8-shell命令汇总
帮助命令
man:详细的帮助信息
man ls # 查看ls命令的帮助信息
参数 -f 加上-f可以查看内置命令,比如cd
[root@192 ~]# man -f cd # 查看内置命令cd的帮助信息 cd (1) - GNU Bourne-Again SHell (GNU 命令解释程序 “Bourne二世”) cd (3tcl) - 改变工作目录 cd (1p) - change the working directory [root@192 ~]# man 1p cd # 查看内置命令cd在1p中的帮助信息
显示出来的信息说明
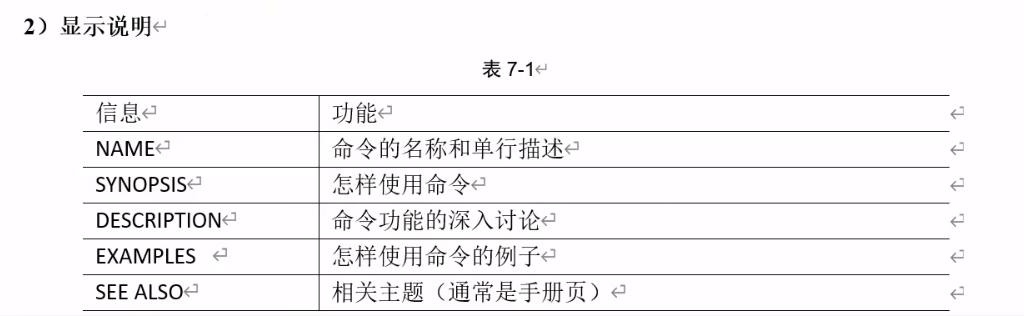
示例:
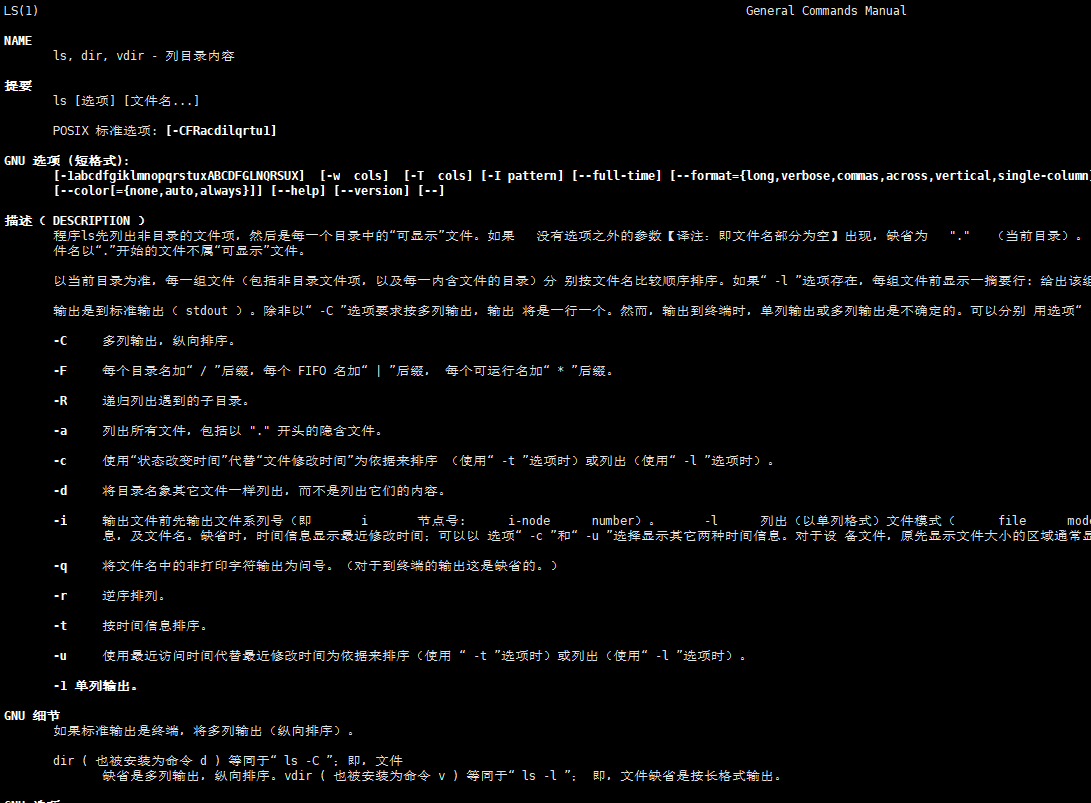
help:获得shell内置命令的帮助信息
[root@192 ~]# help cd # 查看cd的帮助信息 cd: cd [-L|[-P [-e]]] [dir] Change the shell working directory. Change the current directory to DIR. The default DIR is the value of the HOME shell variable. The variable CDPATH defines the search path for the directory containing DIR. Alternative directory names in CDPATH are separated by a colon (:). A null directory name is the same as the current directory. If DIR begins with a slash (/), then CDPATH is not used. If the directory is not found, and the shell option `cdable_vars' is set, the word is assumed to be a variable name. If that variable has a value, its value is used for DIR. Options: -L force symbolic links to be followed -P use the physical directory structure without following symbolic links -e if the -P option is supplied, and the current working directory cannot be determined successfully, exit with a non-zero status The default is to follow symbolic links, as if `-L' were specified. Exit Status: Returns 0 if the directory is changed, and if $PWD is set successfully when -P is used; non-zero otherwise.
