android window(二)从getSystemService到WindowManagerGlobal
在Activity调用getSystemService(WINDOW_SERVICE) 调用的是父类ContextThemeWrapper
package android.view; public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper { @Override public Object getSystemService(String name) { if (LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) { if (mInflater == null) { mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(getBaseContext()).cloneInContext(this); } return mInflater; } return getBaseContext().getSystemService(name); } }
这里getBaseContext返回是context的实现类ContextImpl
//ContextImpl @Override public Object getSystemService(String name) { return SystemServiceRegistry.getSystemService(this, name); } //SystemServiceRegistry public static Object getSystemService(ContextImpl ctx, String name) { ServiceFetcher<?> fetcher = SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.get(name); return fetcher != null ? fetcher.getService(ctx) : null; }
SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS是一个map,key为WINDOW_SERVICE时,对应的value是什么?
ContextImpl.java 的源码
208 class ContextImpl extends Context { //... 628 registerService(WINDOW_SERVICE, new ServiceFetcher() { 629 Display mDefaultDisplay; 630 public Object getService(ContextImpl ctx) { 631 Display display = ctx.mDisplay; 632 if (display == null) { 633 if (mDefaultDisplay == null) { 634 DisplayManager dm = (DisplayManager)ctx.getOuterContext(). 635 getSystemService(Context.DISPLAY_SERVICE); 636 mDefaultDisplay = dm.getDisplay(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY); 637 } 638 display = mDefaultDisplay; 639 } 640 return new WindowManagerImpl(display); 641 }}); 1829 @Override 1830 public Object getSystemService(String name) { 1831 ServiceFetcher fetcher = SYSTEM_SERVICE_MAP.get(name); 1832 return fetcher == null ? null : fetcher.getService(this); 1833 } //... }
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager { private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance(); private final Display mDisplay; private final Window mParentWindow; //... public WindowManagerImpl createLocalWindowManager(Window parentWindow) { return new WindowManagerImpl(mDisplay, parentWindow); } public WindowManagerImpl createPresentationWindowManager(Display display) { return new WindowManagerImpl(display, mParentWindow); } @Override public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) { mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow); } @Override public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) { mGlobal.updateViewLayout(view, params); } @Override public void removeView(View view) { mGlobal.removeView(view, false); } @Override public void removeViewImmediate(View view) { mGlobal.removeView(view, true); } @Override public Display getDefaultDisplay() { return mDisplay; } }
public interface WindowManager extends ViewManager { //... }
public interface ViewManager { public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params); public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params); public void removeView(View view); }
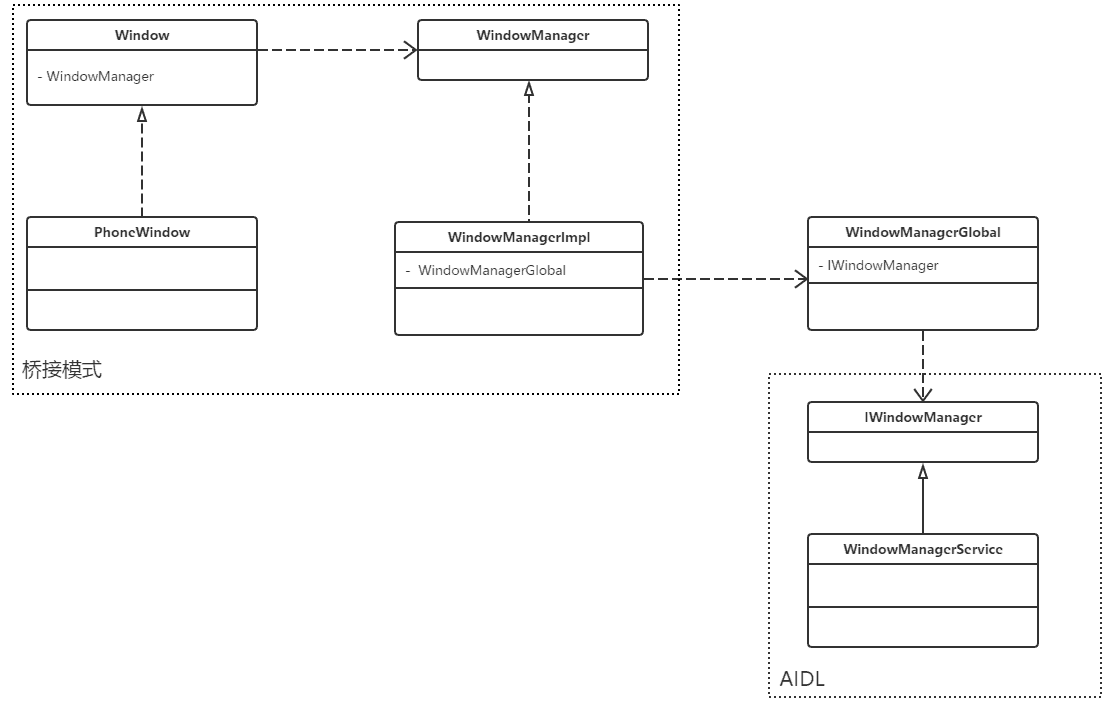
WindowManager的addView的过程,WindowManager是个接口,它的实现类是WindowManagerImpl类,而WindowManagerImpl又把相关逻辑交给了WindowManagerGlobal处理。WindowManagerGlobal是个单例类,它在进程中只存在一个实例,是它内部的addView方法最终创建了我们的核心类ViewRootImpl。
