edvr笔记
█ 0. 名词解释:
可变性卷积 Deformable Convolution.
其中额外的偏移量是 学会了允许网络获取信息 从其常规局部邻域,提高常规卷积的能力。
█ 1. 现状
基准测试从两个方面挑战现有方法:
(1) 如何在给定大运动的情况下对齐多个帧,以及
(2)如何有效地融合不同运动和模糊的不同帧。
a novel Video
Restoration framework with Enhanced Deformable convolutions, termed EDVR,
增强可变形卷积
-
to handle large motions。
级联和可变形 (PCD) 对齐模块,在哪个框架中对齐是在特征级别feature level使用可变形卷积 using deformable convolutions 以粗到细 a coarse-to-fine manner的方式完成的。
Cascading and Deformable (PCD)级联和可变形 alignment module 对齐模块 -
to emphasize important features for subsequent restoration.强调后续修复的重要功能。
a Temporal and Spatial Attention (TSA) fusion module 时间和空间注意 (TSA) 融合模块, 在时间和空间上都应用了哪种注意力,
特征提取、对齐、融合和 重建。
当视频包含遮挡 occlusion,、大运动和严重模糊时,挑战在于对齐和融合模块 alignment and fusion modules的设计
为获得高质量输出,必须(1)对齐并建立多个帧之间的准确对应关系,以及(2)有效融合 对齐的特征进行重建
○ 1.1 Alignment.对齐
现有两种方法
1) estimating optical flow field between the reference and its neighboring frames
通过显式估计参考帧与其相邻帧之间的光流场
2)by dynamic filtering or deformable convolution
通过动态滤波 或可变形卷积 进行补偿
存在的问题:
1)precise flow estimation and accurate warping can be challenging and timeconsuming for flow-based methods.
对于基于流的方法而言,精确的流量估计和准确的变形可能具有挑战性且耗时。
2)within a single scale of resolution.
In the case of large motions,
it is difficult to perform motion compensation either explicitly or implicitly
在单一分辨率范围内 很难 明确或隐含地 进行运动补偿
○ 1.2 Fusion.
现有的方法:
1)使用卷积对所有帧 use convolutions to perform early fusion on all frames
2)采用循环网络逐渐融合多帧 adopt recurrent networks to gradually逐渐 fuse multiple frames
存在的问题:
这些现有方法都没有考虑 每帧的潜在视觉信息underlying visual informativeness——– 不同的帧和位置对重建的信息性或有益性并不相同,因为某些帧或区域受到不完美对齐和模糊 imperfect alignment and blurring 的影响。
○ 1.3 我们的解决方案:
模型可以解决的问题:可扩展到各种视频恢复任务,包括超分辨率和去模糊。
包括的模块:
1)对齐模块:级联和可变形卷积 Cascading and Deformable convolutions(PCD),
2) fusion module融合模块:时间和空间注意 Temporal and Spatial Attention (TSA)。
○ 1.3.1 PCD
受启发于: TDAN
使用 可变形卷积以对齐 每个相邻帧 到 特征级别的参考帧。
Different from TDAN, we perform alignment in a coarse-to-fine manner to
handle large and complex motions.
我们以粗到细的方式执行对齐以处理大而复杂的动作。
具体的 Specifically:
我们使用一个金字塔结构pyramid structure 首先在较低尺度上对齐特征粗略估计 coarse estimations,
然后传播偏移量和 将特征对齐到更高的比例 以促进facilitate 精确运动补偿,类似于光流中采用的概念估计 。
此外,我们在金字塔对齐操作之后级联 cascade 了一个额外的可变形卷积 deformable, 提高对齐的鲁棒性。
○ 1.3.2 TSA 融合模块 Temporal and Spatial Attention
我们通过计算参考帧 和 每个相邻帧的特征之间的 元素相关性 来引入时间注意力。来为了更好的考虑每一帧的视觉信息。
相关系数对每个位置的每个相邻特征进行加权,表明它对重建参考图像的信息量有多大。
█ 2. 具体的模型
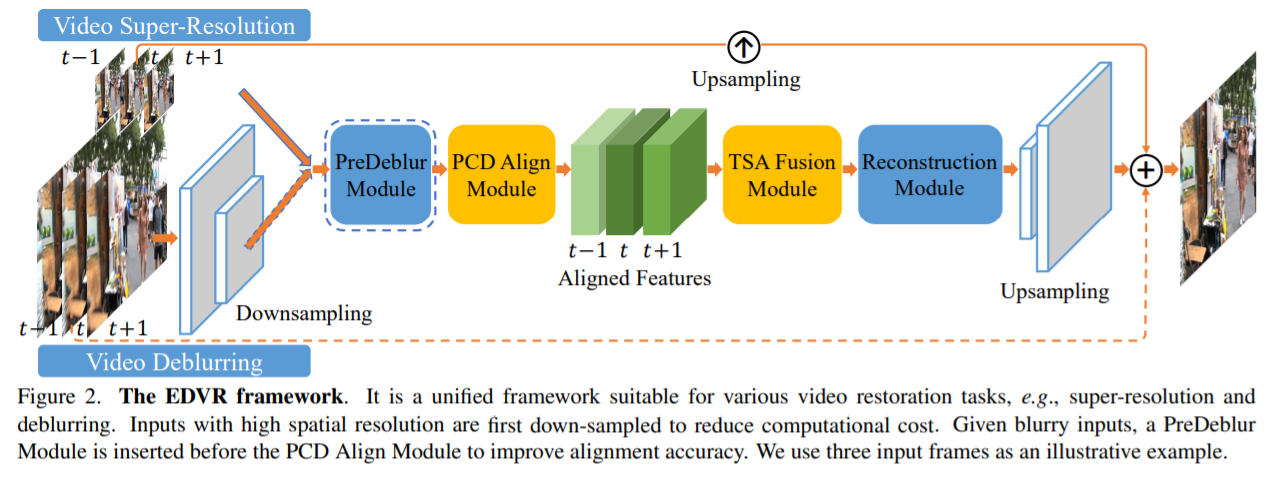
first down-sampled to reduce computational cost
在 PCD 对准模块之前插入PreDeblur模块以提高对准精度
Each neighboring frame is aligned to the reference one by the PCD alignment module at the feature level. 每个相邻帧都由 PCD 对齐模块在特征级别与 参考帧对齐.