命令 --help 查看某个命令的帮助信息
ls --help # 查看ls的帮助信息
type:查看命令的类型
[root@192 ~]# type cd cd 是 shell 内嵌
快捷键

文件目录相关
-
pwd:显示当前工作目录的绝对路径
[root@192 桌面]# pwd /root/桌面
-
ls:列出目录的内容
- 选项说明:
- -a:显示全部文件,包括以.开头的隐藏文件
- -l:长数据串列出,显示详细信息
- 目录或文件名
- 选项说明:
[root@192 桌面]# ls -al 总用量 3712 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 86 12月 11 15:28 . dr-xr-x---. 15 root root 4096 1月 9 21:08 .. -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 434 12月 11 15:28 .txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3790761 12月 11 15:28 尚硅谷Linux (大数据 javaEE Python 开发通用版).pdf
-
ll:相当于ls -l
-
cd:切换目录
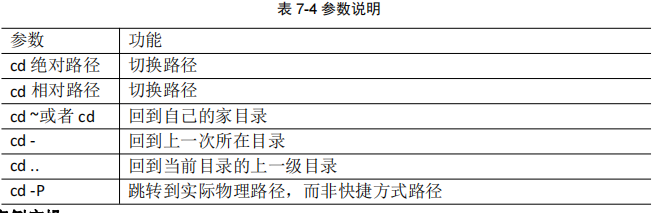
[root@192 ~]# ls # root下的目录及文件 anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg profile 公共 模板 视频 图片 文档 下载 音乐 桌面 [root@192 ~]# cd 桌面 # 进入root/桌面 [root@192 桌面]# cd ../视频/ # 进入父目录的其他子目录(桌面和视频是在同一目录下的) [root@192 视频]#
-
su 用户名:切换用户
[root@192 ~]# su atguigu # 切换到atguigu这个用户 [atguigu@192 root]$
-
mkdir:创建一个目录
[root@192 a]# mkdir a1 b1 # 同时创建a1和b1两个目录 [root@192 a]# ll # 查看 总用量 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 1月 10 10:29 a1 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 1月 10 10:29 b1 [root@192 a]# mkdir -p c1/c2/c3 # 创建多层目录,需要使用-p [root@192 a]#
-
rmdir:删除一个空目录
[root@192 a]# rmdir c1 # c1目录非空,所以提示删除失败 rmdir: 删除 "c1" 失败: 目录非空 [root@192 a]# rmdir a1 # a1为空目录,所以能删除 [root@192 a]# ll # 删除后查看 总用量 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 1月 10 10:29 b1 drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 16 1月 10 10:29 c1
-
touch:创建空文件