可以看到这里的WindowManagerImpl 的主要功能都是通过WindowManagerGlobal来实现的
public final class WindowManagerGlobal { private static final String TAG = "WindowManager"; //... private static WindowManagerGlobal sDefaultWindowManager; private static IWindowManager sWindowManagerService; private static IWindowSession sWindowSession; private final Object mLock = new Object(); private final ArrayList<View> mViews = new ArrayList<View>(); private final ArrayList<ViewRootImpl> mRoots = new ArrayList<ViewRootImpl>(); private final ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams> mParams = new ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams>(); private final ArraySet<View> mDyingViews = new ArraySet<View>(); private Runnable mSystemPropertyUpdater; private WindowManagerGlobal() { } public static WindowManagerGlobal getInstance() { synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) { if (sDefaultWindowManager == null) { sDefaultWindowManager = new WindowManagerGlobal(); } return sDefaultWindowManager; } } public static IWindowManager getWindowManagerService() { synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) { if (sWindowManagerService == null) { sWindowManagerService = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface( ServiceManager.getService("window")); } return sWindowManagerService; } } public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() { synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) { if (sWindowSession == null) { try { InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance(); IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService(); sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession( new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() { @Override public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) { ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale); } }, imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext()); ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(windowManager.getCurrentAnimatorScale()); } catch (RemoteException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to open window session", e); } } return sWindowSession; } } public static IWindowSession peekWindowSession() { synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) { return sWindowSession; } } public String[] getViewRootNames() { synchronized (mLock) { final int numRoots = mRoots.size(); String[] mViewRoots = new String[numRoots]; for (int i = 0; i < numRoots; ++i) { mViewRoots[i] = getWindowName(mRoots.get(i)); } return mViewRoots; } } public View getRootView(String name) { synchronized (mLock) { for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) { final ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(i); if (name.equals(getWindowName(root))) return root.getView(); } } return null; } public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow) { //... root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); view.setLayoutParams(wparams); mViews.add(view); mRoots.add(root); mParams.add(wparams); } // do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things try { root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView); } catch (RuntimeException e) { // BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up. synchronized (mLock) { final