 1 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
4 2 4 5 6 ---------------------- ----------------------
7 6 5 7 8 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 2 0 0 2 2 0 3
initial goal Hamming = 5 + 0 Manhattan = 10 + 0
一个重要的优化的是避免往优先队列里放入太多重复的情况,具体来说就是拓展节点时丢弃先前转换来的情况:
8 1 3 8 1 3 8 1 8 1 3 8 1 3
4 2 4 2 4 2 3 4 2 4 2 5
7 6 5 7 6 5 7 6 5 7 6 5 7 6
predecessor search node neighbor neighbor neighbor
(disallow)
这样做不能保证完全不出现重复的情况,不过也已经好很多了,再用 SET 什么的保证完全不重复反而可能会带来更大的开销(Checklist 如是说)。
第二个优化是把汉明距离和曼哈顿距离存下来,不用需要的时候再重新算一遍。另外,存在没有解的情况,课程说这种情况随便交换两个数字后就是可解的(证明不清楚,感兴趣的或许可以参考:proof)。所以,为了处理无解的情况,我们还要同步进行另一个 A* 搜索,二者有一对数字相反,后者找到了解,那前者就是无解的。
任务摘要
Board and Solver data types. Organize your program by creating an immutable data type Board with the following API:
public class Board { public Board(int[][] blocks) // construct a board from an n-by-n array of blocks // (where blocks[i][j] = block in row i, column j) public int dimension() // board dimension n public int hamming() // number of blocks out of place public int manhattan() // sum of Manhattan distances between blocks and goal public boolean isGoal() // is this board the goal board? public Board twin() // a board that is obtained by exchanging any pair of blocks public boolean equals(Object y) // does this board equal y? public Iterable<Board> neighbors() // all neighboring boards public String toString() // string representation of this board (in the output format specified below) public static void main(String[] args) // unit tests (not graded) }Also, create an immutable data type Solver with the following API:
public class Solver { public Solver(Board initial) // find a solution to the initial board (using the A* algorithm) public boolean isSolvable() // is the initial board solvable? public int moves() // min number of moves to solve initial board; -1 if unsolvable public Iterable<Board> solution() // sequence of boards in a shortest solution; null if unsolvable public static void main(String[] args) // solve a slider puzzle (given below) }
详细参见:specification。
问题分析
时隔好久(上次提交是去年四月份。。。),再看原来通过的代码,好像没什么好讲的东西,不大记得当初碰到了什么问题。两个类绝大部分的计算,都在构造时进行,Board() 算了汉明距离和曼哈顿距离存好,Solver() 交替跑了两个 A*。
Board 里的 twin() 方法算一个自己发挥的部分:
public Board twin() {
int[][] copy = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
copy[i][j] = tiles[i][j];
}
}
if (copy[0][0] == 0) swap(copy, 0, 1, 1, 1);
else if (copy[0][1] == 0) swap(copy, 0, 0, 1, 0);
else swap(copy, 0, 0, 0, 1);
Board twinBoard = new Board(copy);
return twinBoard;
}
要求交换两个非零数字,如果前面两个不是零我就直接交换前两,要是确定有一个为零,那再随便交换两个(反正只有一个零)。
另外提下 equals() 方法,Checklist 里也有回答:
How do I implement equals()? Java has some arcane rules for implementing equals(), discussed on p. 103 of Algorithms, 4th edition. Note that the argument to equals() is required to be Object. You can also inspect Date.java or Transaction.java for online examples.
于是乎,这是书上的相关内容:
- 如果该对象的引用和参数对象的引用相同,返回 true。这项测试在成立时能够免去其他所有工作。
- 如果参数为空(null),根据约定返回 false(还可以避免在下面的代码中使用空引用)。
- 如果两个对象的类不同,返回 false。要得到一个对象的类,可以使用 getClass() 方法。请注意我们会使用 == 来判断 Class 类型的对象是否相等,因为同一种类型的所有对象的 getClass() 方法一定能够返回相同的引用。
- 将参数对象的类型从 Object 转换到相应的类型(因为前一项测试已经通过,这种转换必然成功)。
- 如果任意示例变量的值不相同,返回 false。这个不同的类需要不同的考虑。
最后附上我的 equals():
// does this board equal other?
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (other == this) return true;
if (other == null) return false;
if (other.getClass() != this.getClass()) return false;
Board that = (Board) other;
if (that.n != this.n) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (that.tiles[i][j] != this.tiles[i][j]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
Solver 里面不用你写优先队列,写个比较器丢到课程提供的就好。另外,关于还原路径,搜索节点里加个 preNode 就可以从目标一路回到初始。具体可以看:Solver.java,不提。
测试结果
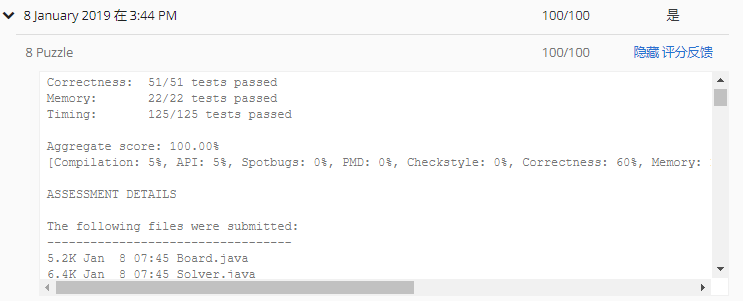
时间不重要,转换班次才让我再次提交,上次提交记录是去年四月份,原来博客欠这么久了。。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)