14.Python基础篇-Set集合
集合的介绍
集合的特点:集合是无序的;不重复的数据集合;他里面的元素是可哈西的(不可变的数据类型),但是集合本身是不可哈希(所以集合做不了字典的键)的。
集合的实际应用场景
- 去重,基础集合不可重复的特点,我们把一个列表变成集合,利用set本身的机制,就可以实现自动去重了
- 关系测试,测试两组数据之间的交集,差集,并集等关系
集合的创建
# set的两种创建方式 # 第一种:使用set方法创建一个set集合 set1 = set({1,2,3}) # 第二种:使用花括号创建一个set集合 set2 = {1,2,3} print(set1,set2) {1,2,3} {1,2,3}
集合-增
add():添加单个元素
my_set = set([1, 2, 3, 4]) my_set.add(4) # 添加单个元素 print(my_set) # 输出: {1, 2, 3, 4}
update():添加一个或多个元素
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4}
my_set.update([5, 6]) # 添加多个元素
print(my_set)
# 输出: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
集合-删
pop()-随机删除,返回删除的元素。
my_set = {1, 2, 3}
my_set.pop() # 随机删除一个元素并返回
print(my_set)
# 输出:{2, 3} (具体输出可能不同)
print("删除的元素是:" + str(my_set.pop())) # 返回删除的元素
print(my_set)
# 输出:删除的元素是:2
{3}
remove()-删除指定元素
my_set = {1, 2, 3}
my_set.remove(3) # 删除指定元素,若元素不存在则抛出 KeyError
print(my_set)
# 输出: {1, 2}
clear()-清空集合
my_set = {1, 2, 3}
my_set.clear() # 清空 set 中所有元素
print(my_set)
# 输出: set()
discard() # 删除元素,若元素不存在则不抛出错误
my_set = {1, 2, 3}
my_set.discard(3)
print(my_set)
# 输出: {1, 2}
集合-查
1.不支持索引
2.for.in遍历的方法查询
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
for i in set1:
print(i)
# 输出:1
2
3
集合-其他用法
交集(A与B的交集,即A有B也有的)
set_a = {1, 2, 3}
set_b = {3, 4, 5}
# 方式一:使用&符号取交集
intersection_set = set_a & set_b
print(intersection_set) # 输出: {3}
# 方式二:使用 intersection()方法
intersection_set = set_a.intersection(set_b)
print(intersection_set) # 输出: {3}
并集(A与B的并集,即AB排重合并,组成一个新的集合)
# 方式一:使用|符号 set_a = {1, 2, 3} set_b = {3, 4, 5} union_set = set_a | set_b print(union_set) # 输出: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} # 方式二:使用union()方法 union_set = set_a.union(set_b) print(union_set) # 输出: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
差集(A与B的差集,即A有B没有的)
set_a = {1, 2, 3}
set_b = {3, 4, 5}
# 方式一:使用-减号求A与B的差集
difference_set = set_a - set_b
print(difference_set) # 输出: {1, 2}
# 方式二:使用difference()方法求A与B的差集
difference_set = set_a.difference(set_b)
print(difference_set) # 输出: {1, 2}
反交集(也叫对称差集。即A有,但是B没有的;和B有,但是A没有的)
set_a = {1, 2, 3}
set_b = {3, 4, 5}
# 方式一:使用 symmetric_difference() 方法
symmetric_diff = set_a.symmetric_difference(set_b)
print(symmetric_diff) # 输出: {1, 2, 4, 5}
# 方式二:使用 ^ 运算符
symmetric_diff_op = set_a ^ set_b
print(symmetric_diff_op) # 输出: {1, 2, 4, 5}
子集(A的元素是否全部出现在B中)
set_a = {1, 2}
set_b = {1, 2, 3, 4}
# 检查 set_a 是否是 set_b 的子集
# 方式一:使用issubset方法
is_subset = set_a.issubset(set_b)
print(is_subset) # 输出: True
# 方式二:使用<= 运算符
is_subset_op = set_a <= set_b
print(is_subset_op) # 输出: True
超集(A是否包含了B的所有元素)
set_a = {1, 2, 3, 4}
set_b = {1, 2}
# 检查 set_a 是否是 set_b 的超集
# 方式一:使用issuperset方法
is_superset = set_a.issuperset(set_b)
print(is_superset) # 输出: True
# 方式二:使用>= 运算符
is_superset_op = set_a >= set_b
print(is_superset_op) # 输出: True
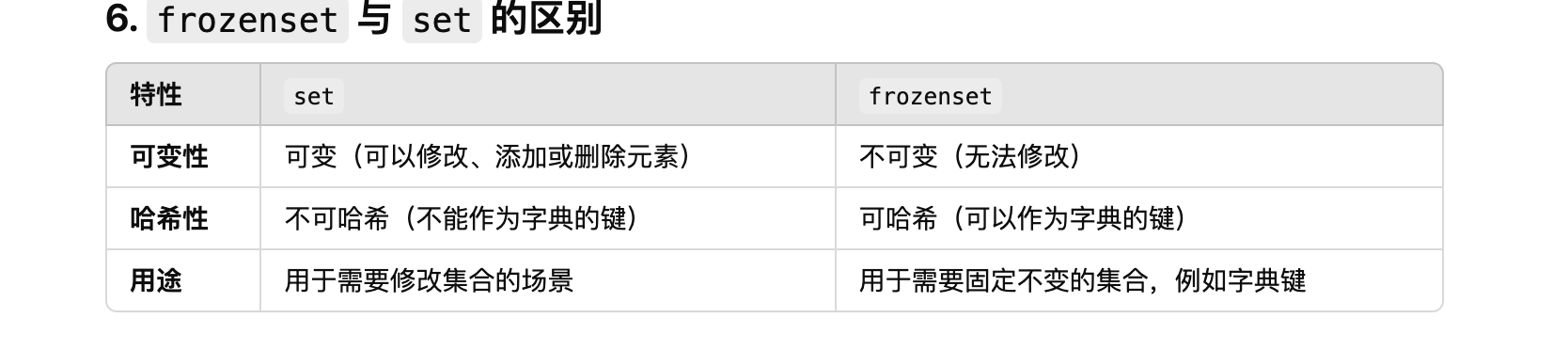
frozenset类型
frozenset是不可变集合,集合中的元素不能被修改、添加或删除。- 由于不可变性,
frozenset可以作为字典的键或存储在其他集合中,而普通的set由于可变,不能用于这些场景。
frozenset() 函数将任何可迭代对象(如列表、元组、集合等)转换为一个不可变集合。不可变:指不能对 frozenset 进行修改操作(如 add()、remove() 等)。
支持求交集,并集差集等。