int index = findViewLocked(view, false); if (index >= 0) { removeViewLocked(index, true); } } throw e; } } public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) { if (view == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null"); } if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams"); } final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams)params; view.setLayoutParams(wparams); synchronized (mLock) { int index = findViewLocked(view, true); ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index); mParams.remove(index); mParams.add(index, wparams); root.setLayoutParams(wparams, false); } } public void removeView(View view, boolean immediate) { if (view == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null"); } synchronized (mLock) { int index = findViewLocked(view, true); View curView = mRoots.get(index).getView(); removeViewLocked(index, immediate); if (curView == view) { return; } throw new IllegalStateException("Calling with view " + view + " but the ViewAncestor is attached to " + curView); } } public void closeAll(IBinder token, String who, String what) { //... } private void removeViewLocked(int index, boolean immediate) { ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index); View view = root.getView(); if (view != null) { InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance(); if (imm != null) { imm.windowDismissed(mViews.get(index).getWindowToken()); } } boolean deferred = root.die(immediate); if (view != null) { view.assignParent(null); if (deferred) { mDyingViews.add(view); } } } void doRemoveView(ViewRootImpl root) { synchronized (mLock) { final int index = mRoots.indexOf(root); if (index >= 0) { mRoots.remove(index); mParams.remove(index); final View view = mViews.remove(index); mDyingViews.remove(view); } } if (HardwareRenderer.sTrimForeground && HardwareRenderer.isAvailable()) { doTrimForeground(); } } private int findViewLocked(View view, boolean required) { final int index = mViews.indexOf(view); if (required && index < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("View=" + view + " not attached to window manager"); } return index; } //... }
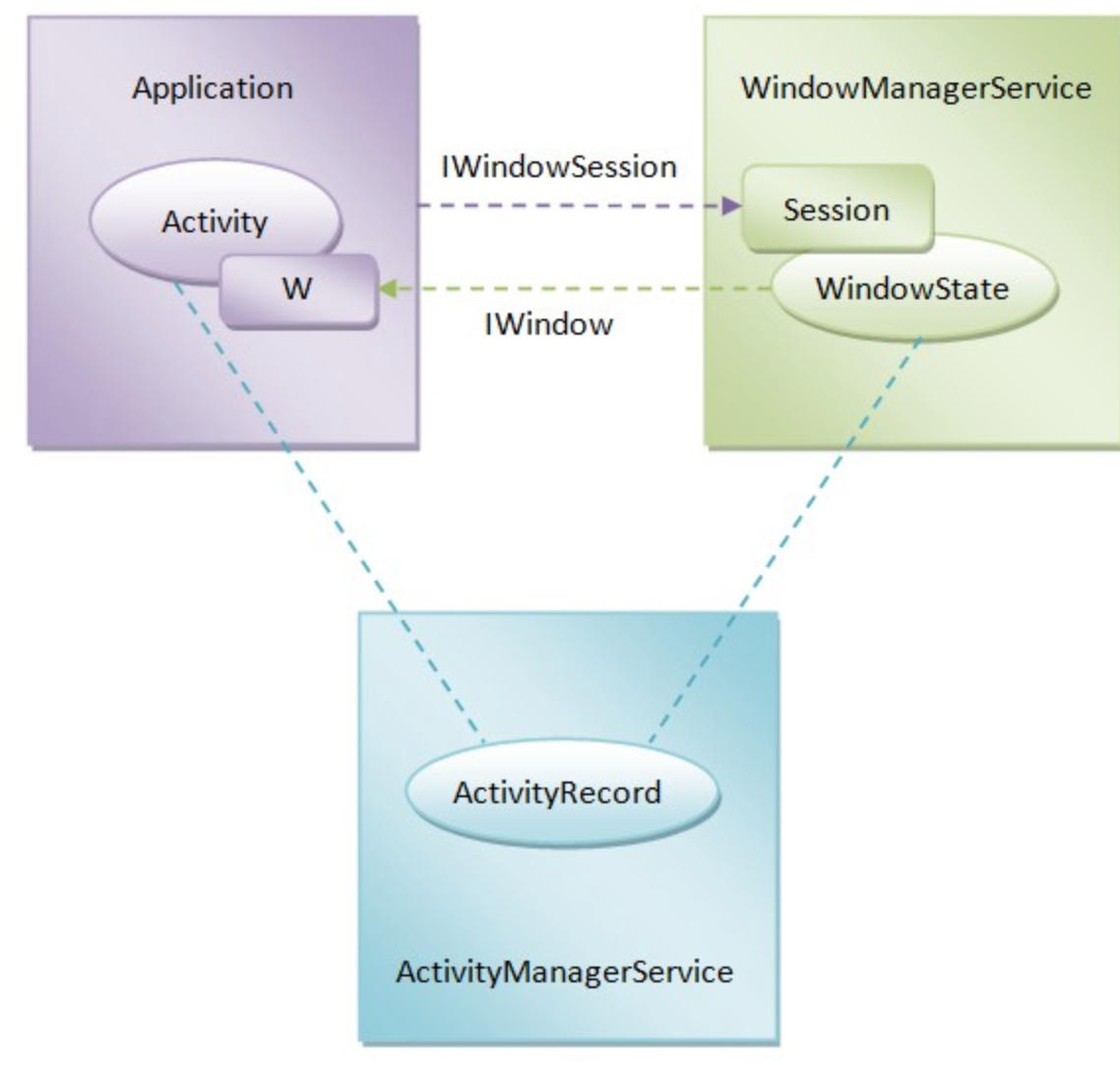
每个应用进程,仅有一个 sWindowSession 对象,它对应了 WmS 中的 Session 子类,WmS 为每一个应用进程分配一个 Session 对象。WindowState 类有一个 IWindow mClient 参数,是由 Session 调用 addToDisplay 传递过来的,对应了 ViewRootImpl 中的 W 类的实例。
WindowManagerGlobal的addView里面初始化了
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow) { //... root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); view.setLayoutParams(wparams); mViews.add(view); mRoots.add(root); mParams.add(wparams); } // do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things try { root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView); } catch (RuntimeException e) { // BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up. synchronized (mLock) { final int index = findViewLocked(view, false); if (index >= 0) { removeViewLocked(index, true); } } throw e; } }
WindowManagerGlobal的窗口管理:
WindowManager的总结
经过前文的分析,相信读者对WindowManager的工作原理有了深入的认识。
-
鉴于窗口布局和控件布局的一致性,WindowManager继承并实现了接口ViewManager。
-
使用者可以通过Context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)来获取一个WindowManager的实例。这个实例的真实类型是WindowManagerImpl。WindowManagerImpl一旦被创建就确定了通过它所创建的窗口所属哪块屏幕?哪个父窗口?