[root@192 a]# touch hellolinux.txt # 创建一个空目录 [root@192 a]# ll # 查看结果 总用量 0 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 1月 10 10:29 b1 drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 16 1月 10 10:29 c1 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 10 10:39 hellolinux.txt [root@192 a]# touch b1/b2 # 在b1目录下创建文件:b2 [root@192 a]# cd b1 [root@192 b1]# ll # 查看结果 总用量 0 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 10 10:39 b2
-
cp:复制
- cp 源文件 目标文件
- 参数:-r,递归复制整个文件夹
- \cp:可以去掉覆盖文件的提示
演示一:复制文件 [root@192 a]# cp hellolinux.txt /root/桌面/ # 将当前目录下的helloliux.txt文件复制到桌面 [root@192 a]# cd .. [root@192 桌面]# ls # 进入桌面查看,可以看到hellolinux.txt文件 a hellolinux.txt 尚硅谷Linux (大数据 javaEE Python 开发通用版).pdf 演示二:复制目录 [root@192 桌面]# mkdir b # 在桌面创建一个目录b [root@192 桌面]# ls # 当前桌面下有a和b两个目录,其中a不是空目录 a b hellolinux.txt 尚硅谷Linux (大数据 javaEE Python 开发通用版).pdf [root@192 桌面]# cp -r a b # -r表示复制目录及下面的所有子目录及文件 [root@192 桌面]# cd b # 进入b中查看 [root@192 b]# ls a [root@192 b]# cd a [root@192 a]# ls b1 c1 hellolinux.txt
- rm:删除文件或目录
- -r:可以递归删除目录中的所有内容
- -f:强制执行删除操作,不弹提示
- -v:显示指令的详细执行过程
演示一:删除一个文件 [root@192 桌面]# rm hellolinux.txt rm:是否删除普通空文件 "hellolinux.txt"?y 演示二:不加参数删除目录,无法删除 [root@192 桌面]# rm a rm: 无法删除"a": 是一个目录 演示三:使用-r删除一个目录。可以看到每删除一个文件都会弹出提示 [root@192 桌面]# rm -r a rm:是否进入目录"a"? y rm:是否进入目录"a/b1"? y rm:是否删除普通空文件 "a/b1/b2"?y rm:是否删除目录 "a/b1"?y rm:是否进入目录"a/c1"? y rm:是否进入目录"a/c1/c2"? y rm:是否删除目录 "a/c1/c2/c3"?y rm:是否删除目录 "a/c1/c2"?y rm:是否删除目录 "a/c1"?y rm:是否删除普通空文件 "a/hellolinux.txt"?y rm:是否删除目录 "a"?y 演示四:使用-rf删除目录,且不弹提示 [root@192 桌面]# rm -rf b [root@192 桌面]#
-
mv:移动文件或目录或重命名
- mv 原文件名 新文件名 #重命名
- mv 源文件路径 目标路径 #移动
[root@192 桌面]# mkdir a # 桌面建一个空目录a [root@192 桌面]# ls a 尚硅谷Linux (大数据 javaEE Python 开发通用版).pdf [root@192 桌面]# mv a /root # 移动至/root目录 [root@192 桌面]# cd /root # 进入/root目录查看 [root@192 ~]# ls a anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg profile 公共 模板 视频 图片 文档 下载 音乐 桌面
-
cat:查看文件内容(从第一行开始显示)
- 语法:cat 文件名
- -n:显示行号
- 适用于查看小文件