TSA 融合模块融合不同的图像信息帧。
在网络的末端执行上采样操作以增加空间大小。
最后,通过将预测图像残差添加到直接上采样图像中获得高分辨率帧 O^t。
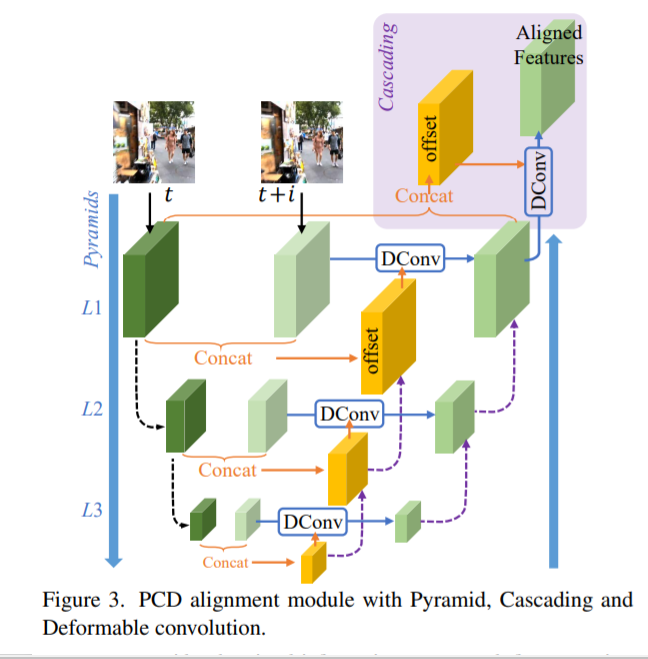
█ 3.2. Alignment with Pyramid, Cascading and Deformable Convolution
3.2. 与金字塔、级联和对齐 可变形卷积
可变形对齐应用于每一帧的特征
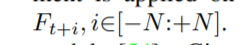
给定一个可变形的卷积核 K 个采样位置
我们将 wk 和 pk 表示为权重 和 分别为第 k 个位置的预先指定的偏移量。
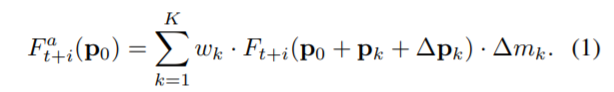
pk 对应的是第几个点,一共有K个

可学习偏移量 ∆pk 和调制标量 ∆mk 是 从相邻帧和参考帧的级联特征预测的:



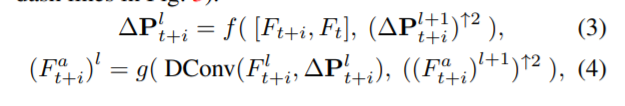
use three-level pyramid,
To reduce computational cost, we do not increase channel numbers as spatial sizes decrease. 我们不会随着空间大小的减小而增加通道数。
图 3 中带有浅紫色背景的部分:在金字塔结构之后,随后的可变形对齐被级联以进一步细化粗对齐的特征
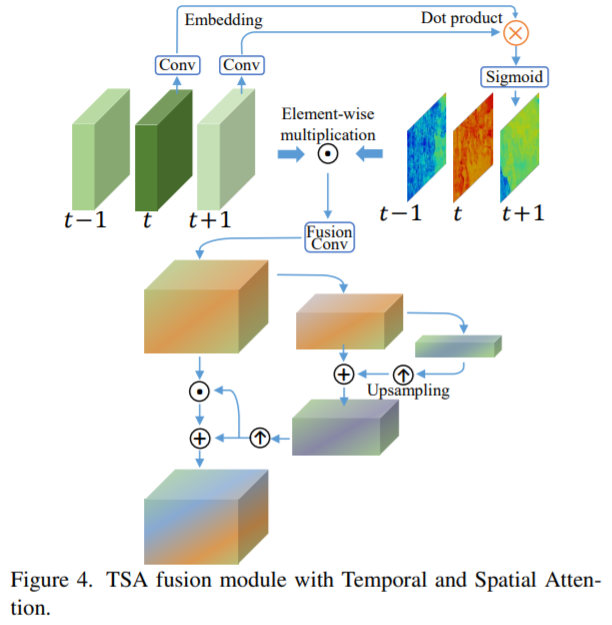
█ 3.3. Fusion with Temporal and Spatial Attention
3.3. 融合时空注意
帧间时间关系和帧内空间关系在融合中至关重要
1) different neighboring frames are not equally informative due to occlusion, blurry regions and parallax problems;
2) misalignment and unalignment arising from the preceding alignment stage adversely affect the subsequent reconstruction performance.
