15.Python基础篇-文件操作
文件的打开与关闭
第一种方法:open函数
open函数:打开一个文件,并返回文件对象。如果文件无法打开,会抛出 OSError异常。
open函数的参数介绍:
file参数
要打开的文件路径。可以是绝对路径也可以是相对路径
mode参数
打开文件的模式。分为:
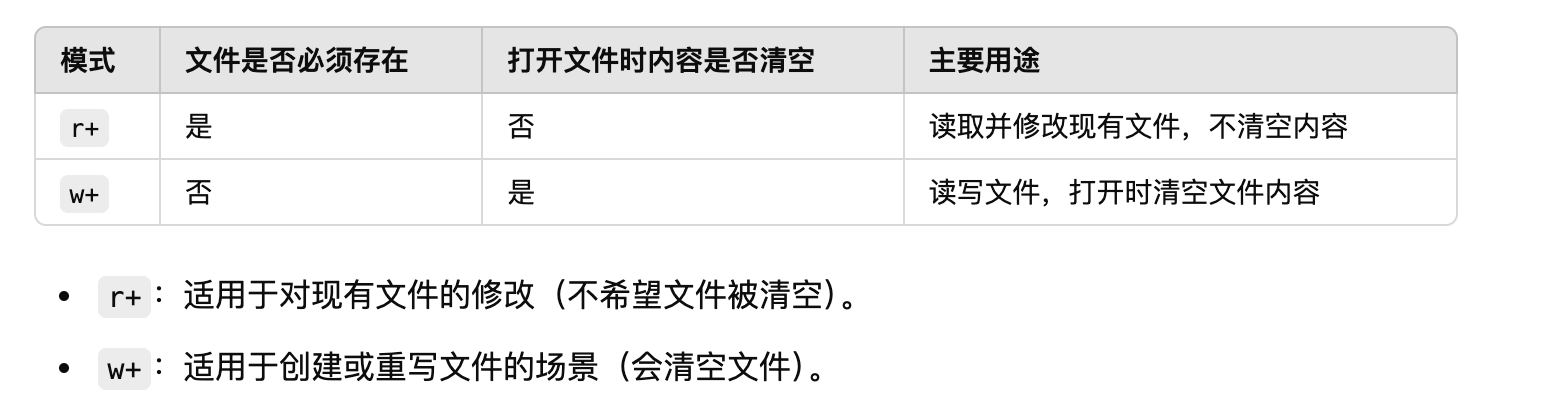
r:只读。文件的指针会放在文件的开头。这是默认模式。
w:写入。如果打开的文件不存在,创建新文件。如果该文件已存在则会删除原有内容,再写入。
a:追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件进行写入。
b:二进制模式打开。常用于非文本文件的操作,比如视频和图片。或在用于网络传输时使用。
+:读写模式:与其他模式组合使用,表示文件既可读也可写(如 'r+'、'w+'、'a+' 等)。
r+与w+的区别:
encoding参数
以何种编码方式打开文件。常用utf-8
示例代码:
file = open('test.txt', 'r+', encoding='UTF-8') file.close()
close()关闭文件
使用open函数时需要用到。每次操作完文件都需要关闭,否则打开的文件将一直占用内存,内存只增不减,导致内存泄露。
第二种方法:with open
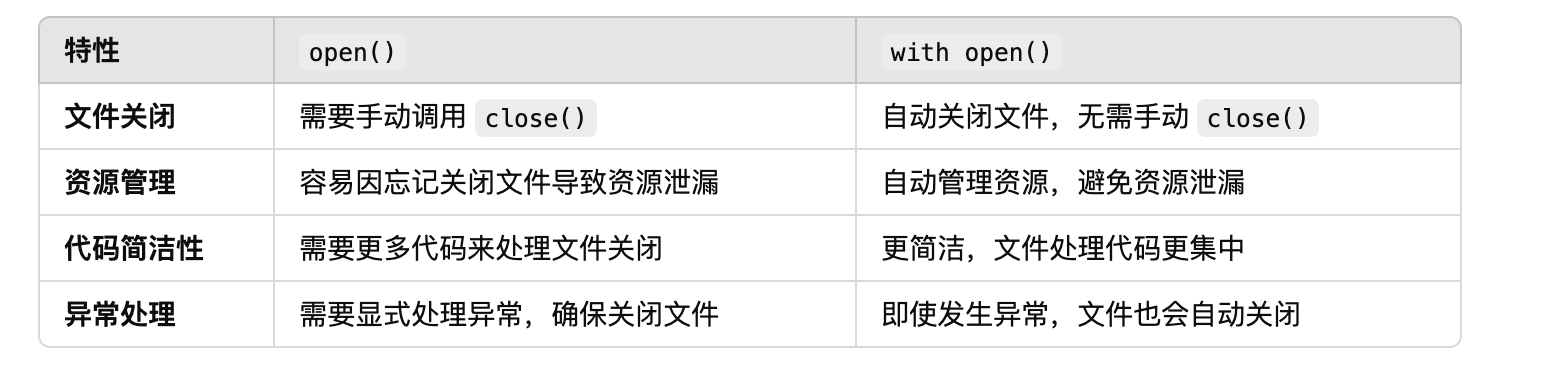
with open也是打开一个文件,与直接使用open方法打开的区别在于:
1.open需要手动调用close方法关闭文件;with open不需要。
2.open需要显式处理异常;with open即使发生异常,文件也会自动关闭
实际应用中应多使用with open的方式。
操作方法介绍
read():一次性读取文件的全部内容。
with open('test.txt', 'r+', encoding='UTF-8') as file: content = file.read() print(content) #输出: 测试文案第一行 测试文案第二行
readline:逐行读取文件,每次读取一行。
with open('test.txt', 'r+', encoding='UTF-8') as file: content = file.readline() print(content) # 输出: 测试文案第一行
readlines:读取所有行,返回一个包含每行内容的列表。
with open('test.txt', 'r+', encoding='UTF-8') as file: lines = file.readlines() print(lines) # 输出 ['测试文案第一行\n', '测试文案第二行\n']
# 结合for循环使用 with open('test.txt', 'r+', encoding='UTF-8') as file: for line in file.readlines(): print(line) # 输出 测试文案第一行 测试文案第二行
一次读取全部数据,如果遇到大文件会导致内存占满。所以推荐使用for循环的方式逐行读取。
with open('test.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8') as file: for line in file.readlines(): print(line) # 输出 测试文案第一行 测试文案第二行
write():写入,将原文件清空再写入。
with open('test.txt', 'w', encoding='UTF-8') as file: file.write('写入新的内容')
seek():将文件指针移动到新的位置。
tell():返回文件指针的当前位置(以字节为单位)。
with open('test.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8') as file: print("前五个字符:" + file.read(5)) # 读取前 5 个字符 print("指针当前位置:" + str(file.tell())) # 获取当前指针位置 file.seek(0) # 移动指针到文件开头 print("前五个字符:" + file.read(5)) # 再次读取前 5 个字符 # 输出 前五个字符:测试文案第 指针当前位置:15 前五个字符:测试文案第
修改文件的方式
python并不能直接修改文件。但是可以通过复制文件内容到一个新文件,然后将旧文件删除,新文件重命名的方式实现修改文件。
with open('test.txt', 'r', encoding='UTF-8') as ord_file, open('test.bak', 'w', encoding='UTF-8') as new_file: for line in ord_file.readlines(): if "测试文案" in line: line = line.replace("测试文案", "这是文件") new_file.write(line) # 将读取到的内容写入到新文件 import os os.remove("test.txt") # 删除旧文件 os.rename("test.bak", "test.txt") # 新文件重命名