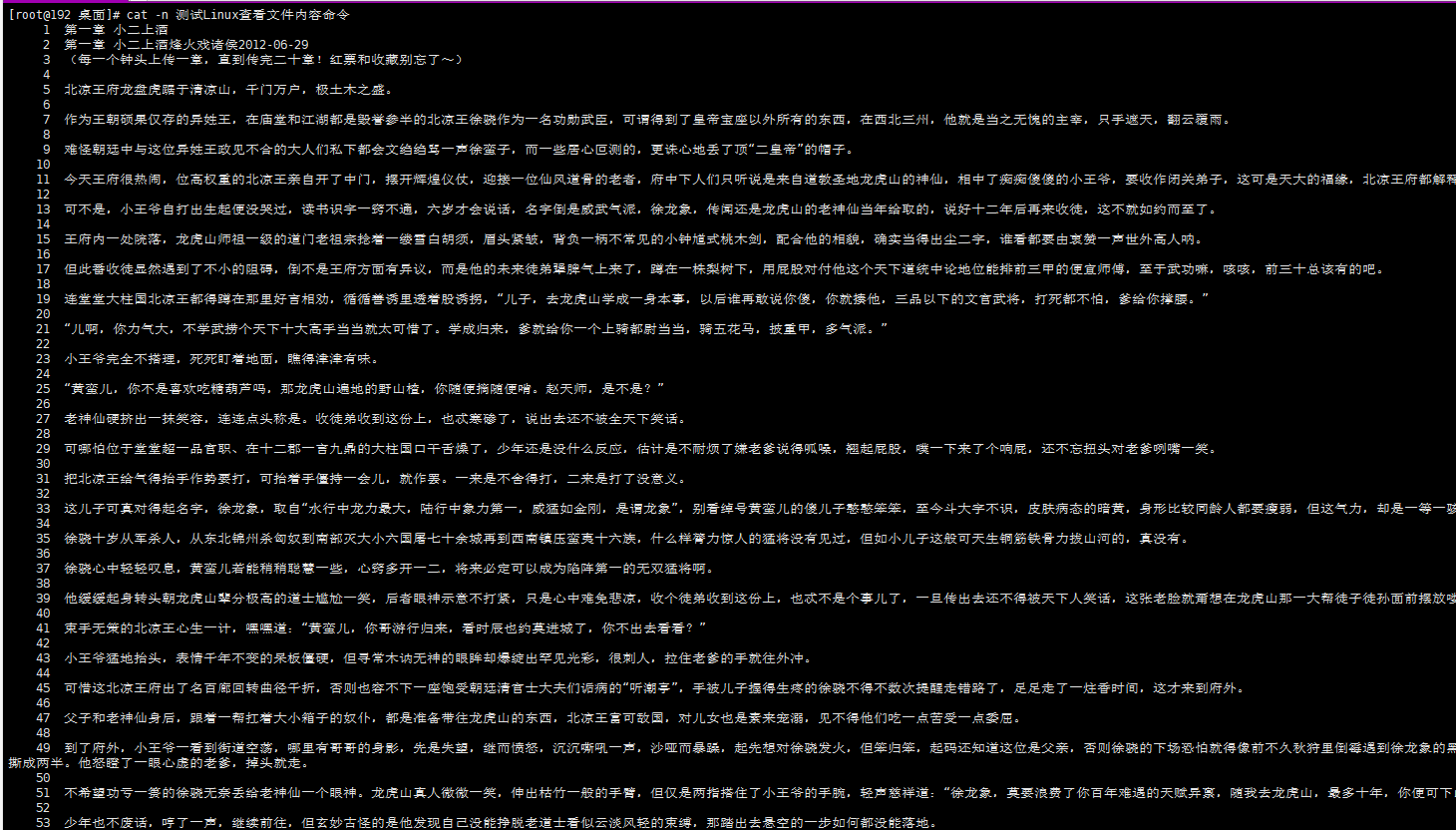
[root@192 桌面]# cat -n 测试Linux查看文件内容命令
展示情况:
-
more:文件内容分屏查看器
- 语法:more 文件名
[root@192 桌面]# more 测试Linux查看文件内容命令

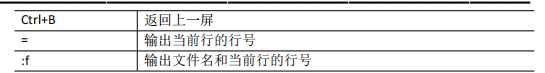
-
less:分屏显示文件内容
- less在显示文件内容时,并不是一次将整个文件加载之后才显示,而是根据显示需要加载内容,适合显示大型文件。
- 语法:less 文件名
[root@192 桌面]# less 测试Linux查看文件内容命令

-
echo:输出内容到控制台,相当于python中的print()
[root@192 桌面]# echo $PATH $输出系统环境变量
[root@192 桌面]# echo hello word hello word [root@192 桌面]# echo "hello \n word" hello \n word [root@192 桌面]# echo -e "hello \n word" # -e表示支持反斜线控制的字符转换 hello word
-
head:显示文件头部内容
- 参数:-n <行数> 文件名
sss@192 Desktop % head -n 10 testLinux.txt # 查看testLinux.txt文件中的前10行
-
tail:输出文件尾部内容
- -n <行数>:输出文件尾部n行
- -f:显示文件最新追加的内容,监视文件变化
案例:
第一步: xx@192 Desktop % tail -n 5 -f testLinux.txt # 查看testLinux.txt文件中最后5行,并追踪文档的更新 两百精锐铁骑冲刺而出,浩浩荡荡,气势如虹。 头顶一只充满灵气的鹰隼似在领路。 两百铁骑瞬间静止,动作如出一辙,这份娴熟,已经远远超出一般行伍悍卒百战之兵的范畴。 正四品武将折冲都尉翻身下马,一眼看见牵马老仆,立即奔驰到酒肆前,跪下行礼,恭声道:“末将齐当国参见世子殿下!” 而那位口出狂言要给打赏钱的寒酸年轻人只是在睡梦中呢喃了一句,“小二,上酒。”
hello word # 实时更新的内容
第二步:新开一个shell窗口 xx@192 Desktop % echo hello word >> testLinux.txt # 向文件中追加一行内容“helloword”。此命令执行后,窗口1增加打印helloword,结果如下: 两百精锐铁骑冲刺而出,浩浩荡荡,气势如虹。 头顶一只充满灵气的鹰隼似在领路。 两百铁骑瞬间静止,动作如出一辙,这份娴熟,已经远远超出一般行伍悍卒百战之兵的范畴。 正四品武将折冲都尉翻身下马,一眼看见牵马老仆,立即奔驰到酒肆前,跪下行礼,恭声道:“末将齐当国参见世子殿下!” 而那位口出狂言要给打赏钱的寒酸年轻人只是在睡梦中呢喃了一句,“小二,上酒。”
再次查看第一个窗口,会增加hello world
- > 输入输出重定向,和>>追加
- ls -l ->文件:搭配ls使用,将结果写入到指定文件
- ls -l >>文件:将结果追加到指定文件
- cat 文件A >文件B:搭配cat使用,将文件A覆盖到文件B。同理>>为追加
- echo "内容" >> 文件A:搭配echo使用,将内容追加到文件A。同理>为覆盖
# 案例一:ls shaomingbo@192 Java课件 % ls -al > ../../testLinux.txt #将ls -al结果覆盖到桌面上的testLiunx.txt shaomingbo@192 Java课件 % cat ../../testLinux.txt # 查看文件变化 total 32 drwxr-xr-x@ 14 shaomingbo staff 448 1 16 00:18 . drwxr-xr-x 10 shaomingbo staff 320 7 9 2023 .. -rw-r--r--@ 1 