1) 由于遮挡、模糊区域和视差问题,不同的相邻帧的信息量不一样;
2) 前一个对齐阶段引起的未对齐和未对齐对后续重建性能产生不利影响。
so dynamically aggregating聚集 neighboring frames in pixel-level is indispensable不可缺少的。
so 我们提出了 TSA 融合模块 来 在每帧上分配 像素级聚合权重、、 具体来说,我们在融合过程中采用时间和空间注意力。
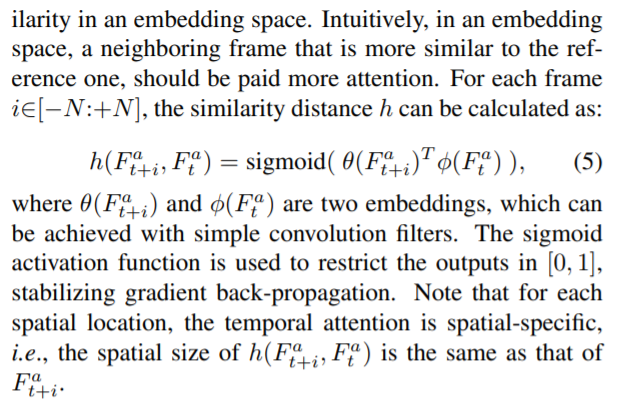
temporal attention:
目标是计算嵌入空间embedding space 中的帧相似度。
直观地说,在嵌入空间中,应该更加注意与参考帧更相似的相邻帧。
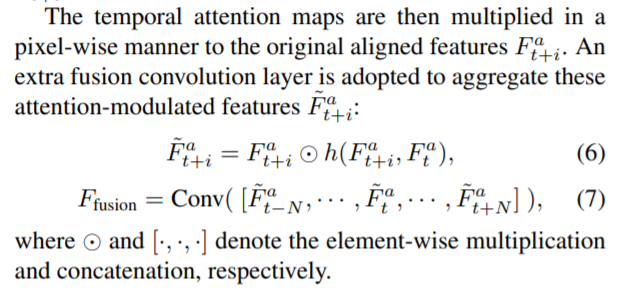
然后根据融合特征计算空间注意掩码。 采用金字塔设计来增加注意力接受领域。 之后,融合特征由掩码通过逐元素乘法和加法进行调制
█ 3.4. Two-Stage Restoration 恢复
具体来说,级联一个类似但更浅的 EDVR 网络来细化第一阶段的输出帧。
好处有两个:
1)它有效地消除了先前模型无法处理的严重运动模糊,提高修复质量;
2)它减轻了输出帧之间的不一致。 两阶段恢复的有效性在第二节中说明。 4.4.
█ 4. 实验
○ 4.1 数据
Vimeo-90K [48] is a widely used dataset for training,
usually along with Vid4 [21] and Vimeo-90K testing dataset
(denoted by Vimeo-90K-T) for evaluation.
○ 4.2 参数
1)The PCD alignment module adopts five residual blocks (RB) to perform feature extraction.
2)use 40 RBs in the reconstruction module and 20 RBs forthe second-stage model.
3)The channel size in each residual block is set to 128。
4)We use RGB patches of size 64×64 and 256×256 as inputs for video SR and deblurring tasks, respectively.
5)Mini-batch size is set to 32.
6)The network takes five consecutive连续的 frames (i.e., N=2) as inputs unless otherwise specified. 除非另有说明
7)We augment增大 the training data with random horizontal flips水平翻转 and 90◦ rotations.

9)We train our model with Adam optimizer [14] by setting β1=0.9 and β2=0.999.
10)The learning rate is initialized as 4×10−4
We initialize deeper networks by parameters from shallower ones for faster convergence.
我们通过来自较浅网络的参数初始化较深的网络以加快收敛速度。