-
WindowManagerImpl除了保存了窗口所属的屏幕以及父窗口以外,没有任何实质性的工作。窗口的管理都交由WindowManagerGlobal的实例完成。
-
WindowManagerGlobal在一个进程中只有一个实例。
-
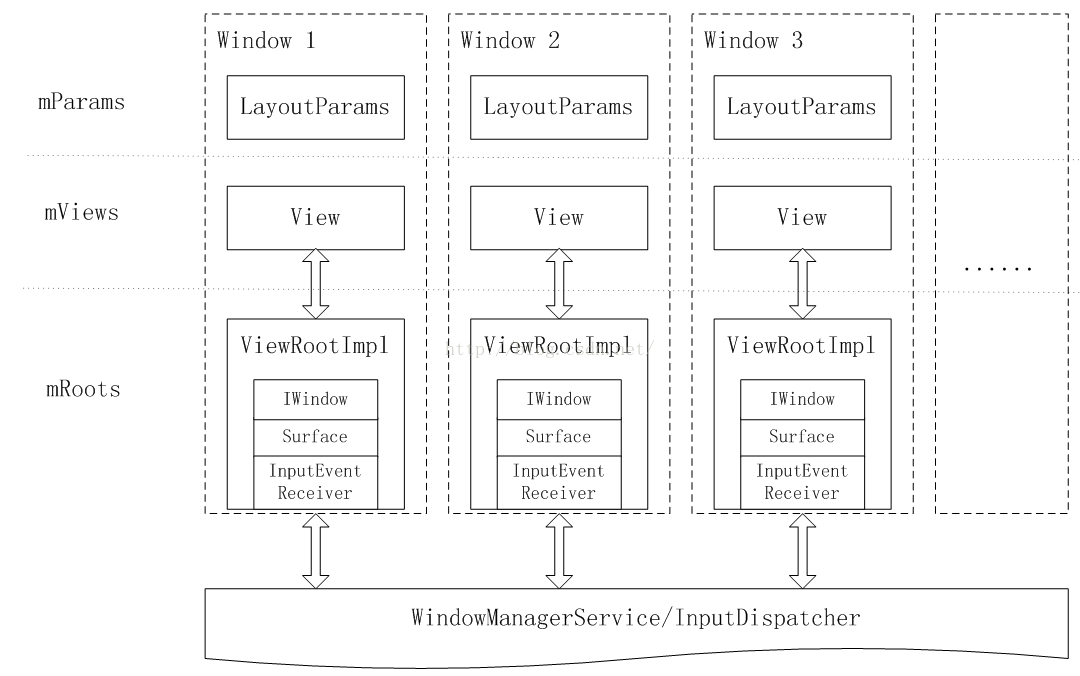
WindowManagerGlobal在3个数组中统一管理整个进程中的所有窗口的信息。这些信息包括控件、布局参数以及ViewRootImpl三个元素。
-
除了管理窗口的上述3个元素以外,WindowManagerGlobal将窗口的创建、销毁与布局更新等任务交付给了ViewRootImpl完成。
说明 在实际的应用开发过程中,有时会在logcat的输出中遇到有关WindowLeaked的异常输出。WindowLeaked异常发生与WindowManagerGlobal中,其原因是Activity在destroy之前没有销毁其附属窗口,如对话框、弹出菜单等。
如此看来,WindowManager的实现仍然是很轻量的。窗口的创建、销毁与布局更新都指向了一个组件:ViewRootImpl。