shaomingbo staff 12292 1 16 00:20 .DS_Store drwxr-xr-x 7 shaomingbo staff 224 12 14 2022 JDBC ... # 案例二:搭配echo shaomingbo@192 Desktop % echo "hello word" >> testLinux.txt # 追加一行内容:“hello word” shaomingbo@192 Desktop % cat testLinux.txt # 查看文件变化 hello word hello word shaomingbo@192 Desktop %
-
In:软连接
- 概念:软链接也称为符号链接,类似于 windows 里的快捷方式,有自己的数据块,主要存放
了链接其他文件的路径
- 语法:ln -s [原文件或目录] [软链接名]
- 选项:-s:表示创建一个软连接,不加-s表示创建的是一个硬链接。
- 概念:软链接也称为符号链接,类似于 windows 里的快捷方式,有自己的数据块,主要存放
案例:
# 案例一:创建一个软连接 [root@192 ~]# ln -s profile /pf # 创建一个软连接到根目录 [root@192 ~]# cd / [root@192 /]# ll 总用量 28 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 12月 6 18:18 bin -> usr/bin dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 12月 6 18:35 boot drwxr-xr-x. 19 root root 3260 1月 19 17:06 dev drwxr-xr-x. 144 root root 8192 1月 8 20:26 etc drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 21 12月 6 18:33 home lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 12月 6 18:18 lib -> usr/lib lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 9 12月 6 18:18 lib64 -> usr/lib64 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 4月 11 2018 media drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 4月 11 2018 mnt drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 16 12月 6 18:25 opt lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 1月 19 17:10 pf -> profile ... # 案例二:删除一个软连接 [root@192 ~]# rm -rf /pf # pf后面一定不要加/,加上会把软链接对应的真实目录下内容删掉 [root@192 ~]#
-
history:查看历史执行的命令
演示:
[root@192 /]# history 1 ls 2 cd .. 3 ls 4 ifconfig 5 ls 6 cd 桌面/ 7 ls 8 cp /etc/profile /root 9 ls 10 cd /root 11 ls 12 vim progile 13 vim profile 14 ifconfig 15 ping 192.168.1.97 16 ping www.baidu.com ....





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律